
Concept explainers
The sulfamate ion, H2NSO3–, can be thought of as having been formed from the amide ion, NH2–, and sulphur trioxide, SO3.
(a) What are the electron-pair and molecular geometries or the amide ion and or SO3? What are the hybridizations of the N and S atoms, respectively?
(b) Sketch a structure for the sulfamate ion, and estimate the bond angles.
(c) What changes in hybridization do you expect for N and S in the course of the reaction
NH2– + SO3 → H2N—SO3–?
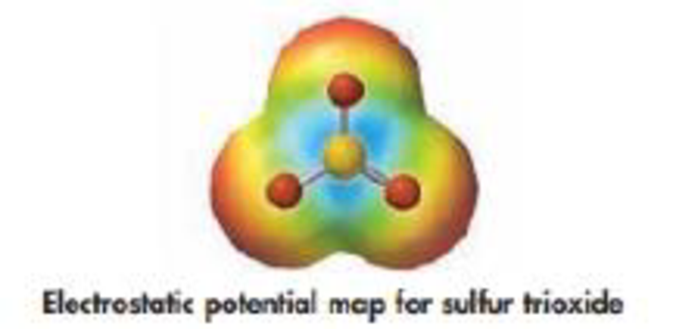
(d) Is SO3 the donor of an electron pair or the acceptor of an electron pair in the reaction with amide ion? Does the electrostatic potential map shown below confirm your prediction?
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 9 Solutions
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity, Hybrid Edition (with OWLv2 24-Months Printed Access Card)
- The temperature on a sample of pure X held at 1.25 atm and -54. °C is increased until the sample boils. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.42 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 2 0 0 200 400 temperature (K) Xarrow_forwardQUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' STEP 1 by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the photo attached*arrow_forwardpressure (atm) 3 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 0 0 200 temperature (K) 400 аarrow_forward
- er your payment details | bar xb Home | bartleby x + aleksogi/x/isl.exe/1o u-lgNskr7j8P3jH-1Qs_pBanHhviTCeeBZbufuBYT0Hz7m7D3ZcW81NC1d8Kzb4srFik1OUFhKMUXzhGpw7k1 O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 1 3- 0- 0 200 Explanation Check temperature (K) 400 X Q Search L G 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved Terms of Use Privacy Cearrow_forward5.arrow_forward6.arrow_forward
- 0/5 alekscgi/x/sl.exe/1o_u-IgNglkr7j8P3jH-IQs_pBaHhvlTCeeBZbufuBYTi0Hz7m7D3ZcSLEFovsXaorzoFtUs | AbtAURtkqzol 1HRAS286, O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 3 pressure (atm) + 0- 0 5+ 200 temperature (K) 400 Explanation Check X 0+ F3 F4 F5 F6 F7 S 2025 McGraw Hill LLC All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Privacy Center Accessibility Q Search LUCR + F8 F9 F10 F11 F12 * % & ( 5 6 7 8 9 Y'S Dele Insert PrtSc + Backsarrow_forward5.arrow_forward9arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning




