
Concept explainers
(1)
To draw: A cross-section diagram that shows in the H zone.
Introduction: Myofilaments within the myofibrils are organized in a continuous manner with cylindrical units called sarcomeres. Inside the skeletal muscle fibers, there are several repeating sarcomeres arranged within a section of a myofibril. Overlapping of thick and thin filaments constitutes each sarcomere.
(1)
Explanation of Solution
Pictorial representation: Fig.1 represents the H zone though cross-section of muscle fiber.
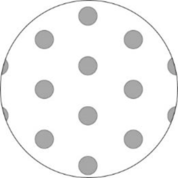
Fig.1: H zone
H zone is the central portion of the A band that is present only in the resting sarcomere. The H zone region does not have overlapping thin filament. It only has thick filament.
(2)
To draw: A cross-section diagram that shows in the I band.
(2)
Explanation of Solution
Pictorial representation: Fig.1 represents the I band though cross-section of muscle fiber.
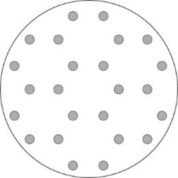
Fig.1: I zone
I band is the only region that contains thin filament and extends from both directions of Z disk. At the region of maximal shortening, the thin filaments of the muscle fiber are pulled parallel along the thick filaments. This leads to decrease of I bands.
(3)
To draw: A cross-section diagram that shows at the M line.
(3)
Explanation of Solution
Pictorial representation: Fig.1 represents the M line though cross-section of muscle fiber.
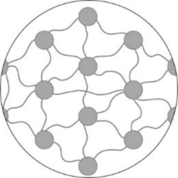
Fig.1: M line
M line is the narrow, dark band in the center region of the H zone known as M line that corresponds to proteins link together at the central region of the adjacent thick filament.
(4)
To draw: A cross-section diagram that shows in the Z line.
(4)
Explanation of Solution
Pictorial representation: Fig.1 represents the Z line though cross-section of muscle fiber.
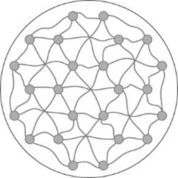
Fig.1: Z line
The sarcomeres are composed of thin and thick overlapping filaments. It is delineated by Z disks on both ends. These disks are composed of specialized proteins that are perpendicular to myofilaments and function as an anchor for the thin filament.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Vander's Human Physiology
- Describe the principle of homeostasis.arrow_forwardExplain how the hormones of the glands listed below travel around the body to target organs and tissues : Pituitary gland Hypothalamus Thyroid Parathyroid Adrenal Pineal Pancreas(islets of langerhans) Gonads (testes and ovaries) Placentaarrow_forwardWhat are the functions of the hormones produced in the glands listed below: Pituitary gland Hypothalamus Thyroid Parathyroid Adrenal Pineal Pancreas(islets of langerhans) Gonads (testes and ovaries) Placentaarrow_forward
- Describe the hormones produced in the glands listed below: Pituitary gland Hypothalamus Thyroid Parathyroid Adrenal Pineal Pancreas(islets of langerhans) Gonads (testes and ovaries) Placentaarrow_forwardPlease help me calculate drug dosage from the following information: Patient weight: 35 pounds, so 15.9 kilograms (got this by dividing 35 pounds by 2.2 kilograms) Drug dose: 0.05mg/kg Drug concentration: 2mg/mLarrow_forwardA 25-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with a 2-day history of fever, chills, severe headache, and confusion. She recently returned from a trip to sub-Saharan Africa, where she did not take malaria prophylaxis. On examination, she is febrile (39.8°C/103.6°F) and hypotensive. Laboratory studies reveal hemoglobin of 8.0 g/dL, platelet count of 50,000/μL, and evidence of hemoglobinuria. A peripheral blood smear shows ring forms and banana-shaped gametocytes. Which of the following Plasmodium species is most likely responsible for her severe symptoms? A. Plasmodium vivax B. Plasmodium ovale C. Plasmodium malariae D. Plasmodium falciparumarrow_forward
- please fill in missing parts , thank youarrow_forwardplease draw in the answers, thank youarrow_forwarda. On this first grid, assume that the DNA and RNA templates are read left to right. DNA DNA mRNA codon tRNA anticodon polypeptide _strand strand C с A T G A U G C A TRP b. Now do this AGAIN assuming that the DNA and RNA templates are read right to left. DNA DNA strand strand C mRNA codon tRNA anticodon polypeptide 0 A T G A U G с A TRParrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





