
Subpart (a):
The equilibrium price and the quantity of haircuts and total surplus.
Subpart (a):
Explanation of Solution
Supply curve: The supply equation is
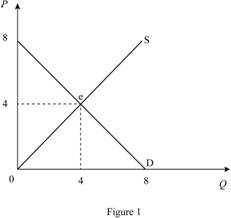
In Figure 1, horizontal axis measures quantity and vertical axis measures price. The curve D indicates demand and the curve S indicates supply. Market reaches the equilibrium at point ‘e’ where the demand curve intersects with supply curve.
Equilibrium price can be calculated as follows.
Equilibrium price is $4.
Equilibrium quantity can be calculated by substituting the equilibrium price in to supply equation.
Thus, equilibrium quantity is 4 units.
Consumer surplus is $8.
Producer surplus is $8.
Total surplus can be calculated as follows.
Total surplus is $16.
Concept introduction:
Consumer surplus: It is the difference between the highest willing price of the consumer and the actual price that the consumer pays.
Producer surplus: It is the difference between the minimum accepted price for the producer and the actual price received by the producer.
Equilibrium price: It is the market price determined by equating the supply to the demand. At this equilibrium point, the supply will be equal to the demand and there will be no excess demand or
Subpart (b):
The equilibrium price and the quantity of haircuts and total surplus.
Subpart (b):
Explanation of Solution
The world price for the good is $1. Thus, when the country opens the market for trade, the price becomes $1 in domestic country too. Figure 2 describe this situation.
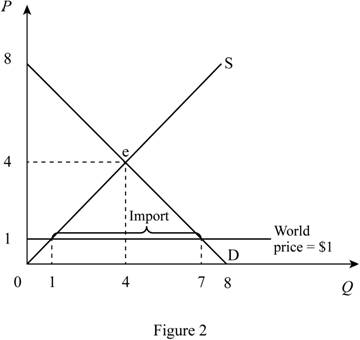
In Figure 2, horizontal axis measures quantity and vertical axis measures price. The curve D indicates demand and the curve S indicates supply. Market reaches the equilibrium at point ‘e’ where the demand curve intersects with supply curve.
When the competitor (Rest of the world) sells a good at price $1, in domestic country equilibrium price become equal to world price. Thus, equilibrium price in the domestic country is $1.
Equilibrium domestic supply can be calculated by substituting the domestic equilibrium price in to supply equation.
Thus, equilibrium quantity is 1 unit.
Equilibrium domestic demand can be calculated by substituting the domestic equilibrium price in to demand equation.
Thus, equilibrium domestic demand is 7 units.
Total imports can be calculated as follows.
Domestic imports are 6 units.
Consumer surplus can be calculated as follows.
Consumer surplus is $24.5.
Producer surplus can be calculated as follows.
Producer surplus is $0.5.
Total surplus can be calculated as follows.
Total surplus is $25.
Concept introduction:
Consumer surplus: It is the difference between the highest willing price of the consumer and the actual price that the consumer pays.
Producer surplus: It is the difference between the minimum accepted price for the producer and the actual price received by the producer.
Equilibrium price: It is the market price determined by equating the supply to the demand. At this equilibrium point, the supply will be equal to the demand and there will be no excess demand or excess supply in an economy. Thus, the economy will be at equilibrium.
Subpar (c):
The equilibrium price and the quantity of haircuts and total surplus.
Subpar (c):
Explanation of Solution
When domestic country impose tariff of $1, the price in domestic country increases from $1 to $2. This increase in price is shown in the Figure 3.
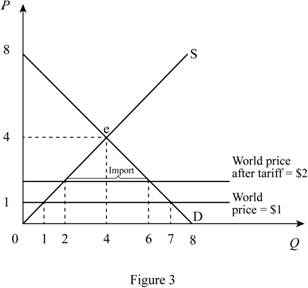
In Figure 3, horizontal axis measures quantity and vertical axis measures price. The curve D indicates demand and the curve S indicates supply. Market reaches the equilibrium at point ‘e’ where the demand curve intersects with supply curve. Price is increases from $1 to $2 due to the tariff of $1.
Domestic equilibrium price can be calculated as follows.
New domestic price is $2.
Equilibrium domestic supply can be calculated by substituting the domestic equilibrium price in to supply equation.
Thus, equilibrium quantity is 2 units.
Equilibrium domestic demand can be calculated by substituting the domestic equilibrium price in to demand equation.
Thus, equilibrium domestic demand is 6 units.
Total imports can be calculated as follows.
Domestic imports are 4 units.
Consumer surplus can be calculated as follows.
Consumer surplus is $18.
Producer surplus can be calculated as follows.
Producer surplus is $2.
Government revenue can be calculated as follows.
Government revenue is 4.
Total surplus can be calculated as follows.
Total surplus is $24.
Concept introduction:
Consumer surplus: It is the difference between the highest willing price of the consumer and the actual price that the consumer pays.
Producer surplus: It is the difference between the minimum accepted price for the producer and the actual price received by the producer.
Equilibrium price: It is the market price determined by equating the supply to the demand. At this equilibrium point, the supply will be equal to the demand and there will be no excess demand or excess supply in an economy. Thus, the economy will be at equilibrium.
Subpart (d):
Calculate total gains and deadweight loss .
Subpart (d):
Explanation of Solution
Total gains from opening up trade can be calculated as follows.
Total gains are$8.
Deadweight loss can be calculated as follows.
Deadweight loss is $1.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
- The following table provides information on two technology companies, IBM and Cisco. Use the data to answer the following questions. Company IBM Cisco Systems Stock Price Dividend (trailing 12 months) $150.00 $50.00 $7.00 Dividend (next 12 months) $7.35 Dividend Growth 5.0% $2.00 $2.15 7.5% 1. You buy a futures contract instead of purchasing Cisco stock at $50. What is the one-year futures price, assuming the risk-free interest rate is 6%? Remember to adjust the futures price for the dividend of $2.15.arrow_forward5. Consider a one-year European-style call option on Cisco stock. The strike is $50.85, which is the forward price. The risk-free interest rate is 6%. Assume the stock price either doubles or halves each period. The price movement corresponds to u = 2 and d = ½ = 1/u. S1 = $100 Call payoff= SO = $50 S1 = $25 Call payoff= What is the call payoff for $1 = $100? What is the call payoff for S1 = $25?arrow_forwardMC The diagram shows a pharmaceutical firm's demand curve and marginal cost curve for a new heart medication for which the firm holds a 20-year patent on its production. Assume this pharmaceutical firm charges a single price for its drug. At its profit-maximizing level of output, it will generate a total profit represented by OA. areas J+K. B. areas F+I+H+G+J+K OC. areas E+F+I+H+G. D. - it is not possible to determine with the informatio OE. the sum of areas A through K. (...) Po P1 Price F P2 E H 0 G B Q MR D ōarrow_forward
- Price Quantity $26 0 The marketing department of $24 20,000 Johnny Rockabilly's record company $22 40,000 has determined that the demand for his $20 60,000 latest CD is given in the table at right. $18 80,000 $16 100,000 $14 120,000 The record company's costs consist of a $240,000 fixed cost of recording the CD, an $8 per CD variable cost of producing and distributing the CD, plus the cost of paying Johnny for his creative talent. The company is considering two plans for paying Johnny. Plan 1: Johnny receives a zero fixed recording fee and a $4 per CD royalty for each CD that is sold. Plan 2: Johnny receives a $400,000 fixed recording fee and zero royalty per CD sold. Under either plan, the record company will choose the price of Johnny's CD so as to maximize its (the record company's) profit. The record company's profit is the revenues minus costs, where the costs include the costs of production, distribution, and the payment made to Johnny. Johnny's payment will be be under plan 2 as…arrow_forwardWhich of the following is the best example of perfect price discrimination? A. Universities give entry scholarships to poorer students. B. Students pay lower prices at the local theatre. ○ C. A hotel charges for its rooms according to the number of days left before the check-in date. ○ D. People who collect the mail coupons get discounts at the local food store. ○ E. An airline offers a discount to students.arrow_forwardConsider the figure at the right. The profit of the single-price monopolist OA. is shown by area D+H+I+F+A. B. is shown by area A+I+F. OC. is shown by area D + H. ○ D. is zero. ○ E. cannot be calculated or shown with just the information given in the graph. (C) Price ($) B C D H FIG шо E MC ATC A MR D = AR Quantityarrow_forward
- Consider the figure. A perfectly price-discriminating monopolist will produce ○ A. 162 units and charge a price equal to $69. ○ B. 356 units and charge a price equal to $52 for the last unit sold only. OC. 162 units and charge a price equal to $52. OD. 356 units and charge a price equal to the perfectly competitive price. Dollars per Unit $69 $52 MR 162 356 Output MC Darrow_forwardThe figure at right shows the demand line, marginal revenue line, and cost curves for a single-price monopolist. Now suppose the monopolist is able to charge a different price on each different unit sold. The profit-maximizing quantity for the monopolist is (Round your response to the nearest whole number.) The price charged for the last unit sold by this monopolist is $ (Round your response to the nearest dollar.) Price ($) 250 225- 200- The monopolist's profit is $ the nearest dollar.) (Round your response to MC 175- 150 ATC 125- 100- 75- 50- 25- 0- °- 0 20 40 60 MR 80 100 120 140 160 180 200 Quantityarrow_forwardThe diagram shows a pharmaceutical firm's demand curve and marginal cost curve for a new heart medication for which the firm holds a 20-year patent on its production. At its profit-maximizing level of output, it will generate a deadweight loss to society represented by what? A. There is no deadweight loss generated. B. Area H+I+J+K OC. Area H+I D. Area D + E ◇ E. It is not possible to determine with the information provided. (...) 0 Price 0 m H B GI A MR MC D Outparrow_forward
- Consider the figure on the right. A single-price monopolist will produce ○ A. 135 units and charge a price equal to $32. B. 135 units and generate a deadweight loss. OC. 189 units and charge a price equal to the perfectly competitive price. ○ D. 189 units and charge a price equal to $45. () Dollars per Unit $45 $32 MR D 135 189 Output MC NGarrow_forwardSuppose a drug company cannot prevent resale between rich and poor countries and increases output from 3 million (serving only the rich country with a price of $80 per treatment) to 9 million (serving both the rich and the poor countries with a price of $30 per treatment). Marginal cost is constant and equal to $10 per treatment in both countries. The marginal revenue per treatment of increasing output from 3 million to 9 million is equal to ○ A. $20 per treatment, which is greater than the marginal cost of $10 per treatment and thus implies that profits will rise. ○ B. $20 per treatment, which is greater than zero and thus implies that profits will rise. ○ C. $30 per treatment, which is greater than the marginal cost of $10 per treatment and thus implies that profits will rise. ○ D. $5 per treatment, which is less than the marginal cost of $10 per treatment and thus implies that profits will fall. ○ E. $30 per treatment, which is less than the marginal revenue of $80 per treatment…arrow_forwardConsider the figure. A single-price monopolist will have a total revenue of Single-Price Monopolist OA. 84×$13. O B. 92x $13. OC. 84×$33. OD. 92 x $33. C Price ($) $33 $13 MC MR D 84 92 Output The figure is not drawn to scale.arrow_forward
 Principles of MicroeconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781305156050Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of MicroeconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781305156050Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Cou...EconomicsISBN:9781285165875Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Cou...EconomicsISBN:9781285165875Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781285165912Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781285165912Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Microeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa...EconomicsISBN:9781305506893Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Microeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa...EconomicsISBN:9781305506893Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning Macroeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa...EconomicsISBN:9781305506756Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Macroeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa...EconomicsISBN:9781305506756Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning Economics: Private and Public Choice (MindTap Cou...EconomicsISBN:9781305506725Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Economics: Private and Public Choice (MindTap Cou...EconomicsISBN:9781305506725Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning





