
(Learning Objective 5: Explore an actual bankruptcy; calculate leverage ratio, ROA, debt ratio, and times-Interest-earned ratio) In 2002, Enron Corporation filed for Chapter 11 Q bankruptcy protection, shocking the business community: How could a company so large and successful go bankrupt? This case explores the causes and the effects of Enron's bankruptcy.
At December 31, 2000, and for the four years ended on that date. Enron reported the following (amounts in millions):
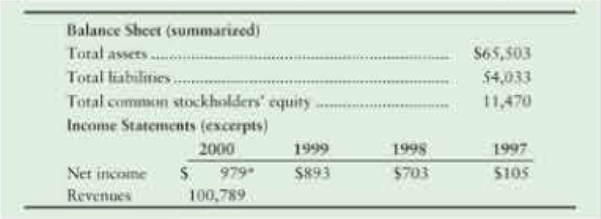
Unknown to Investors and lenders, Enron also controlled hundreds of
During the four-year period up to December 31, 2000, Enron’s stock price shot up from $17.50 to $90.56. Enron used its escalating stock price to finance the purchase of the SPEs by guaranteeing lenders that Enron would give them Enron stock if the SPEs could not pay their loans.
In 2001, the SEC launched an Investigation into Enron's accounting practices. It was alleged that Enron should have been including the SPEs In its financial statements all along. Enron then restated net income for the years up to 2000, wiping out nearly $600 million of total net income (and total assets) for this four-year period. Assume that $300 million of this loss applied to 2000. Enron's stock price tumbled, and the guarantees to the SPEs' lenders added millions to Enron's liabilities (assume the full amount of the SPEs' debt was included). To make matters worse, the assets of the SPEs lost much of their value; assume that their market value is only $500 million.
Requirements
1. Compute the debt ratio that Enron reported at the end of 2000. By using the DuPont Model, compute Enron's return on total assets (ROA) for 2000. For this purpose, use only total assets at the end of 2000, rather than the average of 1999 and 2000.
2. Compute Enron's leverage ratio for 2000. Use total assets and total
3. Add the asset and liability information about the SPEs to the reported amounts provided in the table. Recompute all ratios after including the SPEs in Enron's financial statements. Also compute Enron's times-interest-earned ratio both ways for 2000. Assume that the changes to Enron's financial position occurred during 2000.
4. Why does it appear that Enron failed to include the SPEs in its financial statements? How do you view Enron after including the SPEs in the company's financial statements? (Challenge)
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 9 Solutions
Financial Accounting (12th Edition) (What's New in Accounting)
- Xavier Company is going through a Chapter 7 bankruptcy. All assets have been liquidated, and the company retains only $25,200 in free cash. The following debts, totaling $38,050, remain: Government claims to unpaid taxes Salary during last month owed to Mr. Key (not an officer) Administrative expenses Salary during last month owed to Ms. Rankin (not an officer) Unsecured accounts payable $6,000 17,825 2,450 5,225 6,550 Indicate how much money will be paid to the creditor associated with each debt. (Be sure to list liabilities in the order of priority.) Administrative expenses Salary during last month owed to Mr. Key and Ms. Rankin Government claims to unpaid taxesarrow_forwardrrarrow_forwardXavier Company is going through a Chapter 7 bankruptcy. All assets have been liquidated, and the company retains only $26,200 in free cash. The following debts, totaling $43,050, remain: Indicate how much money will be paid to the creditor associated with each debt.arrow_forward
- Xavier Company is going through a Chapter 7 bankruptcy. All assets have been liquidated, and the company retains only $26,800 in free cash. The following debts, totaling $46,050, remain: $ 7,600 Government claims to unpaid taxes Salary during last month owed to Mr. Key (not an officer) Administrative expenses 19,425 4,050 Salary during last month owed to Ms. Rankin (not an officer) Unsecured accounts payable 6,825 8,150 Indicate how much money will be paid to the creditor associated with each debt. Types of Debts Amountsarrow_forwardam.101.arrow_forward(b) Grouper' major customer shocked the industry on January 14 by declaring bankruptcy. There had been no warning to ANBS of this customer's impending financial collapse, and Grouper had not accrued any Allowance for Expected Credit Losses specific to this customer. At the end of the fiscal year, the customer owed more than $130,000 to Grouper. Identify the effect that it will have on Grouper's 2023 net income. Ignore taxes. Net income will ✓ by $arrow_forward
