
Concept explainers
Throughput costing (continuation of 9-21). The variable
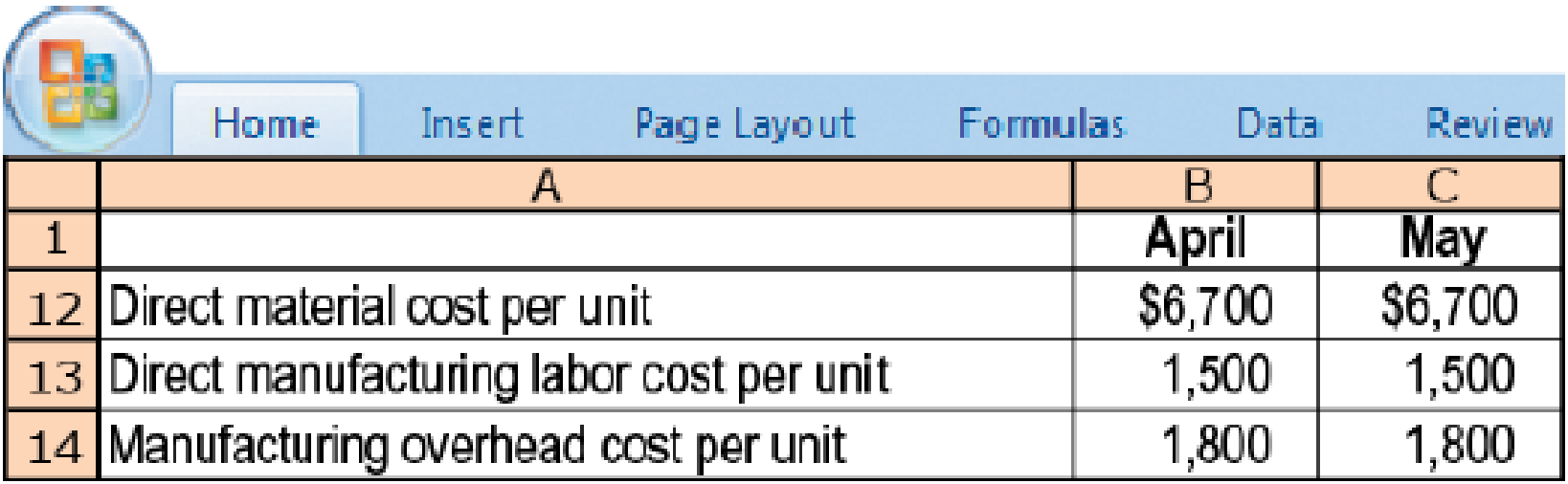
- 1. Prepare income statements for Nascar Motors in April and May 2017 under throughput costing.
Required
- 2. Contrast the results in requirement 1 with those in requirement 1 of Exercise 9-21.
- 3. Give one motivation for Nascar Motors to adopt throughput costing.
