
a.
Ascertain the product cost and gross profit margin percentages of each product.
a.
Explanation of Solution
Ascertain the product cost and gross profit margin percentages of each product.
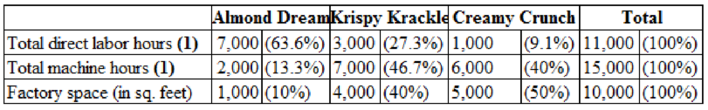
Table (1)
| Total rent for factory space: | $15,000 per month |
| Total machine operating costs: | $30,000 per month |
| Total other | $24,500 per month |
| Total cases produced per month | 3,000 cases |
Table (2)
Product allocation base:
| Fraction: | Labor (%) | Machine hours (%) | Factory Space (%) |
| Almond Dream | 63.6% | 13.3% | 10% |
| Krispy Krackle | 27.3 | 46.7 | 40 |
| Creamy Crunch | 9.1 | 40.0 | 50 |
Table (3)
Allocated costs:
| Allocated costs: | Total | Per Case | |
| Almond Dream | = | $21,072 | $21.07 |
| Krispy Krackle | = | 26,699 | 26.70 |
| Creamy Crunch | = | 21,730 | 21.73 |
Table (4)
Allocated Production Costs:
|
Almond Dream |
Krispy Krackle |
Creamy Crunch | |
| Material cost | $8.00 | $2.00 | $9.00 |
| Direct labor | 42.00 | 18.00 | 6.00 |
| Allocated overhead | 21.07 | 26.70 | 21.73 |
| Production cost per case | $71.07 | $46.70 | $36.73 |
| Selling price (b) | $85.00 | $55.00 | $35.00 |
| Product cost | (71.07) | (46.70) | (36.73) |
| $13.93 | $8.30 | $(1.73) | |
| Profit margin ratio (c) = (a/b) | 16.4% | 15.1% | (4.9)% |
Table (5)
Note (1):
Totals equal hours per case times 1,000 cases.
Hence, the product costs and gross profit margin percentage for the products Almond Dream, Krispy Krackle, and Creamy Crunch are $71.07, and 16.4%, $46.70, and 15.1%, and $36.73, and (4.9)%, respectively.
b.
Identify whether the management would recommend dropping any product.
b.
Explanation of Solution
Identify whether the management would recommend dropping any product.
It would be recommended by the management to drop Creamy Crunch, based on the gross profit margin rule, and the table above. 50% of the factory space is used by the product Creamy Crunch, and so it is allocated half of the rent costs. When compared to the two products, the selling price is comparitively low. These are the two characteristics which make this product appear relatively unprofitable.
c.
Identify whether any of the remaining products should be dropped from the product line.
c.
Explanation of Solution
Identify whether any of the remaining products should be dropped from the product line.
| Almond Dream | Krispy Krackle | |||
| Direct labor hours per case | 7 | 3 | ||
| Machine hours per case | 2 | 7 | ||
| Factory space (in sq.ft.) (1) | 2,000 | (33.3%) | 4,000 | (66.7%) |
| Case of output per month | 2,000 | 1,000 | ||
| Labour hours required | 14,000 | (82.4) | 3,000 | (17.6%) |
| Machine hours required | 4,000 | (36.4) | 7,000 | (63.6%) |
Table (6)
Note (1):
4,000 square feet of space will be left available by this product mix.
| Total rent for factory space: | $15,000 per month |
| Total machine operating costs: | $30,000 per month |
| Total other overhead: | $24,500 per month |
| Total cases produced per month | 3,000 cases |
| Total labor hours per month | 17,000 |
| Total machine hours | 11,000 hours |
Table (7)
Product allocation base:
| Fraction: | Labor (%) | Machine hours (%) | Factory Space (%) |
| Almond Dream | 82.4% | 36.4% | 33.3% |
| Krispy Krackle | 17.6 | 63.6 | 66.7 |
Table (8)
Allocated costs:
| Allocated costs: | Total | Per Case | |
| Almond Dream | = | $36,108 | $18.05 |
| Krispy Krackle | = | 33,392 | 33.39 |
Table (9)
Allocated Production Costs:
|
Almond Dream |
Krispy Krackle | |
| Material cost | $8.00 | $2.00 |
| Direct labor | 42.00 | 18.00 |
| Allocated overhead | 18.05 | 33.39 |
| Production cost per case | $68.05 | $53.39 |
| Selling price (b) | $85.00 | $55.00 |
| Product cost | (68.05) | (53.39) |
| Profit (loss) (a) | $16.95 | $1.61 |
| Profit margin ratio (c) = (a/b) | 19.9% | 2.9% |
Table (10)
The management should continue to produce Almond Dream, and should Drop Frispy Krackle, based on the gross profit margins of Krispy Krackle, and Almond Dream. The most profitable product is likely to be Almond Dream. However, its margin ratio is only 13.9%.
Calculate the margin ratio of Almond Dream:
|
Almond Dream | |
| Material cost | $8.00 |
| Direct labor | 42.00 |
| Allocated overhead | 23.17 |
| Production cost per case | $73.17 |
| Selling price (b) | $85.00 |
| Product cost | (73.17) |
| Profit (loss) (a) | $11.83 |
| Profit margin ratio (c) = (a/b) | 13.9% |
Table (11)
Almond Dream, and Krispy Krackle are found to be equally profitable, if the gross margin for the three products are computed at maximum production:
| Almond Dream | or | Krispy Krackle | or | Creamy Crunch | ||
| Cases | 3,000 | 3,000 | 3,000 | |||
| Costs | ||||||
| Materials | $ 24,000 | $ 6,000 | $ 27,000 | |||
| Labor | 126,000 | 54,000 | 18,000 | |||
| Overhead | + | 69,500 | + | 69,500 | + | 69,500 |
| $219,500 | $129,500 | $114,500 | ||||
| Revenue | $255,000 | $165,000 | $105,000 | |||
| Total costs | – | 219,500 | – | 129,500 | – | 114,500 |
| Gross margin | $ 35,500 | $ 35,500 | $ (9,500) |
Table (12)
Hence, in decision making, too much of allocated cost numbers are not to be made.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Fundamentals of Cost Accounting
- Kepler Manufacturing has $18,000 of ending finished goods inventory as of December 31, 2023. If beginning finished goods inventory was $8,000 and the cost of goods sold (COGS) was $55,000, how much would Kepler report for cost of goods manufactured?arrow_forwardMosco Industries manufactures a single product and follows a JIT policy where ending inventory must equal 20% of the next month's sales. It estimates that November's ending inventory will consist of 32,000 units. December and January sales are estimated to be 210,000 and 225,000 units, respectively. Mosco assigns variable overhead at a rate of $2.85 per unit of production. Fixed overhead equals $375,000 per month. Compute the number of units to be produced and the total budgeted overhead that would appear on the factory overhead budget for the month of December.arrow_forwardCan you explain this general accounting question using accurate calculation methods?arrow_forward
- Anderson owns securities with a tax basis of $8,400. He gives them to Taylor when they are worth only $6,900. Taylor held these securities until they were worth $9,300 and sold them. What amount of gain does he have to report on this sale? a) $650 b) $400 c) $900 d) $1,100arrow_forwardCan you demonstrate the proper approach for solving this financial accounting question with valid techniques?arrow_forwardPlease provide the answer to this general accounting question with proper steps.arrow_forward
- RBI company issues $500,000 face value bonds with a 6% stated interest rate, payable semiannually. The bonds sell for $532,000 (at a premium) and have 10 years until maturity. Using the straight-line method, what is the amount of premium amortization for each semiannual interest payment?arrow_forwardCan you solve this general accounting problem using accurate calculation methods?arrow_forwardI Want Answerarrow_forward
- I need help finding the accurate solution to this general accounting problem with valid methods.arrow_forwardJuno Manufacturing used$42,000 of direct materials and incurred $55,000 of direct labor costs during the month of August. The company applied $28,000 of overhead to its products.If the cost of goods manufactured was $135,000 and the ending work in process inventory was $18,000, the beginning work in process must have been equal to_.arrow_forwardPlease explain the correct approach for solving this financial accounting question.arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





