
Concept explainers
Algers Company produces dry fertilizer. At the beginning of the year, Algers had the following
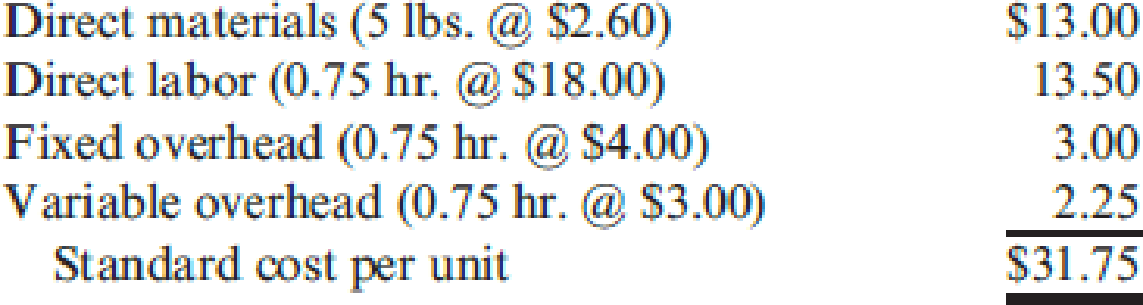
Algers computes its
- a. Units produced: 53,000
- b. Direct materials purchased: 274,000 pounds at $2.50 per pound
- c. Direct materials used: 270,300 pounds
- d. Direct labor: 40,100 hours at $17.95 per hour
- e. Fixed overhead: $161,700
- f. Variable overhead: $122,000
Required:
- 1. Compute price and usage variances for direct materials.
- 2. Compute the direct labor rate and labor efficiency variances.
- 3. Compute the fixed overhead spending and volume variances. Interpret the volume variance.
- 4. Compute the variable overhead spending and efficiency variances.
- 5. Prepare
journal entries for the following:- a. The purchase of direct materials
- b. The issuance of direct materials to production (Work in Process)
- c. The addition of direct labor to Work in Process
- d. The addition of overhead to Work in Process
- e. The incurrence of actual overhead costs
- f. Closing out of variances to Cost of Goods Sold
1.
Compute the direct materials price variance and the direct materials usage variance.
Explanation of Solution
Direct material price variance: The variation in between actual price and estimated price paid for materials multiplied by the actual quantity is called material price variance. It is used to determine difference in price paid for material the price that was supposed to be paid for material.
The following formula is used to calculate direct material price variance:
Direct material usage (efficiency) variance: It is a measure that determines the variation in between actual and standard quantity of input multiplied by the standard unit price is called material usage variance.
The following formula is used to calculate direct material usage variance:
Compute the direct materials price variance:
Compute the direct materials usage variance:
Working note 1: Calculate the standard quantity:
Therefore, the direct materials price variance and the usage variance is $27,400 F and $613,780 U respectively.
2.
Calculate the direct labor rate variance and labor efficiency variance.
Explanation of Solution
Direct Labor Rate Variance: The direct labor rate variance is a measure to determine the variation in the estimated cost of the direct labor and the actual cost of the direct labor and is multiplied by the actual hours is called direct labor rate variance.
The following formula is used to calculate the direct labor rate variance:
Direct labor efficiency variance is a measure that determines the difference between the estimated labor hours and the actual labor hours used and is multiplied by the standard rate per hour is called material usage variance.
The following formula is used to calculate direct labor efficiency variance:
Calculate the direct labor rate variance:
Calculate the labor efficiency variance:
Working note 2: Calculate the standard hours:
Therefore, the direct labor rat variance and the efficiency variance are $2,005 F and $6,300 U respectively.
3.
Calculate the fixed overhead spending and volume variance.
Explanation of Solution
Fixed overhead spending variance: It is the difference between actual fixed overhead and the budgeted fixed overhead.
Favorable variance occurs only when the fixed overhead is less than the budgeted overhead. Unfavorable variance occurs only when the fixed overhead is more than the budgeted overhead.
The following formula is used to calculate fixed overhead spending variance:
Fixed overhead volume variance: It is the difference between budgeted fixed overhead and the applied fixed overhead.
The following formula is used to calculate fixed overhead volume variance:
Calculate the fixed overhead spending volume variance:
Fixed overhead spending:
Step 1: Compute the budgeted fixed overhead.
Step 2: Calculate the fixed overhead spending variance.
Working note 3: Calculate the standard fixed overhead rate:
Working note 4: Calculate the direct labor hour per unit:
Working note 5: Calculate the actual hours:
Volume variance:
Step 1: Compute the applied fixed overhead.
Step 2: Compute the volume variance.
