
Find the reactions and all bar forces for the truss.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The Young’s modulus E of the beam is
The area (A) of all the bars is
Identify Zero Force Members:
In a two member forces, if both the members are not parallel and the no external loads or reactions acts at that joint. Then, the force in both the members is zero.
Calculation:
Show the free body diagram of the truss as shown in Figure 1.
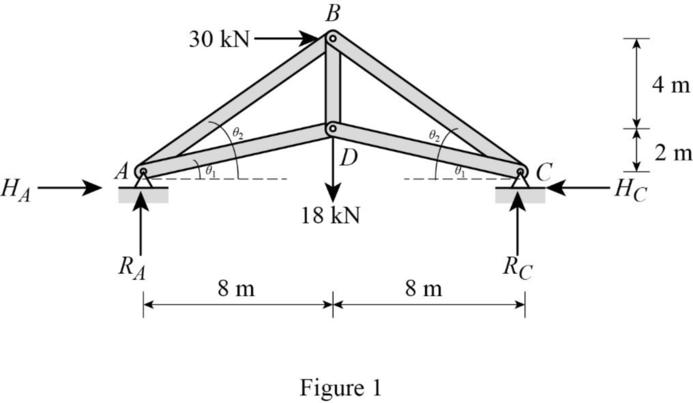
Refer Figure 1.
Find the length of the member AB and BC as follows:
Consider triangle ABD.
By symmetry of truss,
Find the length of the member AD and DC as follows:
Consider triangle ADC.
By symmetry of truss,
Find the angle
Find the angle
Consider the horizontal reaction at C as the redundant.
Remove the redundant at C to get the released structure.
Show the released structure with applied load as shown in Figure 2.
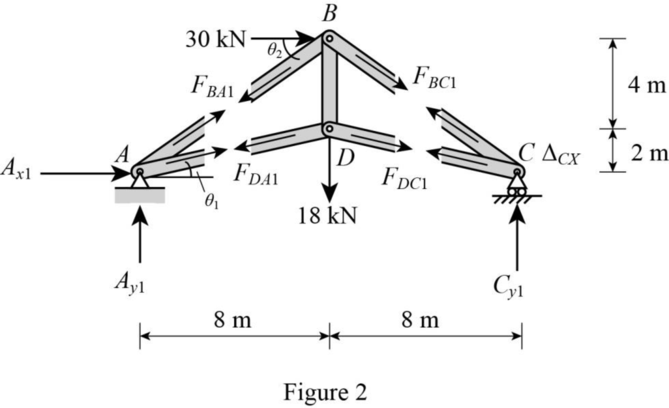
Refer Figure 2.
Find the reactions at A, D, and C as follows:
Apply Equation of Equilibrium,
Find the forces
Refer Figure 2.
Consider Joint C.
Apply Equation of Equilibrium,
Consider joint B.
Apply Equation of Equilibrium,
Consider joint D.
Apply Equation of Equilibrium,
Show the P forces in the members of the truss due to the applied load at C as shown in Table 1.
| Members | |
| AB | |
| BC | |
| AD | |
| DC | |
| DB |
Table 1
Show the released structure loaded with unit horizontal load at C as shown in Figure 2.
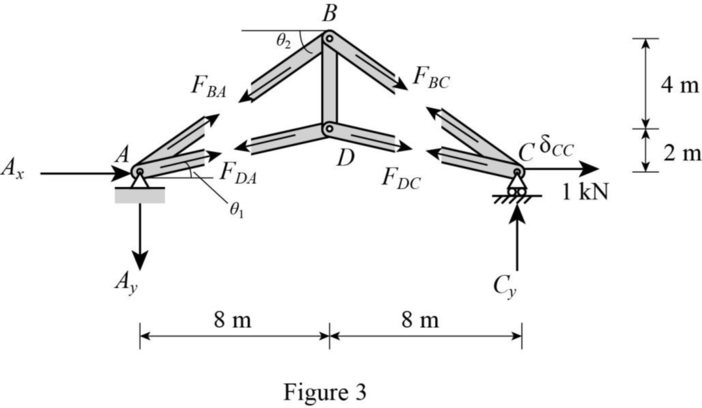
Refer Figure 3.
By symmetry of the truss,
Consider Joint D.
Apply Equation of Equilibrium,
Solve Equation (1) and (2).
By symmetry of the truss,
Consider Joint B.
