
(a)
Interpretation:
It is to be predicted which of the two nucleophiles in the given pair will react faster with
Concept introduction:
The minimum amount of energy required by reacting molecules to reach the transition state is called the activation energy.
For nucleophilic substitution reactions, if the reactant is the same, the activation energy increases with increasing stability of the substitution product.
The reaction is faster when the energy barrier between the reactants and products is small. When energy difference between reactants and the transition state is smaller than the energy difference between products and transition state, the reactants are highly reactive and reaction is faster. Highly reactive reactant molecules serve as strong nucleophiles. The reactants are less reactive and the reaction slower, when the transition state is closer in energy to the products than the reactants.
Answer to Problem 9.4P
(i) Among the two nucleophiles, the nucleophile
(ii) Among the two nucleophiles, the nucleophile
Explanation of Solution
(i) The first given pair of nucleophiles is
The reactions of each of these nucleophiles with
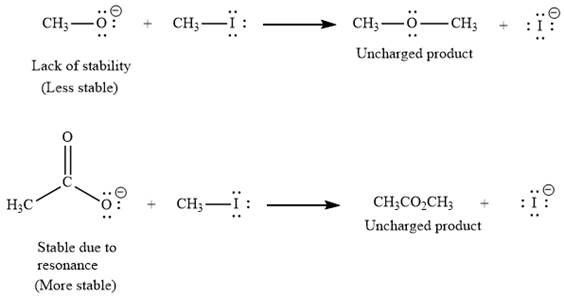
There is a significant difference in charge stability on the reactant side but not on the product side because the negative charge in
(ii) The second given pair of nucleophiles is
The reactions of each of these nucleophiles with
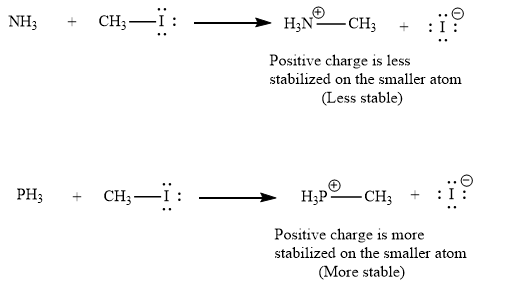
There is a significant difference in charge stability on the product side but not on the reactant side. Because a positive charge is more stable on phosphorous atom than on nitrogen atom, the product of the nucleophilic substitution involving
Therefore, the energy barrier involving
As nucleophilicity of the attacking species increases in
(b)
Interpretation:
It is to be determined which of the given pairs is the stronger nucleophile.
Concept introduction:
The minimum amount of energy required by reacting molecules to reach the transition state is called the activation energy. For nucleophilic substitution reactions, if the reactant is the same, the activation energy increases with increasing stability of the substitution product. When energy difference between reactants and the transition state is smaller than the energy difference between products and transition state, the reactants are highly reactive and reaction is faster. Highly reactive reactant molecules serves as strong nucleophiles.
Answer to Problem 9.4P
(i) Among the pair of nucleophiles,
(ii) Among the two nucleophiles,
Explanation of Solution
(i) The first given pair of nucleophiles is
In part (a), it is determined that the reaction of
(ii) The first given pair of nucleophiles is
In part (a), it is determined that the reaction of
Among the two given nucleophiles, the stronger nucleophile is the one that exhibits a faster reaction.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
EBK GET READY FOR ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- I need help with the followingarrow_forwardFor Raman spectroscopy/imaging, which statement is not true regarding its disadvantages? a) Limited spatial resolution. b) Short integration time. c) A one-dimensional technique. d) Weak signal, only 1 in 108 incident photons is Raman scattered. e) Fluorescence interference.arrow_forwardUsing a cell of known pathlength b = 1.25115 x 10-3 cm, a water absorption spectrum was measured. The band at 1645 cm-1, assigned to the O-H bending, showed an absorbance, A, of 1.40. a) Assuming that water density is 1.00 g/mL, calculate the water molar concentration c (hint: M= mole/L) b) Calculate the molar absorptivity, a, of the 1645 cm-1 band c) The transmitted light, I, can be written as I= Ioexp(-xb), where x is the absorption coefficient (sometimes designated as alpha), Io is the input light, and b is the cell pathlength. Prove that x= (ln10)*x*c. (Please provide a full derivation of the equation for x from the equation for I). d) Calculate x for the 1645 cm-1 bandarrow_forward
- For CARS, which statement is not true regarding its advantages? a) Contrast signal based on vibrational characteristics, no need for fluorescent tagging. b) Stronger signals than spontaneous Raman. c) Suffers from fluorescence interference, because CARS signal is at high frequency. d) Faster, more efficient imaging for real-time analysis. e) Higher resolution than spontaneous Raman microscopy.arrow_forwardDraw the major product of the Claisen condensation reaction between two molecules of this ester. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Incorrect, 5 attempts remaining 1. NaOCH3/CH3OH 2. Acidic workup Select to Draw O Incorrect, 5 attempts remaining The total number of carbons in the parent chain is incorrect. Review the reaction conditions including starting materials and/or intermediate structures and recount the number of carbon atoms in the parent chain of your structure. OKarrow_forwardUsing a cell of known pathlength b = 1.25115 x 10-3 cm, a water absorption spectrum was measured. The band at 1645 cm-1, assigned to the O-H bending, showed an absorbance, A, of 1.40. a) Assuming that water density is 1.00 g/mL, calculate the water molar concentration c (hint: M= mole/L) b) Calculate the molar absorptivity, a, of the 1645 cm-1 band c) The transmitted light, I, can be written as I= Ioexp(-xb), where x is the absorption coefficient (sometimes designated as alpha), Io is the input light, and b is the cell pathlength. Prove that x= (ln10)*x*c d) Calculate x for the 1645 cm-1 bandarrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