Exercise 9-21
9-21 Variable and absorption costing, explaining operating-income differences. Nascar Motors assembles and sells motor vehicles and uses
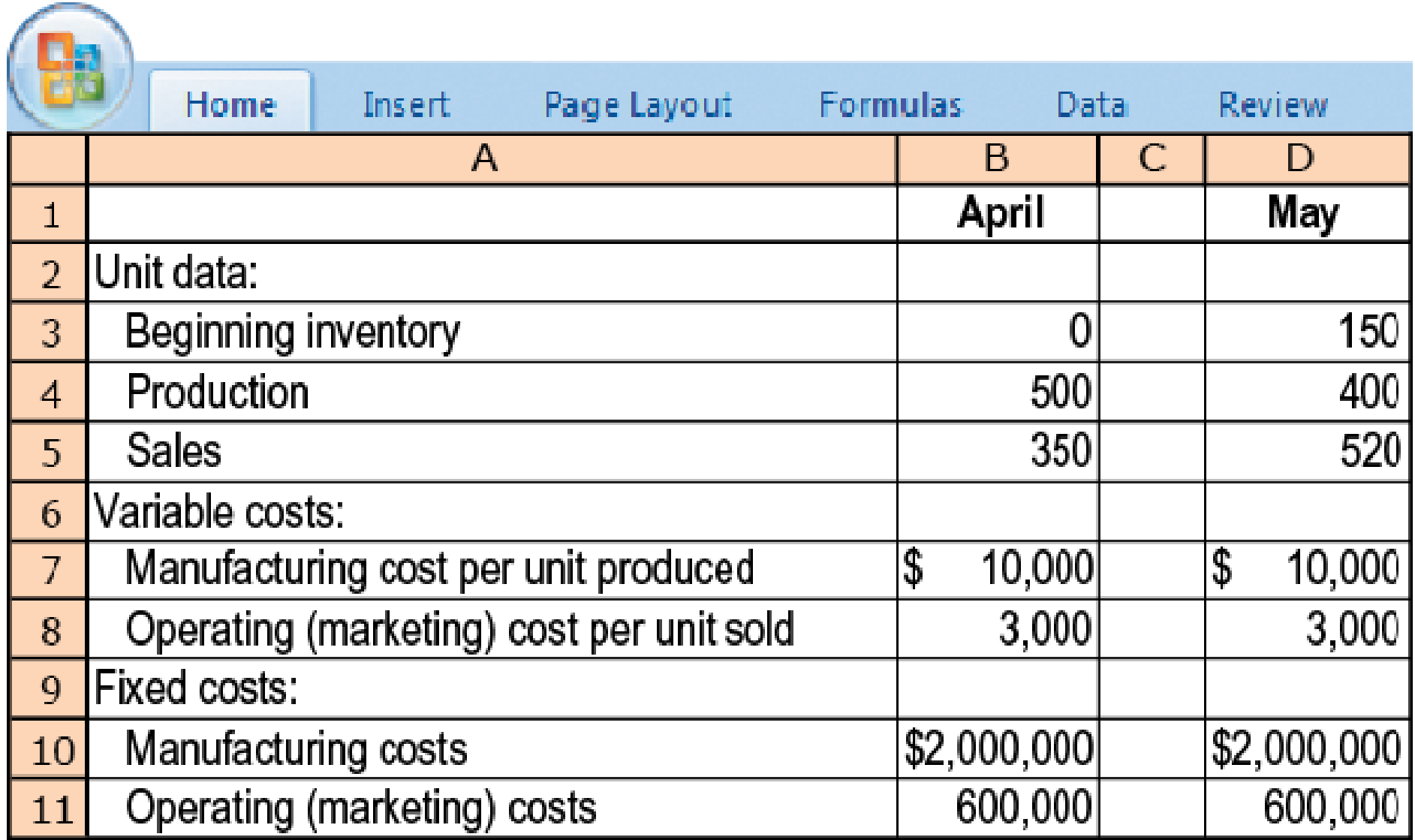
The selling price per vehicle is $24,000. The budgeted level of production used to calculate the budgeted fixed manufacturing cost per unit is 500 units. There are no price, efficiency, or spending variances. Any production-volume variance is written off to cost of goods sold in the month in which it occurs.
- 1. Prepare April and May 2017 income statements for Nascar Motors under (a) variable costing and (b) absorption costing.
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

Chapter 9 Solutions
Horngren's Cost Accounting, Student Value Edition Plus MyLab Accounting with Pearson eText - Access Card Package (16th Edition)
Additional Business Textbook Solutions
Financial Accounting: Tools for Business Decision Making, 8th Edition
Accounting Information Systems (14th Edition)
Gitman: Principl Manageri Finance_15 (15th Edition) (What's New in Finance)
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis (16th Edition)
Foundations of Financial Management
- Principles of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning  Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning
Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning Essentials of Business Analytics (MindTap Course ...StatisticsISBN:9781305627734Author:Jeffrey D. Camm, James J. Cochran, Michael J. Fry, Jeffrey W. Ohlmann, David R. AndersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Essentials of Business Analytics (MindTap Course ...StatisticsISBN:9781305627734Author:Jeffrey D. Camm, James J. Cochran, Michael J. Fry, Jeffrey W. Ohlmann, David R. AndersonPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning





