
(Learning Objectives 4, 5, 6: Report liabilities on the
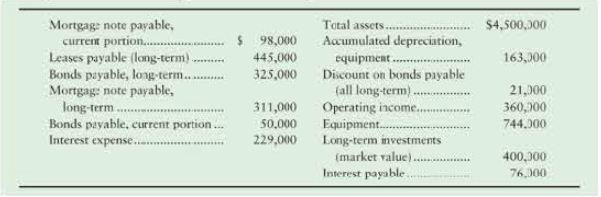
Requirements
1. Show how each relevant item would be reported on the Brigham Foods classified balance sheet. Include headings and totals for current liabilities and long-term liabilities.
2. Answer the following questions about Brigham Food's financial position at December 31, 2018:
- a. What is the carrying amount of the bonds payable (combine the current and long-tenn amounts)?
- b. Why is the interest-payable amount so much less than the amount or interest expense?
3. How many times did Brigham Foods cover its interest expense during 2018?
4. Assume that all of the existing liabilities are included in the information provided. Calculate the leverage ratio and debt ratio of the company. Use yearend figures in place of averages where needed for the purpose of calculating ratios in this problem. Evaluate the health of the company from a leverage point of view. Assume the company only has common stock issued and outstanding. What other information would be helpful in making your evaluation?
5. Independent of your answer to (4), assume that Footnote 8 of the financial statements includes commitments for long-term operating leases over the next 15 years in the amount of $3,800,000. If the company had to capitalize these leases in 2018, how would it change the leverage ratio and the debt ratio? How would this impact your assessment of the company's health from a leverage point of view?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 9 Solutions
Financial Accounting (12th Edition) (What's New in Accounting)
 Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning
