
Problem 9-23 Ratio analysis
The following financial statements apply to Karl Company:
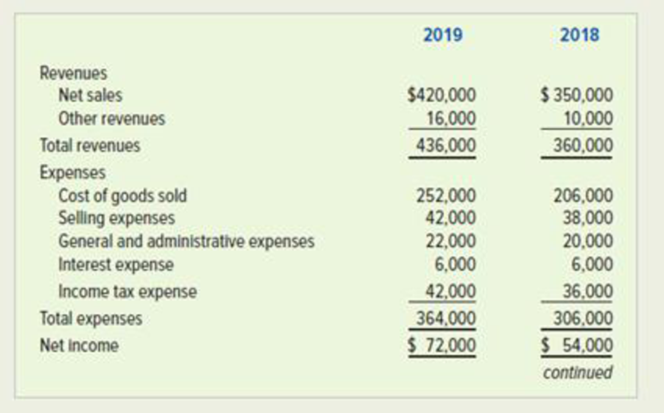
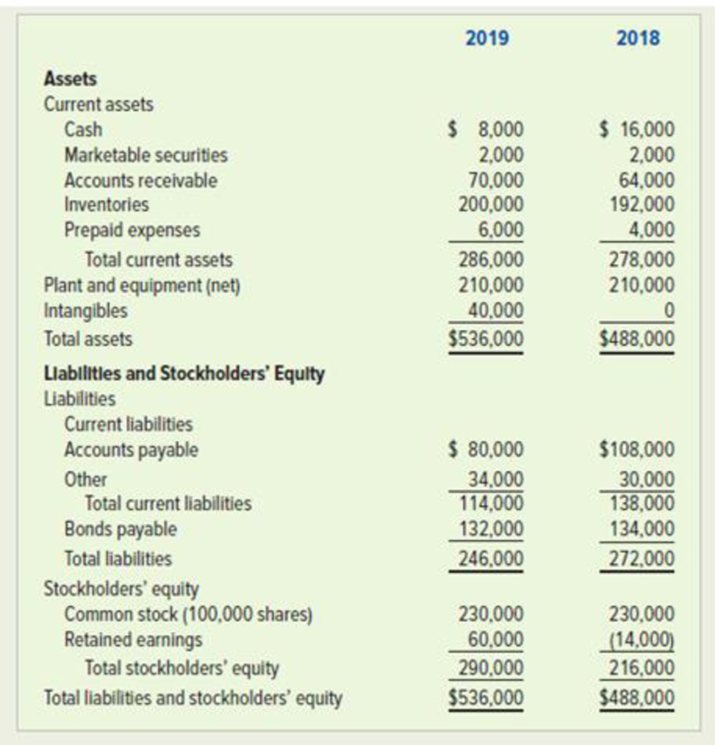
Required
Calculate the following ratios for 2018 and 2019. When data limitations prohibit computing averages, use year-end balances in your calculations. Round computations to two decimal points.
- a. Net margin.
- b.
Return on investment . - c. Return on equity.
- d. Earnings per share.
- e. Price-earnings ratio (market prices at the end of 2018 and 2019 were $11.88 and $9.54, respectively).
- f. Book value per share of common stock.
- g. Times interest earned.
- h.
Working capital . - i.
Current ratio . - j. Quick (acid-test) ratio.
- k.
Accounts receivable turnover. - l. Inventory turnover.
- m. Debt to equity ratio.
- n. Debt to assets ratio.
a.
Compute net margin of Company K for 2019 and 2018.
Explanation of Solution
Net margin: It is one of the profitability ratios. Profit margin ratio is used to measure the percentage of net income that is being generated per dollar of revenue or sales.
Compute net margin of Company K for 2019 and 2018:
| Ratios and Formula | 2019 | 2018 |
|
Net margin: |
Table (1)
Thus, the net margin of Company K for 2019 and 2018 are 17.14% and 15.42% respectively.
b.
Compute return on investment of Company K for 2019 and 2018.
Explanation of Solution
Return on investments (assets): Return on investments (assets) is the financial ratio which determines the amount of net income earned by the business with the use of total assets owned by it. It indicates the magnitude of the company’s earnings with relative to its total assets. Return on investment is calculated as follows:
Compute return on investment of Company K for 2019 and 2018:
| Ratios and Formula | 2019 | 2018 |
|
Return on investment: |
Table (2)
Note: Since, the beginning total assets for 2018 are not given. So, the total amount of total assets for 2018 is assumed as average total assets.
Working note:
(1) Determine the amount of average total assets for 2019.
Thus, the return on investment of Company K for 2019 and 2018 are 14.06% and 11.07% respectively.
c.
Compute return on equity of Company K for 2019 and 2018.
Explanation of Solution
Return on equity: It is a profitability ratio that measures the profit generating ability of the company from the invested money of the shareholders. The formula to calculate the return on equity is as follows:
Compute return on equity of Company K for 2019 and 2018:
| Ratios and Formula | 2019 | 2018 |
|
Return on equity: |
Table (3)
Note: Since, the beginning stockholders’ equity for 2018 is not given. So, the total amount of stockholders’ equity for 2018 is assumed as average total stockholders’ equity.
Working Note:
(2) Determine the amount of average total stockholders’ equity for 2019.
Thus, the return on equity of Company K for 2019 and 2018 are 28.46% and 25% respectively.
d.
Compute earnings per share of Company K for 2019 and 2018.
Explanation of Solution
Earnings per Share: Earnings per share help to measure the profitability of a company. Earnings per share are the amount of profit that is allocated to each share of outstanding stock.
Compute earnings per share of Company K for 2019 and 2018:
| Ratios and Formula | 2019 | 2018 |
|
Earnings per share: |
Table (4)
Thus, the earnings per share of Company K for 2019 and 2018 are $0.72 per share and $0.54 per share respectively.
e.
Compute price-earnings ratio of Company K for 2019 and 2018.
Explanation of Solution
Price/Earnings Ratio: The price/earnings ratio shows the market value of the amount invested to earn $1 by a company. It is major tool used by investors for making decisions related to the investment in a company.
Compute price-earnings ratio of Company K for 2019 and 2018:
| Ratios and Formula | 2019 | 2018 |
|
Price-earnings ratio: |
Table (5)
Note: The earnings per share for both years are computed in requirement d.
Thus, the price-earnings ratio of Company K for 2019 and 2018 are 13.25 times and 22 times respectively.
f.
Compute book value per share of common stock of Company K for 2019 and 2018.
Explanation of Solution
Book value per share of common stock: This ratio is a measure of a share of common stock that is used to determine the value of per share based on the equity available to the common stockholders. This ratio is calculated by using the formula:
Compute book value per share of common stock of Company K for 2019 and 2018:
| Ratios and Formula | 2019 | 2018 |
|
Book value per share of common stock: |
Table (6)
Thus, the book value per share of common stock of Company K for 2019 and 2018 are $2.90 per share and $2.16 per share respectively.
g.
Compute times interest earned of Company K for 2019 and 2018.
Explanation of Solution
Time’s interest earned: Number of times interest is earned quantifies the number of times the earnings before interest and taxes can pay the interest expense. First, determine the sum of income before income tax and interest expense. Then, divide the sum by interest expense.
Compute times interest earned of Company K for 2019 and 2018:
| Ratios and Formula | 2019 | 2018 |
|
Times interest earned: |
Table (7)
Working Note:
(3) Determine the amount of earnings before interest and expenses for 2019.
(4) Determine the amount of earnings before interest and expenses for 2018.
Thus, the times interest earned ratio of Company K for 2019 and 2018 is 20.00 times and 16.00 times respectively.
h.
Compute working capital of Company K for 2019 and 2018.
Explanation of Solution
Working capital: Working capital refers to the excess amount of current assets over its current liabilities of a business. It measures the excess funds that are required for the companies to carry out their day to day operations, excluding any new funds that have been invested during the year. Working capital is calculated by using the formula:
Compute working capital of Company K for 2019 and 2018:
| Ratios and Formula | 2019 | 2018 |
|
Working Capital: |
Table (8)
Thus, the working capital of Company K for 2019 and 2018 is $172,000 and $140,000 respectively.
i.
Compute current ratio of Company K for 2019 and 2018.
Explanation of Solution
Current ratio: Current ratio is one of the liquidity ratios, which measures the capacity of the company to meet its short-term obligations using its current assets. Current ratio is calculated by using the formula:
Compute current ratio of Company K for 2019 and 2018:
| Ratios and Formula | 2019 | 2018 |
|
Current ratio: |
Table (9)
Thus, the current ratio of Company K for 2019 and 2018 is 2.50:1 and 2.01:1 respectively.
j.
Compute quick ratio of Company K for 2019 and 2018.
Explanation of Solution
Quick ratio: It is a ratio used to determine a company’s ability to pay back its current liabilities by liquid assets that are current assets except inventory and prepaid expenses.