- Government claims to unpaid taxes Salary during last month owed to Mr. Key (not an officer) Administrative expenses Salary during last month owed to Ms. Rankin (not an officer) Unsecured accounts payable Required: Indicate how much money will be paid to the creditor associated with each debt. Types of Debts Administrative expenses Salary during last month owed to Mr. Key and Ms. Rankin Government claims to unpaid taxes Amounts $ 4,150 $ 7,700 19,525 4,150 5,930 8,250arrow_forwardShi Company is going through a Chapter 7 bankruptcy. All assets have been liquidated, and the company retains only $26,600 in free cash. The following debts, totaling $45,050, remain: Government claims to unpaid taxes Salary during last month owed to Mr. Key (not an officer) Administrative expenses Salary during last month owed to Ms. Rankin (not an officer) Unsecured accounts payable $ 7,400 19,225 3,850 Indicate how much money will be paid to the creditor associated with each debt. Types of Debts Administrative expenses Salary during last month owed to Mr. Key and Ms. Rankin 6,625 7,950 Answer is complete but not entirely correct. Amounts 3,850 $12.850 $ 3,716 $26,600 Government claims to unpaid taxesarrow_forwardShi Company is going through a Chapter 7 bankruptcy. All assets have been liquidated, and the company retains only $27,500 in free cash. The following debts, totaling $49,550, remain: Government claims to unpaid taxes Salary during last month owed to Mr. Key (not an officer) Administrative expenses Salary during last month owed to Ms. Rankin (not an officer) Unsecured accounts payable Required: Indicate how much money will be paid to the creditor associated with each debt. Types of Debts Amounts Administrative expenses $ 4,750 Salary during last month owed to Mr. Key and Ms. Rankin Government claims to unpaid taxes $ 0 $ 8,300 20,125 4,750 5,960 8,850arrow_forward
- Shi Company is going through a Chapter 7 bankruptcy. All assets have been liquidated, and the company retains only $26,000 in free cash. The following debts, totaling $42,050, remain: Government claims to unpaid taxes Salary during last month owed to Mr. Key (not an officer) Administrative expenses Salary during last month owed to Ms. Rankin (not an officer) Unsecured accounts payable Required: Indicate how much money will be paid to the creditor associated with each debt. Types of Debts Administrative expenses Amounts $ 3,250 Salary during last month owed to Mr. Key and Ms. Rankin Government claims to unpaid taxes 0 $ 6,800 18,625 3,250 5,890 7,350arrow_forwardhi Company is going through a Chapter 7 bankruptcy. All assets have been liquidated, and the company retains only $27,400 in free cash. The following debts, totaling $49,050, remain: Government claims to unpaid taxes $ 8,200 Salary during last month owed to Mr. Key(not an officer) 20,025 Administrative expenses 4,650 Salary during last month owed to Ms. Rankin (not an officer) 7,425 Unsecured accounts payable 8,750 Indicate how much money will be paid to the creditor associated with each debt.arrow_forwardShi Company is going through a Chapter 7 bankruptcy. All assets have been liquidated, and the company retains only $26,200 in free cash. The following debts, totaling $43,050, remain: $ 7,000 Government claims to unpaid taxes Salary during last month owed to Mr. Key (not an officer) Administrative expenses 19,200 3,450 Salary during last month owed to Ms. Rankin (not an officer) Unsecured accounts payable 5,850 7,550 Indicate how much money will be paid to the creditor associated with each debt. Types of Debts Amounts Administrative expenses Government claims to unpaid taxes Salary during last month owed to Mr. Key and Ms. Rankinarrow_forward
 EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT Business Its Legal Ethical & Global EnvironmentAccountingISBN:9781305224414Author:JENNINGSPublisher:Cengage
Business Its Legal Ethical & Global EnvironmentAccountingISBN:9781305224414Author:JENNINGSPublisher:Cengage





