
Concept explainers
Draw Lewis structures for the following organic molecules: (a) methanol (CH3OH); (b) ethanol (CH3CH2OH); (c) tetraethyllead [Pb(CH2CH3)4], which was used in “leaded gasoline”; (d) methylamine (CH3NH2), which is used in tanning; (e) mustard gas (ClCH2CH2SCH2CH2Cl), a poisonous gas used in World War I; (f) urea [(NH2)2CO], a fertilizer; and (g) glycine (NH2CH2COOH), an amino acid.
(a)
Interpretation:
Lewis structure of
Concept Introduction:
Electron dot structure also known as Lewis dot structure represents the number of valence electrons of an atom or constituent atoms bonded in a molecule. Each dot corresponds to one electron.
Explanation of Solution
Total valence electrons in
Accordingly Lewis structure of
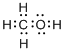
(b)
Interpretation:
Lewis structure of
Concept Introduction:
Electron dot structure also known as Lewis dot structure represents the number of valence electrons of an atom or constituent atoms bonded in a molecule. Each dot corresponds to one electron.
Explanation of Solution
Total valence electrons in
Accordingly Lewis structure of
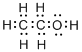
(c)
Interpretation:
Lewis structure of tetraethyllead has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Electron dot structure also known as Lewis dot structure represents the number of valence electrons of an atom or constituent atoms bonded in a molecule. Each dot corresponds to one electron.
Explanation of Solution
Tetraethyllead is four ethyl groups bonded to lead atom.
Structure of ethyl group is,
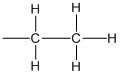
Tetraethyllead has molecular formula
Total valence electrons in Tetraethyllead is,
Accordingly structure of
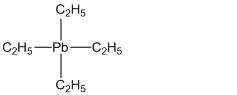
In the above structure

For simplicity the above structure is written as
(d)
Interpretation:
Lewis structure of
Concept Introduction:
Electron dot structure also known as Lewis dot structure represents the number of valence electrons of an atom or constituent atoms bonded in a molecule. Each dot corresponds to one electron.
Explanation of Solution
Total valence electrons in
Accordingly Lewis structure of
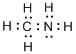
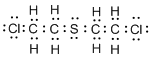
(e)
Interpretation:
Lewis structure of mustard gas
Concept Introduction:
Electron dot structure also known as Lewis dot structure represents the number of valence electrons of an atom or constituent atoms bonded in a molecule. Each dot corresponds to one electron.
Explanation of Solution
Total valence electrons in
Accordingly Lewis structure of
(f)
Interpretation:
Lewis structure of urea
Concept Introduction:
Electron dot structure also known as Lewis dot structure represents the number of valence electrons of an atom or constituent atoms bonded in a molecule. Each dot corresponds to one electron.
Explanation of Solution
Total valence electrons in
Accordingly Lewis structure of
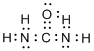
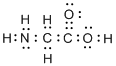
(g)
Interpretation:
Lewis structure of glycine (
Concept Introduction:
Electron dot structure also known as Lewis dot structure represents the number of valence electrons of an atom or constituent atoms bonded in a molecule. Each dot corresponds to one electron.
Explanation of Solution
Total valence electrons in
Accordingly Lewis structure of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Chemistry
- Incorrect Feedback: Your answer is incorrect. Predict the major products of the following organic reaction: ཤིགས་བྱ རྩ་ཅད་ཀྱིས་༢༩ + Some important notes: A ^ ? • Draw the major product, or products, of the reaction in the drawing area below. • If there aren't any products, because no reaction will take place, check the box below the drawing area instead. • Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products that are enantiomers. E Check 0 لا Save For La ©2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of All F9 Aarrow_forwardPredict the major products of the following organic reaction: + Δ A ? Some important notes: • Draw the major product, or products, of the reaction in the drawing area below. • If there aren't any products, because no reaction will take place, check the box below the drawing area instead. • Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products that are enantiomers. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Privaarrow_forwardesc 2 Incorrect Feedback: Your answer is incorrect. Can the molecule on the right-hand side of this organic reaction be made in good yield from no more than two reactants, in one step, by moderately heating the reactants? ? A O • If your answer is yes, then draw the reactant or reactants in the drawing area below. You can draw the reactants in any arrangement you like. . If your answer is no, check the box under the drawing area instead. Check F1 ! @ X C Save For Later Submit Assignment 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibility 80 et A ད 1 4 F2 F3 F4 F5 F6 F7 F8 F9 F10 F11 F12 # $ 45 % A 6 87 & * 8 9 ) 0 + ||arrow_forward
- Can the molecule on the right-hand side of this organic reaction be made in good yield from no more than two reactants, in one step, by moderately heating the reactants? ?A Δ O • If your answer is yes, then draw the reactant or reactants in the drawing area below. You can draw the reactants in any arrangement you like. • If your answer is no, check the box under the drawing area instead. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibilit ku F11arrow_forward१ eq ine teaching and × + rn/takeAssignment/takeCovalentActivity.do?locator-assignment-take [Review Topics] [References] Write an acceptable IUPAC name for the compound below. (Only systematic names, not common names are accepted by this question.) Keep the information page open for feedback reference. The IUPAC name is In progress mit Answer Retry Entire Group 5 more group attempts remaining Cengage Learning | Cengage Technical Support Save and Exitarrow_forwardDraw the molecules.arrow_forward
- Draw the mechanism for the acid-catalyzed dehydration of 2-methyl-hexan-2-ol with arrows please.arrow_forward. Draw the products for addition reactions (label as major or minor) of the reaction between 2-methyl-2-butene and with following reactants : Steps to follow : A. These are addition reactions you need to break a double bond and make two products if possible. B. As of Markovnikov rule the hydrogen should go to that double bond carbon which has more hydrogen to make stable products or major product. Here is the link for additional help : https://study.com/academy/answer/predict-the-major-and-minor-products-of-2-methyl- 2-butene-with-hbr-as-an-electrophilic-addition-reaction-include-the-intermediate- reactions.html H₂C CH3 H H3C CH3 2-methyl-2-butene CH3 Same structure CH3 IENCESarrow_forwardDraw everything on a piece of paper including every single step and each name provided using carbons less than 3 please.arrow_forward
- Topics] [References] Write an acceptable IUPAC name for the compound below. (Only systematic names, not common names are accepted by this question.) Keep the information page open for feedback reference. H The IUPAC name isarrow_forward[Review Topics] [References] Write an acceptable IUPAC name for the compound below. (Only systematic names, not common names are accepted by this question.) Keep the information page open for feedback reference. The IUPAC name is Submit Answer Retry Entire Group 9 more group attempts remainingarrow_forwardPlease draw.arrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
