
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
For the given substrate, when
Concept introduction:
As the number of alkyl groups on the carbon bonded to the leaving group increases, the
Answer to Problem 9.69P
The major E1 product for the given reaction is shown below:
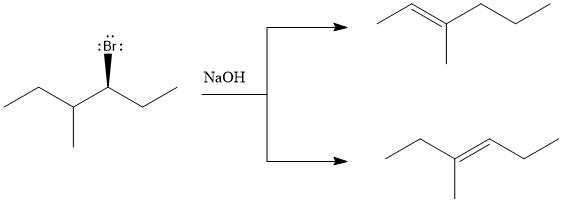
Explanation of Solution
Elimination usually takes place so as to produce the most stable, i.e., highly alkyl substituted, alkene.
The possible E1 products are obtained by eliminating the leaving group and a proton on carbon adjacent to the one bonded to the leaving group. Here the
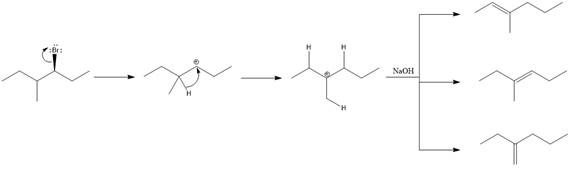
The first and second alkene product is highly substituted than the third alkene product. Therefore, the first and second alkene products are more stable. The base in this reaction is OH, which is not bulky, so the first and second products are the major products.

From the stability of the product formed, the major E1 product is drawn.
(b)
Interpretation:
For the given substrate, when
Concept introduction:
As the number of alkyl groups on the carbon bonded to the leaving group increases, the rate of E1 reaction increases. Each additional alkyl group, which is electron donating, stabilizes the carbocation intermediate produced and thus helps the leaving group leave. The
Answer to Problem 9.69P
The major E1 product for the given reaction is shown below:
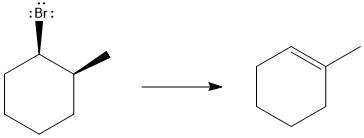
Explanation of Solution
Elimination usually takes place so as to produce the most stable, i.e., highly alkyl substituted, alkene.
The possible E1 products are obtained by eliminating the leaving group and a proton on carbon adjacent to the one bonded to the leaving group. Here the
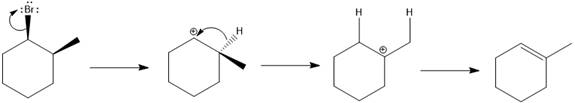
From the stability of the product formed, the major E1 product is drawn.
(c)
Interpretation:
For the given substrate, when
Concept introduction:
As the number of alkyl groups on the carbon bonded to the leaving group increases, the rate of E1 reaction increases. Each additional alkyl group, which is electron donating, stabilizes the carbocation intermediate produced and thus helps the leaving group leave. The
Answer to Problem 9.69P
The major E1 product for the given reaction is shown below:
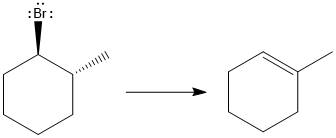
Explanation of Solution
Elimination usually takes place so as to produce the most stable, i.e., highly alkyl substituted, alkene.
The possible E1 products are obtained by eliminating the leaving group and a proton on carbon adjacent to the one bonded to the leaving group. Here the
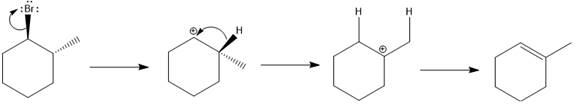
From the stability of the product formed, the major E1 product is drawn.
(d)
Interpretation:
For the given substrate, when
Concept introduction:
As the number of alkyl groups on the carbon bonded to the leaving group increases, the rate of E1 reaction increases. Each additional alkyl group, which is electron donating, stabilizes the carbocation intermediate produced and thus helps the leaving group leave. The
Answer to Problem 9.69P
The major E1 product for the given reaction is shown below:
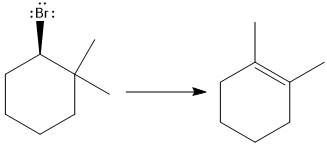
Explanation of Solution
Elimination usually takes place so as to produce the most stable that means highly alkyl substituted alkene.
The possible E1 products are obtained by eliminating the leaving group and a proton on the carbon adjacent to the one bonded to the leaving group. Here the
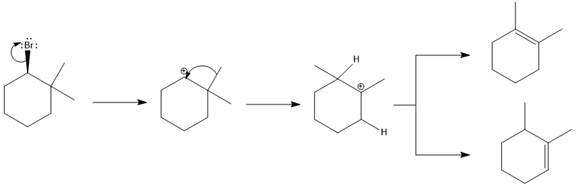
The first alkene product is highly substituted than the second alkene product. Therefore, the first alkene product is more stable. The base in this reaction is OH, which is not bulky, so the first and second products are the major products.

From the stability of the product formed, the major E1 product is drawn.
(e)
Interpretation:
For the given substrate, when
Concept introduction:
As the number of alkyl groups on the carbon bonded to the leaving group increases, the rate of E1 reaction increases. Each additional alkyl group, which is electron donating, stabilizes the carbocation intermediate produced and thus helps the leaving group leave. The
Answer to Problem 9.69P
The major E1 product for the given reaction is shown below:
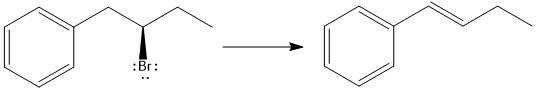
Explanation of Solution
Elimination usually takes place so as to produce the most stable that means highly alkyl substituted alkene.
The possible E1 products are obtained by eliminating the leaving group and a proton on the carbon adjacent to the one bonded to the leaving group. Here the
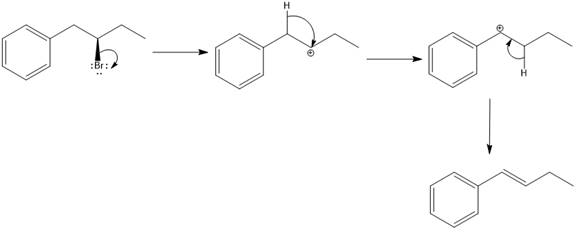
From the stability of the product formed, the major E1 product is drawn.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
EBK GET READY FOR ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- A mixture of C7H12O2, C9H9OCl, biphenyl and acetone was put together in a gas chromatography tube. Please decide from the GC resutls which correspond to the peak for C7,C9 and biphenyl and explain the reasoning based on GC results. Eliminate unnecessary peaks from Gas Chromatography results.arrow_forwardIs the molecule chiral, meso, or achiral? CI .CH3 H₂C CIarrow_forwardPLEASE HELP ! URGENT!arrow_forward
- Identify priority of the substituents: CH3arrow_forwardHow many chiral carbons are in the molecule? OH F CI Brarrow_forwardA mixture of three compounds Phen-A, Acet-B and Rin-C was analyzed using TLC with 1:9 ethanol: hexane as the mobile phase. The TLC plate showed three spots of R, 0.1 and 0.2 and 0.3. Which of the three compounds (Phen-A; Acet-B or Rin-C) would have the highest (Blank 1), middle (Blank 2) and lowest (Blank 3) spot respectively? 0 CH: 0 CH, 0 H.C OH H.CN OH Acet-B Rin-C phen-A A A <arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
