
Concept explainers
Complete the following table:
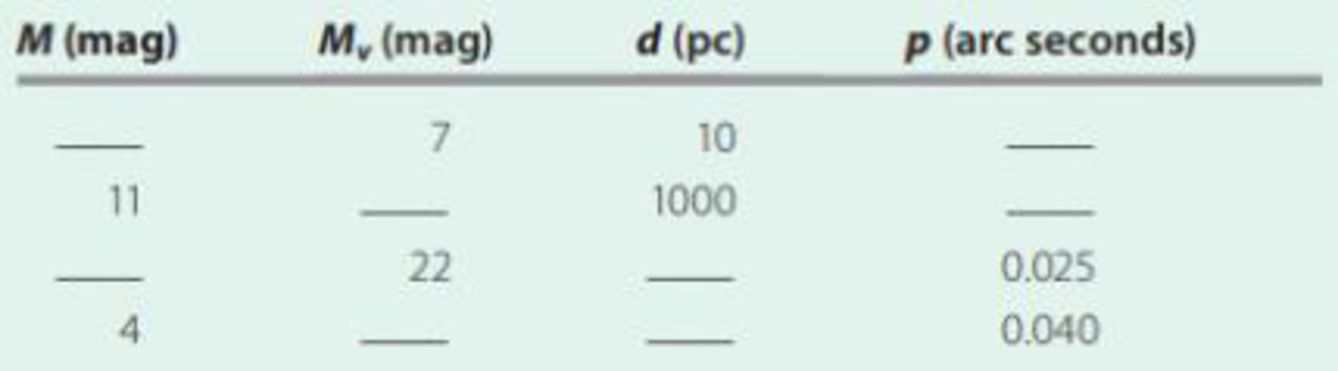
Complete the given table with proper values.
Answer to Problem 5P
The required table is given below:
| | | | |
| 7 | 7 | 10 | 0.1 |
| 11 | 1 | 1000 | 0.001 |
| 25 | 22 | 40 | 0.025 |
| 4 | 2 | 25 | 0.040 |
Explanation of Solution
Write the equation for the relation between absolute and apparent visual magnitude.
Here,
Write the expression between the relation of distance and parallax distance.
Here,
Conclusion:
First table:
Substitute,
Substitute,
Second table:
Substitute,
Substitute,
Third table:
Substitute,
Substitute,
Fourth table:
Substitute,
Substitute,
Thus, the required table is given below:
| | | | |
| 7 | 7 | 10 | 0.1 |
| 11 | 1 | 1000 | 0.001 |
| 25 | 22 | 40 | 0.025 |
| 4 | 2 | 25 | 0.040 |
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Bundle: Foundations of Astronomy, Enhanced, 13th + LMS Integrated MindTap Astronomy, 2 terms (12 months) Printed Access Card
- Three charged particles are located at the corners of an equilateral triangle as shown in the figure below (let q = 1.00 μC, and L = 0.850 m). Calculate the total electric force on the 7.00-μC charge. magnitude direction N ° (counterclockwise from the +x axis) y 7.00 με 9 L 60.0° x -4.00 μC ①arrow_forward(a) Calculate the number of electrons in a small, electrically neutral silver pin that has a mass of 9.0 g. Silver has 47 electrons per atom, and its molar mass is 107.87 g/mol. (b) Imagine adding electrons to the pin until the negative charge has the very large value 1.00 mC. How many electrons are added for every 109 electrons already present?arrow_forward(a) A physics lab instructor is working on a new demonstration. She attaches two identical copper spheres with mass m = 0.180 g to cords of length L as shown in the figure. A Both spheres have the same charge of 6.80 nC, and are in static equilibrium when 0 = 4.95°. What is L (in m)? Assume the cords are massless. 0.180 Draw a free-body diagram, apply Newton's second law for a particle in equilibrium to one of the spheres. Find an equation for the distance between the two spheres in terms of L and 0, and use this expression in your Coulomb force equation. m (b) What If? The charge on both spheres is increased until each cord makes an angle of 0 = 9.90° with the vertical. If both spheres have the same electric charge, what is the charge (in nC) on each sphere in this case? 9.60 Use the same reasoning as in part (a), only now, use the length found in part (a) and the new angle to solve for the charge. ncarrow_forward
- A proton moves at 5.20 x 105 m/s in the horizontal direction. It enters a uniform vertical electric field with a magnitude of 8.40 × 103 N/C. Ignore any gravitational effects. (a) Find the time interval required for the proton to travel 6.00 cm horizontally. 83.33 Your response differs from the correct answer by more than 10%. Double check your calculations. ns (b) Find its vertical displacement during the time interval in which it travels 6.00 cm horizontally. (Indicate direction with the sign of your answer.) 2.77 Your response differs from the correct answer by more than 10%. Double check your calculations. mm (c) Find the horizontal and vertical components of its velocity after it has traveled 6.00 cm horizontally. = 5.4e5 Your response differs significantly from the correct answer. Rework your solution from the beginning and check each step carefully. I + 6.68e4 Your response differs significantly from the correct answer. Rework your solution from the beginning and check each step…arrow_forward(a) A physics lab instructor is working on a new demonstration. She attaches two identical copper spheres with mass m = 0.180 g to cords of length L as shown in the figure. A Both spheres have the same charge of 6.80 nC, and are in static equilibrium when = 4.95°. What is L (in m)? Assume the cords are massless. 