
Concept explainers
Find the total stress
Answer to Problem 9.1P
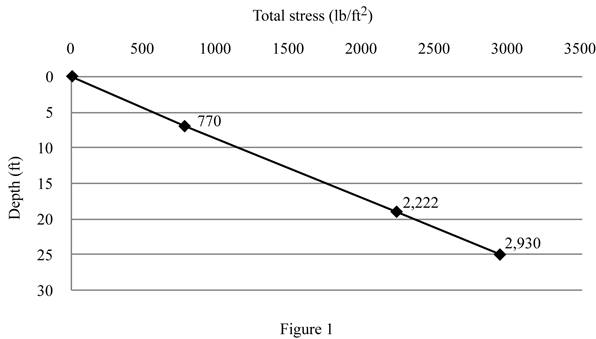
The total stress at point A is
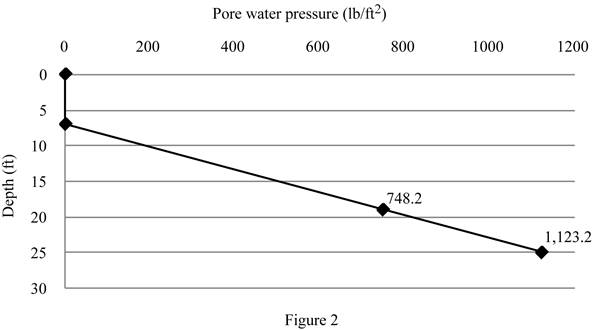
The pore water pressure at point A is
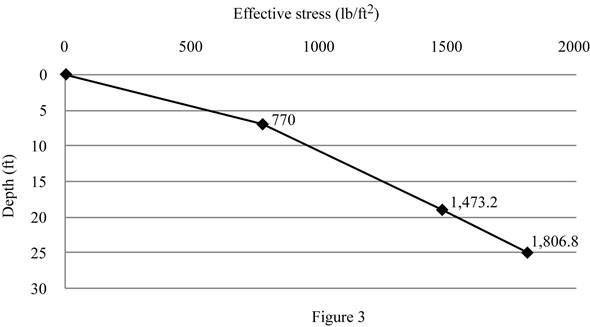
The effective stress at point A is
The total stress at point B is
The pore water pressure at point B is
The effective stress at point B is
The total stress at point C is
The pore water pressure at point C is
The effective stress at point C is
The total stress at point D is
The pore water pressure at point D is
The effective stress at point D is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The thickness
The thickness
The thickness
The dry unit weight
The saturated unit weight
The saturated unit weight
Calculation:
Calculate the total stress at point A (0 ft).
Thus, the total stress at point A is
Calculate the pore water pressure at point A (0 ft).
Thus, pore water pressure at point A is
Calculate the effective stress at point A (0 ft) using the relation.
Substitute 0 for
Thus, effective stress at point A is
Calculate the total stress at point B (7 ft) using the relation.
Substitute
Thus, total stress at point B is
Calculate the pore water at point B (7 ft) using the relation.
Thus, the pore water pressure at point B is
Calculate the effective stress at point B (7 ft) using the relation.
Substitute
Thus, the effective stress at point B is
Calculate the total stress at point C (19 ft) using the relation.
Substitute
Thus, the total stress at point C is
Calculate the pore water pressure at point C (19 ft) using the relation.
Here,
Take the unit weight of the water as
Substitute
Thus, the pore water pressure at point C is
Calculate the effective stress at point C (19 ft) using the relation.
Substitute
Thus, the effective stress at point C is
Calculate the total stress at point D (25 ft) using the relation.
Substitute
Thus, the total stress at point D is
Calculate the pore water pressure at point D (25 ft) using the relation.
Substitute
Thus, the pore water pressure at point D is
Calculate the effective stress at point D (25 ft) using the relation.
Substitute
Thus, the effective stress at point D is
Show the plot between depth and total stress as in Figure 1.
Show the plot between depth and pore water pressure as in Figure 2.