Apply Equation of Equilibrium,
Show the Q forces in the members of the truss due to the unit load at C as shown in Table 2.
| Members | |
| AB | |
| BC | |
| CD | |
| AC | |
| DB |
Table 2
Find the deflection
| Members | |||||
| AB | 10 | ||||
| BC | 10 | ||||
| AD | 8.246 | ||||
| DC | 8.246 | ||||
| DB | 4 |
Table 3
Refer Table 3.
Find the horizontal reaction at C as follows:
Thus, the horizontal reaction at C is
Find final forces in the truss as shown in Table 4.
| Members | ||||
| AB | -31.89 | 6.80 | ||
| BC | -31.89 | -30.7 | ||
| AD | -31.89 | -7.5 | ||
| DC | -31.89 | -7.5 | ||
| DB | -31.89 | 14.34 |
Table 4
Show the final support reaction as shown in Table 5.
| Support Reactions | ||||
| Members | ||||
| -30 | -1 | -31.89 | 1.89 | |
| -2.25 | 0 | -31.89 | -2.25 | |
| 20.25 | 1 | -31.89 | 20.25 | |
Table 5
Thus, the reactions and all bar forces for the truss is tabulate in table 4 and table 5.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
UCD FUND OF STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS 5E
- A project requires 125 cubic yards of concrete sidewalk to be placed, for which 165 workhours have been budgeted. The latest weekly progress report shows that 78 cubic yards have been placed and 103 workhours have been expended to date. What is the status of the concrete placement? Significantly under budget. On budget. Significantly over budget. Status cannot be determined with information supplied.arrow_forwardRefer to exhibit #098. At what depth was water encountered?arrow_forwardWhat is the reaction moment at A for the frame shown? a. 222.1 k-ft b. 107.8 k-ft c. 20.8 k-ft d. 23.25 k-ftarrow_forward
- “When a conflict exists between the project floor plans and detailed material schedule relative to size or number, which of the following usually governs in typical order of precedence?arrow_forwardWhat are the critical activitiesarrow_forwardApproximately how many pounds of water are necessary to hydrate 100 pounds of type I Portland cement? 30 50 75 94arrow_forward
- 7:05 3.1 Trabajo en clase.pptx .III LTE 8 Trabajo en clases 3.1 C9 X 20 W8 X 21 5-15. PL¹× 12 Fy = 50 klb/plg² KL = 16 pies KL 21 pies 2 plg MC 13 × 50 PL × 12 Fy = 42 klb/plg2 Fy = 36 klb/plg² 8 plg K k MC8 × 21.4 KL = 20 piesarrow_forwardThe steel frameword below is used to support the reinforced concrete slab used for an office area above the first storey. The slab is 210 mm thick. Sketch the loading that acts along members BE and FED. Use a = 2.15 m and b = 5.25 m. Refer to the 2024 OBC live load table. The unit weight for the concrete is 24.15 kN/m3.find:Loading for member BE Loading for member FED Live and Dead Loadsarrow_forwardFor the simply supported beam below, draw both the shear force (VFD) and ending moment (BDM) diagrams. Please show all equations and free body diagrams (FBD). Note: I want a cut through each of the three sections of the beam, with all related forces calculated and shown on the VFD and BMD.Reaction Forces Shear Force DiagramMaximum Shear ForceEquation for cut 1, 2, 3 respectively.Confirmation of Reaction ForcesBending Moment DiagramMaximum Bending Momentarrow_forward
- For the structural frame below, draw the shear force (VFD) and bending moment (BMD) diagrams for each of the three members of the frame. The frame is pin connected at A, C and D and fixed at joint B.Find:VFD & BMD for segment AB VFD & BMD for segment BCVFD & BMD for segment CD Reaction Forces VFD Equations BMD EquationsFree Body Diagramsarrow_forwardDetermine the horizontal and vertical reactions at A and C for the two member frame below. Use P1 = 3.2 kN, P2 = 14.5 kN/m, L1 = 3.3 m, and L2 = 2.3 m. Free Body DiagramsTriangular Load Use of Pin Reaction Forcesarrow_forwardDetermine the reaction forces at supports A and C for the compound beam. Assume C is fixed, B is a pin, and A is a roller. Use P1 = 16 kN/m, P2 = 21 kN, L1 = 3.5 m, L2 = 1.5 m, and L3 – 1.5 m. needs:Triangular Load Use of Pin Reaction Forcesfree body diagramsarrow_forward

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning





