
a.
Ascertain the product cost and gross profit margin percentages of each product.
a.
Explanation of Solution
Ascertain the product cost and gross profit margin percentages of each product.
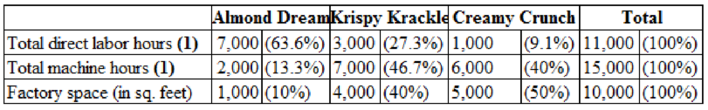
Table (1)
| Total rent for factory space: | $15,000 per month |
| Total machine operating costs: | $30,000 per month |
| Total other | $24,500 per month |
| Total cases produced per month | 3,000 cases |
Table (2)
Product allocation base:
| Fraction: | Labor (%) | Machine hours (%) | Factory Space (%) |
| Almond Dream | 63.6% | 13.3% | 10% |
| Krispy Krackle | 27.3 | 46.7 | 40 |
| Creamy Crunch | 9.1 | 40.0 | 50 |
Table (3)
Allocated costs:
| Allocated costs: | Total | Per Case | |
| Almond Dream | = | $21,072 | $21.07 |
| Krispy Krackle | = | 26,699 | 26.70 |
| Creamy Crunch | = | 21,730 | 21.73 |
Table (4)
Allocated Production Costs:
|
Almond Dream |
Krispy Krackle |
Creamy Crunch | |
| Material cost | $8.00 | $2.00 | $9.00 |
| Direct labor | 42.00 | 18.00 | 6.00 |
| Allocated overhead | 21.07 | 26.70 | 21.73 |
| Production cost per case | $71.07 | $46.70 | $36.73 |
| Selling price (b) | $85.00 | $55.00 | $35.00 |
| Product cost | (71.07) | (46.70) | (36.73) |
| $13.93 | $8.30 | $(1.73) | |
| Profit margin ratio (c) = (a/b) | 16.4% | 15.1% | (4.9)% |
Table (5)
Note (1):
Totals equal hours per case times 1,000 cases.
Hence, the product costs and gross profit margin percentage for the products Almond Dream, Krispy Krackle, and Creamy Crunch are $71.07, and 16.4%, $46.70, and 15.1%, and $36.73, and (4.9)%, respectively.
b.
Identify whether the management would recommend dropping any product.
b.
Explanation of Solution
Identify whether the management would recommend dropping any product.
It would be recommended by the management to drop Creamy Crunch, based on the gross profit margin rule, and the table above. 50% of the factory space is used by the product Creamy Crunch, and so it is allocated half of the rent costs. When compared to the two products, the selling price is comparitively low. These are the two characteristics which make this product appear relatively unprofitable.
c.
Identify whether any of the remaining products should be dropped from the product line.
c.
Explanation of Solution
Identify whether any of the remaining products should be dropped from the product line.
| Almond Dream | Krispy Krackle | |||
| Direct labor hours per case | 7 | 3 | ||
| Machine hours per case | 2 | 7 | ||
| Factory space (in sq.ft.) (1) | 2,000 | (33.3%) | 4,000 | (66.7%) |
| Case of output per month | 2,000 | 1,000 | ||
| Labour hours required | 14,000 | (82.4) | 3,000 | (17.6%) |
| Machine hours required | 4,000 | (36.4) | 7,000 | (63.6%) |
Table (6)
Note (1):
4,000 square feet of space will be left available by this product mix.
| Total rent for factory space: | $15,000 per month |
| Total machine operating costs: | $30,000 per month |
| Total other overhead: | $24,500 per month |
| Total cases produced per month | 3,000 cases |
| Total labor hours per month | 17,000 |
| Total machine hours | 11,000 hours |
Table (7)
Product allocation base:
| Fraction: | Labor (%) | Machine hours (%) | Factory Space (%) |
| Almond Dream | 82.4% | 36.4% | 33.3% |
| Krispy Krackle | 17.6 | 63.6 | 66.7 |
Table (8)
Allocated costs:
| Allocated costs: | Total | Per Case | |
| Almond Dream | = | $36,108 | $18.05 |
| Krispy Krackle | = | 33,392 | 33.39 |
Table (9)
Allocated Production Costs:
|
Almond Dream |
Krispy Krackle | |
| Material cost | $8.00 | $2.00 |
| Direct labor | 42.00 | 18.00 |
| Allocated overhead | 18.05 | 33.39 |
| Production cost per case | $68.05 | $53.39 |
| Selling price (b) | $85.00 | $55.00 |
| Product cost | (68.05) | (53.39) |
| Profit (loss) (a) | $16.95 | $1.61 |
| Profit margin ratio (c) = (a/b) | 19.9% | 2.9% |
Table (10)
The management should continue to produce Almond Dream, and should Drop Frispy Krackle, based on the gross profit margins of Krispy Krackle, and Almond Dream. The most profitable product is likely to be Almond Dream. However, its margin ratio is only 13.9%.
Calculate the margin ratio of Almond Dream:
|
Almond Dream | |
| Material cost | $8.00 |
| Direct labor | 42.00 |
| Allocated overhead | 23.17 |
| Production cost per case | $73.17 |
| Selling price (b) | $85.00 |
| Product cost | (73.17) |
| Profit (loss) (a) | $11.83 |
| Profit margin ratio (c) = (a/b) | 13.9% |
Table (11)
Almond Dream, and Krispy Krackle are found to be equally profitable, if the gross margin for the three products are computed at maximum production:
| Almond Dream | or | Krispy Krackle | or | Creamy Crunch | ||
| Cases | 3,000 | 3,000 | 3,000 | |||
| Costs | ||||||
| Materials | $ 24,000 | $ 6,000 | $ 27,000 | |||
| Labor | 126,000 | 54,000 | 18,000 | |||
| Overhead | + | 69,500 | + | 69,500 | + | 69,500 |
| $219,500 | $129,500 | $114,500 | ||||
| Revenue | $255,000 | $165,000 | $105,000 | |||
| Total costs | – | 219,500 | – | 129,500 | – | 114,500 |
| Gross margin | $ 35,500 | $ 35,500 | $ (9,500) |
Table (12)
Hence, in decision making, too much of allocated cost numbers are not to be made.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Fundamentals Of Cost Accounting (6th Edition)
- General accounting questionarrow_forwardThe balance sheet of BobCreatives at December 31 showed assets of $89,500 and shareholders' equity of $63,000. What were the liabilities at December 31? (FinancialAccounting)arrow_forwardI need help finding the accurate solution to this general accounting problem with valid methods.arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