Compute quick ratio of Company K for 2019 and 2018:
| Ratios and Formula | 2019 | 2018 |
|
Quick ratio: |
Table (10)
Note: Quick assets include cash, marketable securities and accounts receivable.
Thus, the quick ratio of Company K for 2019 and 2018 is 0.70:1 and 0.59:1 respectively.
k.
Compute receivables turnover of Company K for 2019 and 2018.
Explanation of Solution
Account Receivables turnover ratio: Account Receivables turnover ratio is mainly used to evaluate the collection process efficiency. It helps the company to know the number of times the accounts receivable is collected in a particular time period. This ratio is determined by dividing credit sales and average account receivables.
Compute receivables turnover of Company K for 2019 and 2018:
| Ratios and Formula | 2019 | 2018 |
|
Receivables turnover: |
Table (11)
Note: Since, the beginning value of receivable for 2018 is not given. So, the total amount of receivable for 2018 is assumed as average receivables.
Working Note:
(5) Determine the amount of average accounts receivable for 2019.
Thus, the accounts receivable turnover of Company K for 2019 and 2018 is 6.27 times and 5.47 times respectively.
l.
Compute inventory turnover of Company K for 2019 and 2018.
Explanation of Solution
Inventory Turnover Ratio: This ratio is a financial metric used by a company to quantify the number of times inventory is used or sold during the accounting period. It is calculated by using the formula:
Compute inventory turnover of Company K for 2019 and 2018:
| Ratios and Formula | 2019 | 2018 |
|
Inventory turnover: |
Table (12)
Note: Since, the beginning value of inventory for 2018 is not given. So, the total amount of inventory for 2018 is assumed as average inventory.
Working Note:
(6) Determine the amount of average inventory for 2019.
Thus, the inventory turnover of Company K for 2019 and 2018 is 1.28 times and 1.07 times respectively.
m.
Compute debt to equity ratio of Company K for 2019 and 2018.
Explanation of Solution
Debt–to-equity ratio: The debt-to-equity ratio indicates that the company’s debt as a proportion of its stockholders’ equity. The debt-to-equity ratio is calculated using the formula:
Compute debt to equity ratio of Company K for 2019 and 2018:
| Ratios and Formula | 2019 | 2018 |
|
Debt to equity ratio: |
Table (13)
Thus, the debt to equity ratio of Company K for 2019 and 2018 is 0.85:1 and 1.26:1 respectively.
n.
Compute debt to assets ratio of Company K for 2019 and 2018.
Explanation of Solution
Debt to assets ratio: The debt to asset ratio shows the relationship between total asset and the total liability of the company. Debt ratio reflects the financial strategy of the company. It is used to measure the percentage of company’s assets that are financed by long term debts. Debt to assets ratio is calculated by using the formula:
Compute debt to assets ratio of Company K for 2019 and 2018:
| Ratios and Formula | 2019 | 2018 |
|
Debt to assets ratio: |
Table (14)
Thus, the debt to assets ratio of Company K for 2019 and 2018 is 45.89% and 55.73% respectively.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Survey Of Accounting
- I am looking for help with this general accounting question using proper accounting standards.arrow_forwardI need assistance with this general accounting question using appropriate principles.arrow_forwardPlease show me the correct approach to solving this financial accounting question with proper techniques.arrow_forward
- Please provide the solution to this general accounting question using proper accounting principles.arrow_forwardI need help finding the correct solution to this financial accounting problem with valid methods.arrow_forwardPlease explain the solution to this financial accounting problem using the correct financial principles.arrow_forward
- Can you solve this general accounting problem with appropriate steps and explanations?arrow_forwardPlease provide the correct answer to this financial accounting problem using valid calculations.arrow_forwardPlease provide the solution to this general accounting question using proper accounting principles.arrow_forward
- Can you solve this financial accounting problem using appropriate financial principles?arrow_forwardI am looking for the correct answer to this financial accounting problem using valid accounting standards.arrow_forwardI need assistance with this general accounting question using appropriate principles.arrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)AccountingISBN:9781305961883Author:Carl WarrenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)AccountingISBN:9781305961883Author:Carl WarrenPublisher:Cengage Learning College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Financial Reporting, Financial Statement Analysis...FinanceISBN:9781285190907Author:James M. Wahlen, Stephen P. Baginski, Mark BradshawPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Reporting, Financial Statement Analysis...FinanceISBN:9781285190907Author:James M. Wahlen, Stephen P. Baginski, Mark BradshawPublisher:Cengage Learning