Working note 6: Calculate the standard fixed overhead rate:
Working note 7: Calculate the direct labor hour per unit:
Working note 8: Calculate the standard hours:
Therefore, the fixed overhead spending and volume variance are $300 F and $3,000 U respectively.
4.
Calculate the variable overhead spending and efficiency variances.
Explanation of Solution
Overhead Variance: The overhead variance is the difference arising between the real overhead consumed in the production of a product, and the estimated overhead determined in the production of that product.
Spending variances: It arises when management pays an amount which is different from the standard price for purchasing an item. The variable overhead spending variance measures the total effect of differences in the actual variable overhead rate (AVOR) and the standard variable overhead rate (SVOR).
Efficiency variances: It arises when standard direct labor hours expected for actual production different from labor the actual direct labor hours used.
Variable overhead efficiency variance tells managers how much of the total variable manufacturing overhead variance is due to using more or fewer machine hours than anticipated for the actual volume of output.
Compute the variable overhead spending variance:
Step 1: Compute the budgeted variable overhead cost.
Step 2: Compute the variable overhead spending variance.
Compute the variable overhead efficiency variance:
Step 1: Compute the applied variable overhead.
Step 2: Compute the variable overhead efficiency variance.
Working note 9: Calculate the direct labor hour per unit:
Working note 10: Calculate the standard hours:
Therefore, the variable overhead spending and efficiency variance are $1,700 U and $1,050 U respectively.
5.
Prepare journal entries for the given.
Explanation of Solution
Journalizing: It is the process of recording the transactions of an organization in a chronological order. Based on these journal entries recorded, the amounts are posted to the relevant ledger accounts.
Accounting rules for journal entries:
- To increase balance of the account: Debit assets, expenses, losses and credit all liabilities, capital, revenue and gains.
- To decrease balance of the account: Credit assets, expenses, losses and debit all liabilities, capital, revenue and gains.
Prepare journal entries for direct materials and direct labor:
| Date | Accounts title and explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| a. | Direct Materials | 712,400 | |
| Direct Materials Price variance | 27,400 | ||
| Accounts Payable | 685,000 | ||
| (To record the purchase of direct materials) | |||
| b. | Work in Process | 689,000 | |
| Direct Materials Usage Variance | 13,780 | ||
| Direct Materials | 702,780 | ||
| (To record the usage of direct materials) | |||
| c. | Work in Process | 715,500 | |
| Direct Labor Efficiency Variance | 6,300 | ||
| Direct Labor Rate Variance | 2,005 | ||
| Wages Payable | 719,795 | ||
| (To record the use of direct labor) | |||
| d. | Work in Process | 278,250 | |
| Variable Overhead Control | 119,250 | ||
| Fixed Overhead Control | 159,000 | ||
| (To record assign overhead to the production) | |||
| e. | Variable Overhead Control | 122,000 | |
| Fixed Overhead Control | 161,700 | ||
| Miscellaneous Accounts | 283,700 | ||
| (To record incurrence of actual overhead) | |||
| Closing direct materials and direct labor variances: | |||
| f. | Direct Materials Price variance | 27,400 | |
| Direct Labor Rate Variance | 2,005 | ||
| Direct Materials Usage Variance | 13,780 | ||
| Direct Labor Efficiency Variance | 6,300 | ||
| Cost of Goods Sold | 9,325 | ||
| (To close the direct materials and direct labor variances) | |||
| Closing overhead variances: | |||
| Fixed Overhead Volume Variance | 3,000 | ||
| Variable Overhead Spending Variance | 1,700 | ||
| Variable Overhead Efficiency Variance | 1,050 | ||
| Fixed Overhead Spending Variance | 300 | ||
| Fixed Overhead Control | 2,700 | ||
| Variable Overhead Control | 2,750 | ||
| (To close the overhead variances) | |||
| Cost of Goods Sold | 5,750 | ||
| Fixed Overhead Volume Variance | 3,000 | ||
| Variable Overhead Spending Variance | 1,700 | ||
| Variable Overhead Efficiency Variance | 1,050 | ||
| (To close the overhead variances) | |||
| Fixed Overhead Spending Variance | 300 | ||
| Cost of Goods Sold | 300 | ||
| (To close the cost of goods sold) | |||
Table (1)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
EBK CORNERSTONES OF COST MANAGEMENT
- Elara Manufacturing Inc. has provided the following financial data for the year: please answer the financial accounting questionarrow_forwardSunk costs $ A business purchased a delivery truck 5 years ago at a cost of $45,000. It is now planning to replace that truck with a newer one, which would cost $55,000. The old truck has a trade-in value of approximately $13,500. (a1) How much of these truck costs represent sunk costs? 2arrow_forwardProvide answerarrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,





