
Why do we hybtidize atomic orbitals to explain the bonding in covalent compounds? What type of bonds form from hybrid orbitals: sigma or pi? Explain.
Interpretation: A reason corresponding to the hybridizing of atomic orbitals to explain the bonding in covalent compounds is to be stated. The type of bonds that are formed from hybrid orbitals is to be stated.
Concept introduction: Hybrid orbitals are formed by mixing of atomic orbitals when superimposed on each other in various proportions Hybrid orbitals having same energies are suitable for pairing of electrons which leads to the formation of chemical bond. Both sigma and pi bonds are formed from hybrid atomic orbital.
To determine: A reason corresponding to the hybridizing of atomic orbitals to explain the bonding in covalent compounds and the type of bonds that are formed from hybrid orbitals.
Answer to Problem 1RQ
Due to difference between the predicted structure and the experimental structure, it is rationalized that a new set of atomic orbitals is required which result from hybridization. If there is a “head to head” overlap of orbitals then sigma bond is formed and if there is a “side to side” overlap then pi bonds are formed.
Explanation of Solution
Hybrid orbitals are formed by mixing of atomic orbitals when superimposed on each other in various proportions. Hybridized orbitals are used in the formation of covalent compounds.
Due to discrepancy between the predicted structure and the experimental structure, a new set of atomic orbitals are used, commonly known as hybrid orbitals, which are required to explain the bonding structure.
During the formation of hybrid orbitals both type of bonds, sigma and pi, are formed.
Sigma bonds and pi bonds are formed by overlap of atomic orbitals.
Sigma bond is formed when there is a “head to head” overlap of orbitals and pi bond is formed when there is a “side to side” overlap.
Formation of sigma bond is shown in Figure 1.
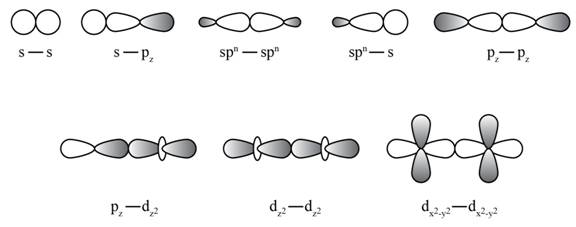
Figure 1
Formation of pi bond is shown in Figure 2.
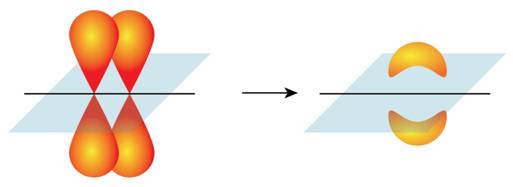
Figure 2
Hybrid orbitals are formed by mixing of atomic orbitals when superimposed on each other in various proportions.
During the formation of hybrid orbitals both type of bonds, sigma and pi, are formed
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Chemistry (AP Edition)
- Calculating the pH at equivalence of a titration 3/5 Izabella A chemist titrates 120.0 mL of a 0.7191M dimethylamine ((CH3)2NH) solution with 0.5501 M HBr solution at 25 °C. Calculate the pH at equivalence. The pk of dimethylamine is 3.27. Round your answer to 2 decimal places. Note for advanced students: you may assume the total volume of the solution equals the initial volume plus the volume of HBr solution added. pH = ☐ ✓ 18 Ar Boarrow_forwardAlcohols can be synthesized using an acid-catalyzed hydration of an alkene. An alkene is combined with aqueous acid (e.. sulfuric acid in water). The reaction mechanism typically involves a carbocation intermediate. > 3rd attempt 3343 10 8 Draw arrows to show the reaction between the alkene and hydronium ion. that 2nd attempt Feedback 1st attempt تعمال Ju See Periodic Table See Hint F D Ju See Periodic Table See Hintarrow_forwardDraw the simplified curved arrow mechanism for the reaction of acetone and CHgLi to give the major product. 4th attempt Π Draw the simplified curved arrow mechanism T 3rd attempt Feedback Ju See Periodic Table See Hint H -H H -I H F See Periodic Table See Hintarrow_forward
- Select the correct reagent to accomplish the first step of this reaction. Then draw a mechanism on the Grignard reagent using curved arrow notation to show how it is converted to the final product. 4th attempt Part 1 (0.5 point) Select the correct reagent to accomplish the first step of this reaction. Choose one: OA Mg in ethanol (EtOH) OB. 2 Li in THF O C. Li in THF D. Mg in THF O E Mg in H2O Part 2 (0.5 point) Br Part 1 Bri Mg CH B CH, 1 Draw intermediate here, but no arrows. © TE See Periodic Table See Hint See Hint ין Harrow_forwardSelect the product for the following reaction. HO HO PCC OH ○ OH O HO ○ HO HO HOarrow_forward5:45 Х Select the final product for the following reaction sequence. O O 1. Mg. ether 2.D.Oarrow_forward
- Based on the chart Two similarities between the molecule with alpha glycosidic linkages. Two similarities between the molecules with beta glycosidtic linkages. Two differences between the alpha and beta glycosidic linkages.arrow_forwardplease help fill in the tablearrow_forwardAnswer F pleasearrow_forward
- 4. Refer to the data below to answer the following questions: The octapeptide saralasin is a specific antagonist of angiotensin II. A derivative of saralasin is used therapeutically as an antihypertensive. Amino acid analysis of saralasin show the presence of the following amino acids: Ala, Arg, His, Pro, Sar, Tyr, Val, Val A.Sar is the abbreviation for sarcosine, N-methyl aminoethanoic acid. Draw the structure of sarcosine. B. N-Terminal analysis by the Edman method shows saralasin contains sarcosine at the N-terminus. Partial hydrolysis of saralasin with dilute hydrochloric acid yields the following fragments: Tyr-Val-His Sar-Arg-Val His-Pro-Ala Val-Tyr-Val Arg-Val-Tyr What is the structure of saralasin?arrow_forwardWhat is the structure of the DNA backbone?arrow_forwardPLEASE PLEASE PLEASE use hand drawn structures when possarrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning





