
The following table gives the current
Travellers Inn (Millions of Dollars)
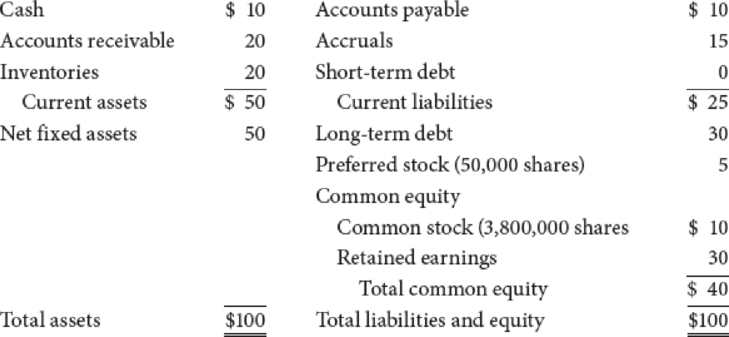
The following facts also apply to TII.
- (1) The long-term debt consists of 29,412 bonds, each having a 20-year maturity, semiannual payments, a coupon rate of 7.6%, and a face value of $1,000. Currently, these bonds provide investors with a yield to maturity of 11.8%. If new bonds were sold, they would have an 11.8% yield to maturity.
- (2) TII’s perpetual
preferred stock has a $100 par value, pays a quarterly dividend per share of $2, and has a yield to investors of 10%. New perpetual preferred stock would have to provide the same yield to investors, and the company would incur a 3.85% flotation cost to sell it. - (3) The company has 3.8 million shares of common stock outstanding, a price per share = P0 = $20, dividend per share = D0 = $1, and earnings per share = EPS0 = $5. The
return on equity (ROE) is expected to be 10%. - (4) The stock has a beta of 1.6%. The T-bond rate is 6%, and RPM is estimated to be 5%.
- (5) TII’s financial vice president recently polled some pension fund investment managers who hold TII’s securities regarding what minimum
rate of return on TII’s common would make them willing to buy the common rather than TII bonds, given that the bonds yielded 11.8%. The responses suggested a risk premium over TII bonds of 3 percentage points. - (6) TII is in the 25% federal-plus-state tax bracket.
Assume that you were recently hired by TII as a financial analyst and that your boss, the treasurer, has asked you to estimate the company’s WACC under the assumption that no new equity will be issued. Your cost of capital should be appropriate for use in evaluating projects that are in the same risk class as the assets TII now operates. Based on your analysis, answer the following questions.
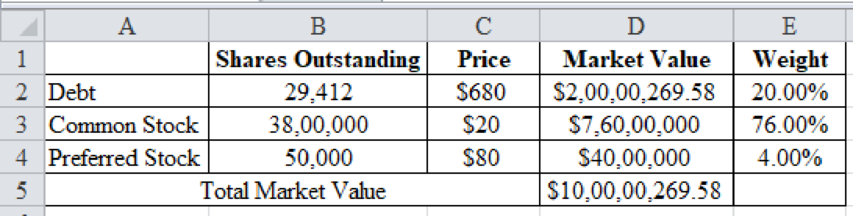
- a. What are the current market value weights for debt, preferred stock, and common stock? (Hint: Do your work in dollars, not millions of dollars. When you calculate the market values of debt and preferred stock, be sure to round the market price per bond and the market price per share of preferred to the nearest penny.)
- b. What is the after-tax cost of debt?
- c. What is the cost of preferred stock?
- d. What is the required return on common stock using
CAPM ? - e. Use the retention growth equation to estimate the expected growth rate. Then use the expected growth rate and the dividend growth model to estimate the required return on common stock.
- f. What is the required return on common stock using the own-bond-yield-plus-judgmental-risk-premium approach?
- g. Use the required return on stock from the CAPM model, and calculate the WACC.
a.
To determine: The market value weights of debt, common stock and preferred stock.
Answer to Problem 17P
The market value weights of debt are 20%, common stock is 76% and preferred stock is 4%.
Explanation of Solution
Determine the market value weights of debt, common stock and preferred stock
Excel Spreadsheet:
Excel Workings:
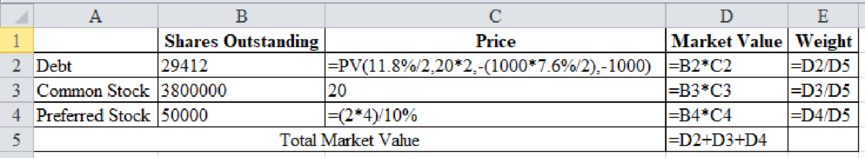
Therefore, the market value weights of debt are 20%, common stock is 76% and preferred stock is 4%.
b.
To determine: The after-tax cost of debt.
Answer to Problem 17P
The after-tax cost of debt is 8.85%.
Explanation of Solution
Determine the after-tax cost of debt
Therefore, the after-tax cost of debt is 8.85%.
c.
To determine: The cost of preferred stock.
Answer to Problem 17P
The cost of preferred stock is 10.40%.
Explanation of Solution
Determine the cost of preferred stock
Therefore, the cost of preferred stock is 10.40%.
d.
To determine: The required return on common stock using CAPM.
Answer to Problem 17P
The required return on common stock using CAPM is 14%.
Explanation of Solution
Determine the required return on common stock using CAPM
Therefore, the required return on common stock using CAPM is 14%.
e.
To determine: The required return on common stock using dividend growth model.
Answer to Problem 17P
The required return on common stock using dividend growth model is 13.40%.
Explanation of Solution
Determine the payout ratio
Therefore, the payout ratio is 20%.
Determine the growth rate
Therefore, the growth rate is 8%.
Determine the required return on common stock using dividend growth model
Therefore, the required return on common stock using dividend growth model is 13.40%.
f.
To determine: The required return on common stock using own-bond-yield-plus-judgmental- risk-premium approach.
Answer to Problem 17P
The required return on common stock using own-bond-yield-plus-judgmental- risk-premium approach is 14.80%.
Explanation of Solution
Determine the required return on common stock using own-bond-yield-plus-judgmental- risk-premium approach
Therefore, the required return on common stock using own-bond-yield-plus-judgmental- risk-premium approach is 14.80%.
g.
To determine: The WACC.
Answer to Problem 17P
The WACC is 12.83%.
Explanation of Solution
Determine the WACC
Therefore, the WACC is 12.83%.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT
- (a) The variables have been stripped of their names. Which one do you think is "household income" ?(b) Calculate the mean, median, and standard deviation of household income. Do these numbers fit with your expectations? (c) Suppose you have two histograms: one where the mean equals the median, and one where the mean is different from the median. How would you expect the two histograms to differ?arrow_forwardJanet Foster bought a computer and printer at Computerland. The printer had a $860 list price with a $100 trade discount and 210210 , n30n30 terms. The computer had a $4,020 list price with a 25% trade discount but no cash discount. On the computer, Computerland offered Janet the choice of (1) paying $150 per month for 17 months with the 18th payment paying the remainder of the balance or (2) paying 6% interest for 18 months in equal payments. Assume Janet could borrow the money for the printer at 6% to take advantage of the cash discount. How much would Janet save? Note: Use 360 days a year. Round your answer to the nearest cent.arrow_forwardDon't used Ai solutionarrow_forward
- Consider the following cash flows on two mutually exclusive projects for the Bahamas Recreation Corporation (BRC). Both projects require an annual return of 14 percent. New Submarine Deepwater Fishing Year Ride 0 -$875,000 1 330,000 2 480,000 3 440,000 -$1,650,000 890,000 730,000 590,000 a-1. Compute the IRR for both projects. (Do not round intermediate calculations and enter your answers as a percent rounded to 2 decimal places, e.g., 32.16.) Deepwater Fishing Submarine Ride 19.16 % 17.50% a-2. Based on the IRR, which project should you choose? Deepwater Fishing Submarine Ride b-1. Calculate the incremental IRR for the cash flows. (Do not round intermediate calculations and enter your answer as a percent rounded to 2 decimal places, e.g., 32.16.) Incremental IRR 14.96 % b-2. Based on the incremental IRR, which project should you choose? Submarine Ride Deepwater Fishingarrow_forwardWhat is the possibility that cases are not readily bounded but may have blurry definitions? How to address Robert Yin statement and how to resolve the ‘not readily bound’ case? Please help explain.arrow_forwardAn investment that is worth $44,600 is expected to pay you $212,205 in X years and has an expected return of 18.05 percent per year. What is X?arrow_forward
- An investment that is worth $27,200 is expected to pay you $62,280 in 5 years and has an expected return of X percent per year. What is X?arrow_forwardDon't used Ai solution and don't used hand raitingarrow_forward3-7. (Working with an income statement and balance sheet) Prepare a balance sheet and income statement for Kronlokken Company from the following scrambled list of items. a. Prepare a common-sized income statement and a common-sized balance sheet. Interpret your findings. Depreciation expense $66,000 Cash 225,000 Long-term debt 334,000 Sales 573,000 Accounts payable 102,000 General and administrative expense 79,000 Buildings and equipment 895,000 Notes payable 75,000 Accounts receivable 153,000 Interest expense 4,750 Accrued expenses 7,900 Common stock 289,000 Cost of goods sold 297,000 Inventory 99,300 Taxes 50,500 Accumulated depreciation 263,000 Prepaid expenses 14,500 Taxes payable 53,000 Retained earnings 262,900 ||arrow_forward
- x3-3. (Preparing an income statement) Prepare an income statement and a common- sized income statement from the following information. MyLab Sales Cost of goods sold General and administrative expenses Depreciation expenses Interest expense Income taxes $525,000 200,000 62,000 8,000 12,000 97,200arrow_forward3-9. (Working with a statement of cash flows) Given the following information, prepare LO3 a statement of cash flows. Increase in accounts receivable Increase in inventories Operating income Interest expense Increase in accounts payable Dividends $25 30 75 25 25 15 20 Increase in net fixed assets 23 Depreciation expense Income taxes 12 17 Beginning cash 20 Increase in common stockarrow_forward3-4. (Preparing a balance sheet) Prepare a balance sheet from the following informa- LO2 tion. What is the net working capital and debt ratio? Cash $50,000 Account receivables 42,700 Accounts payable 23,000 Short-term notes payable 10,500 Inventories 40,000 Gross fixed assets 1,280,000 Other current assets 5,000 Long-term debt 200,000 Common stock 490,000 Other assets 15,000 Accumulated depreciation 312,000 Retained earnings ? MyLabarrow_forward

 Financial Reporting, Financial Statement Analysis...FinanceISBN:9781285190907Author:James M. Wahlen, Stephen P. Baginski, Mark BradshawPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Reporting, Financial Statement Analysis...FinanceISBN:9781285190907Author:James M. Wahlen, Stephen P. Baginski, Mark BradshawPublisher:Cengage Learning


