
(a)
To determine: The experiment that determines the energy absorbed by the given compounds.
(a)
Answer to Problem 1DE
Solution: The experiment that determines the energy absorbed by the given compounds is UV-visible spectrometry.
Explanation of Solution
The energy absorbed by the given compound is calculated by the formula,
Plank’s constant and
The experiment that makes possible to measure the wavelength of the light absorbed by the compound is UV-visible spectrometry.
The maximum wavelength absorbed by the solution of the compound is determined and substituted in the above formula.
Thus, the energy absorbed by the compound is determined.
The experiment that determines the energy absorbed by the given compounds is UV-visible spectrometry.
(b)
To determine: The dependency of the excitation energy on the length of the conjugated system.
(b)
Answer to Problem 1DE
Solution: The increase in the length of the conjugated system causes decreases in the excitation energy.
Explanation of Solution
The
The, distance between the ground state and the excited state determines the energy needed for the excitation.
As the length of the conjugated system increases, the distance between the atom in the chain decreases and hence the distance between the ground state and the excited state decreases. Therefore, the excitation energy decreases.
Thus, the increase in the length of the conjugated system causes decreases in the excitation energy.
The increase in the length of the conjugated system causes decreases in the excitation energy.
(c)
To determine: The additional molecule required to test the energy dependency on the length of the conjugated system.
(c)
Answer to Problem 1DE
Solution: The additional molecule required to test the energy dependency on the length of the conjugated system are
Explanation of Solution
The dependency of the excitation energy on the length of the conjugated system is tested by measuring the
The examples are,
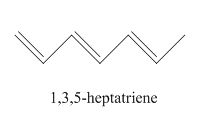
Figure 1
Phenolphthalein
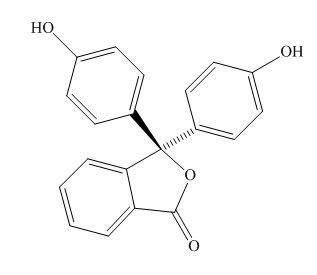
Figure 2
Lycopene
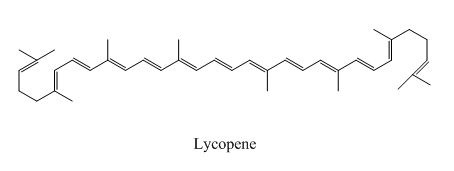
Figure 3
The above examples absorb light of different wavelength, depending upon their conjugation length.
Phenolphthalein,
(d)
To determine: The dependency of the absorption of energy on the delocalization of the electron.
(d)
Answer to Problem 1DE
Solution: The dependency of the absorption of energy on the delocalization of the electron is explained using phenolphthalein.
Explanation of Solution
The excitation of the
The structure of the phenolphthalein is,
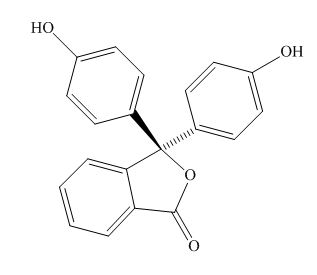
Figure 2
Phenolphthalein is acidic in nature due to the presence of the phenolic hydroxide group. Thus, in the acidic solution, the hydroxide group is not ionised. In the basic solution, the hydoxide group ionizes to form oxide ion that takes part in the resonance and stabilizes the
Phenolphthalein in the acidic solution is colorless, while that in the basic solution is colored. The reason for the same is that, the delocalisation of the electrom takes place in the basic solution and is absent in the acidic solution. Hence, unless the electrons are not delocalised, excitation of the electrons does not take place.
The dependency of the absorption of energy on the delocalization of the electron is explained using phenolphthalein.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
MAST F/ CHEM: THE CENTRAL SCI CODE ALON
- What is the name of the following compound? SiMe3arrow_forwardK Draw the starting structure that would lead to the major product shown under the provided conditions. Drawing 1. NaNH2 2. PhCH2Br 4 57°F Sunny Q Searcharrow_forward7 Draw the starting alkyl bromide that would produce this alkyne under these conditions. F Drawing 1. NaNH2, A 2. H3O+ £ 4 Temps to rise Tomorrow Q Search H2arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