0.150 Draw a free-body diagram, apply Newton's second law for a particle in equilibrium to one of the spheres. Find an equation for the distance between the two spheres in terms of L and 0, and use this expression in your Coulomb force equation. m (b) What If? The charge on both spheres is increased until each cord makes an angle of 0 = 9.90° with the vertical. If both spheres have the same electric charge, what is the charge (in nC) on each sphere in this case? 13.6 ☑ Use the same reasoning as in part (a), only now, use the length found in part (a) and the new angle to solve for the charge. nCarrow_forwardA proton moves at 5.20 x 105 m/s in the horizontal direction. It enters a uniform vertical electric field with a magnitude of 8.40 × 10³ N/C. Ignore any gravitational effects. (a) Find the time interval required for the proton to travel 6.00 cm horizontally. 1.15e-7 ☑ Your response differs significantly from the correct answer. Rework your solution from the beginning and check each step carefully. ns (b) Find its vertical displacement during the time interval in which it travels 6.00 cm horizontally. (Indicate direction with the sign of your answer.) 5.33e-3 ☑ Your response is off by a multiple of ten. mm (c) Find the horizontal and vertical components of its velocity after it has traveled 6.00 cm horizontally. | ↑ + jkm/sarrow_forward
- A proton moves at 5.20 105 m/s in the horizontal direction. It enters a uniform vertical electric field with a magnitude of 8.40 103 N/C. Ignore any gravitational effects. (a) Find the time interval required for the proton to travel 6.00 cm horizontally. (b) Find its vertical displacement during the time interval in which it travels 6.00 cm horizontally. (Indicate direction with the sign of your answer.)arrow_forwardThe figure below shows the electric field lines for two charged particles separated by a small distance. 92 91 (a) Determine the ratio 91/92. 1/3 × This is the correct magnitude for the ratio. (b) What are the signs of q₁ and 92? 91 positive 92 negative ×arrow_forwardPlease help me solve this one more detail, thanksarrow_forward
- A dielectric-filled parallel-plate capacitor has plate area A = 20.0 ccm2 , plate separaton d = 10.0 mm and dielectric constant k = 4.00. The capacitor is connected to a battery that creates a constant voltage V = 12.5 V . Throughout the problem, use ϵ0 = 8.85×10−12 C2/N⋅m2 . Find the energy U1 of the dielectric-filled capacitor. The dielectric plate is now slowly pulled out of the capacitor, which remains connected to the battery. Find the energy U2 of the capacitor at the moment when the capacitor is half-filled with the dielectric. The capacitor is now disconnected from the battery, and the dielectric plate is slowly removed the rest of the way out of the capacitor. Find the new energy of the capacitor, U3. In the process of removing the remaining portion of the dielectric from the disconnected capacitor, how much work W is done by the external agent acting on the dielectric?arrow_forwardIn (Figure 1) C1 = 6.00 μF, C2 = 6.00 μF, C3 = 12.0 μF, and C4 = 3.00 μF. The capacitor network is connected to an applied potential difference Vab. After the charges on the capacitors have reached their final values, the voltage across C3 is 40.0 V. What is the voltage across C4? What is the voltage Vab applied to the network? Please explain everything in steps.arrow_forwardI need help with these questions again. A step by step working out with diagrams that explains more clearlyarrow_forward
 Foundations of Astronomy (MindTap Course List)PhysicsISBN:9781337399920Author:Michael A. Seeds, Dana BackmanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Foundations of Astronomy (MindTap Course List)PhysicsISBN:9781337399920Author:Michael A. Seeds, Dana BackmanPublisher:Cengage Learning Stars and Galaxies (MindTap Course List)PhysicsISBN:9781337399944Author:Michael A. SeedsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Stars and Galaxies (MindTap Course List)PhysicsISBN:9781337399944Author:Michael A. SeedsPublisher:Cengage Learning An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
 AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9781938168284Author:Andrew Fraknoi; David Morrison; Sidney C. WolffPublisher:OpenStax
AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9781938168284Author:Andrew Fraknoi; David Morrison; Sidney C. WolffPublisher:OpenStax Horizons: Exploring the Universe (MindTap Course ...PhysicsISBN:9781305960961Author:Michael A. Seeds, Dana BackmanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Horizons: Exploring the Universe (MindTap Course ...PhysicsISBN:9781305960961Author:Michael A. Seeds, Dana BackmanPublisher:Cengage Learning