Show the plot between depth and effective stress as in Figure 3.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
EBK PRINCIPLES OF GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEER
- Please solve manually, and give any tips on how I can manually recreate the flow net you provide. Thanks.arrow_forwardA group of nine piles. 12m long and 350 mm in diameter, is to be arrenged in a square form in clay soil with an average unconfined compressive strength of 60 KN/m^2. Work out center to center spacing of the piles for a group effeciency factor of 1, Neglect bearing at the tip of the piles.arrow_forwardSOLVE BY NEWTON - RAPHSON METHOD: The equation x³-3x-4=0 is of the form f(x) = 0 where f(1) 0 so there is a solution to the equation between 1 and 3. We shall take this to be 2, by bisection. Find a better approximation to the root.arrow_forward
- Kindly help to provide answers, elaborate with examples and provide useful links for learning purposes. this is regarding building diagnosis.arrow_forwardpounds of steel need to be purchased for the roof plan a table with various steel types and the quantity needed The colums are 18 feet high and weigh 76 ponds per foot include a structural steel material list for the roof framing planarrow_forwardHomework: Determine the proportions of the separate aggregates that will give a gradation within the SCRB wearing coarse specified limits for the aggregates and mix composition for highway pavement asphaltic concrete. The table below shows the results of sieve analysis of samples from the materials available. برو Percent by Weight Passing Sieve Designation Retained on Sieve Designation Coarse Aggregate Fine Aggregate Mineral Filler 3/4 in. (19 mm) 1/2 in. 5 ½ in. (12.5 mm) 3/8 in. 35 ¾ in. (9.5 mm) No. 4 38 No. 4 (4.75 mm) No. 10 17 No. 10 (2 mm) No. 40 5 No. 40 (0.425 mm) No. 80 No. 80 (0.180 mm) No. 200 No. 200 (0.075 mm) Total 18 1118 30 35 5 26 35 60 100 100 100arrow_forward
- For the driven pile shown in figure, estimate the allowable capacity by: (a) Tomlinson a-method, (b)Vijayvergia and Focht A-method. Which one of the two methods are more conservative? Qall =? W.T 18.21 kN/m² 930 L=18m Square pile 27.5cm x 27.5cmarrow_forwardWhat is the vertical deflection at joint C of the truss shown? 75 kN 9 m 7 (3000 mm²) (3000 mm²) (2000 mm²) (3000 mm²) (2000 mm²) 100 kN (3000 mm²) H (3000 mm²) (2000 mm²) (2000 mm²) (3000 mm²)B(3000 mm²) C(3000 mm²)D(3000 mm2)5 a. 9.3 mm↓ b. 9.6 mm↓ c. 8.0 mm ↓ d. 9.1 mm↓ 4 at 6 m = 24 m E = 200 GPa Earrow_forwardINVERSE FROM POINT A TOWARDS POINT B GIVEN THE FOLLOWINGCOORDINATE VALUES: POINT AN=13,163,953.37'E=3,072,227.10' POINT BN=13,163,463.03'E=3,072,129.30' FIND THE FOLLOWING:DISTANCE FROM A TO BNORTH AZIMUTH (NAZ) FROM A TOWARDS BBEARING OF THE LINE FROM A TOWARDS Barrow_forward
- FORWARD FROM POINT B TO POINT A GIVEN THE FOLLOWING: POINT BN=13,163,463.03'E=3,072,129.30' DIRECTION FROM B TO A (NAZ)=276.07529° DISTANCE FROM B TO A = 10.00'arrow_forwardA cheetah is crouched 20 m to the east of an observer. At time t = 0 s, the cheetah begins to run due east toward an antelope that is 50 m to the east of the observer. During the first 2.0 s of the attack, the cheetah's coordinate x varies with time according to the equation x = 20 + 5t?. (a) Find the cheetah's displacement between t1 = 1.0 s and t2 = 2.0 s. (b) Find its average velocity during that interval. (c) Derive an expression for the cheetah's instantaneous velocity as a function of time, and use it to find Vy at t = 1.0 s and t = 2.0 s.arrow_forwardWrite at least 20 words for vocabulary and 10 verbs .for simple present, past, and past participlesarrow_forward
 Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning



