
Concept explainers
a.
Complete the payroll register by filling in all cells for the pay period ended August 31.
a.
Explanation of Solution
Payroll tax:
Payroll tax refers to the tax that are equally contributed by employees and
employer based on the salary and wages of an employee. Payroll tax includes taxes
like federal tax, local income tax, state tax, social security tax and federal and
state
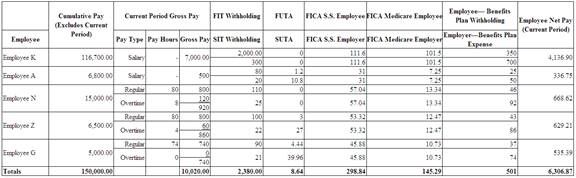
(Table 1)
b.
Prepare
b.
Explanation of Solution
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation |
Debit (Amount in $) |
Credit (Amount in $) |
| August 31 | Salaries expense | 10,020.00 | |
| FICA - Social security taxes payable | 298.84 | ||
| FICA- Medicare taxes payable | 145.29 | ||
|
Federal income taxes payable- Employee | 2,380.00 | ||
|
State income taxes payable- Employee | 388.00 | ||
| Employee benefits plan payable | 501.00 | ||
| Salaries payable | 6306.87 | ||
| (To record the payroll for period) |
(Table 2)
- Salaries expense is a component of
stockholder’s equity and there is an increase in the value of expense. Hence, debit the salaries expense by $10,020.00 - FICA- Social security taxes payable is a liability and there is an increase in the value of liability. Hence, credit the FICA- social security taxes payable by $298.84.
- FICA- Medicare taxes payable is a liability and there is an increase in the value of liability. Hence, credit the FICA- Medicare taxes payable by $145.29
- Federal income taxes payable- employee is a liability and there is an increase in the value of liability. Hence, credit the federal income taxes payable by $2,380.00.
- State income taxes payable- employee is a liability and there is an increase in the value of liability. Hence, credit the state income taxes payable by $388.00.
- Employee benefits plan payable is a liability and there is an increase in the value of liability. Hence, credit the employee benefits plan payable by $501.00.
- Salaries payable is a liability and there is an increase in the value of liability. Hence, credit the salaries payable by $6,306.87.
c.
Prepare journal entry to record the employer’s cash payment of the net payroll of requirement b.
c.
Explanation of Solution
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation |
Debit (Amount in $) |
Credit (Amount in $) |
| August 31 | Salaries payable | 6,306.87 | |
| Cash | 6306.87 | ||
| (To record the payment of payroll) |
(Table 3)
- Salaries payable is a liability and there is a decrease in the value of liability. Hence, debit the salaries payable by $6,306.87.
- Cash is an asset and there is a decrease the value of an asset. Hence, credit the cash by $6,306.87.
d.
Prepare journal entry to record the employer’s payroll taxes including the contribution to the benefits plan.
d.
Explanation of Solution
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation |
Debit (Amount in $) |
Credit (Amount in $) |
| August 31 | Payroll tax expense | 530.53 | |
| FICA - Social security taxes payable | 298.84 | ||
| FICA- Medicare taxes payable | 145.29 | ||
| Federal unemployment taxes payable | 8.64 | ||
| State unemployment taxes payable | 77.76 | ||
| (To record the payroll taxes) |
(Table 4)
- Payroll tax expense is a component of stockholder’s equity and there is an increase in the value of expense. Hence, debit the payroll tax expense by $530.53.
- FICA- Social security taxes payable is a liability and there is an increase in the value of liability. Hence, credit the FICA- social security taxes payable by $298.84.
- FICA- Medicare taxes payable is a liability and there is an increase in the value of liability. Hence, credit the FICA- Medicare taxes payable by $145.29
- Federal unemployment taxes payable is a liability and there is an increase in the value of liability. Hence, credit the federal unemployment taxes payable by $8.64.
- State unemployment taxes payable is a liability and there is an increase in the value of liability. Hence, credit the state unemployment taxes payable by $77.76.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation |
Debit (Amount in $) |
Credit (Amount in $) |
| August 31 | Employee benefits expense | 1,002.00 | |
| Employee benefits plan payable | 1,002.00 | ||
| (To record the cost of employee benefits) |
(Table 5)
- Employee benefits expense is a component of stockholder’s equity and there is an increase in the value of expense. Hence, debit the employee benefits expense by $1,002.00.
- Employee benefits plan payable is a liability and there is an increase in the value of liability. Hence, credit the employee benefits plan payable by $1,002.00.
e.
Prepare journal entry to record to pay all liabilities (except for the net payroll in requirement c) for this biweekly period.
e.
Explanation of Solution
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation |
Debit (Amount in $) |
Credit (Amount in $) |
| August 31 | FICA - Social security taxes payable | 597.68 | |
| FICA- Medicare taxes payable | 290.58 | ||
| Federal income taxes payable- employee | 2,380.00 | ||
| State income taxes payable- employee | 388.00 | ||
| Employee benefits plan payable | 1,503.00 | ||
| Federal unemployment taxes payable | 8.64 | ||
| State unemployment taxes payable | 77.76 | ||
| Cash | 5,245.66 | ||
| (To record payment of FICA, income taxes, SUTA, FUTA, and benefit plan contributions) |
(Table 6)
- FICA- Social security taxes payable is a liability and there is a decrease in the value of liability. Hence, debit the FICA- social security taxes payable by $597.68.
- FICA- Medicare taxes payable is a liability and there is a decrease in the value of liability. Hence, debit the FICA- Medicare taxes payable by $290.58.
- Federal income taxes payable- employee is a liability and there is a decrease in the value of liability. Hence, debit the federal income taxes payable by $2,380.00.
- State income taxes payable- employee is a liability and there is a decrease in the value of liability. Hence, debit the state income taxes payable by $388.00.
- Employee benefits plan payable is a liability and there is a decrease in the value of liability. Hence, debit the employee benefits plan payable by $1,503.00
- Federal unemployment taxes payable is a liability and there is a decrease in the value of liability. Hence, debit the federal unemployment taxes payable by $8.64.
- State unemployment taxes payable is a liability and there is a decrease in the value of liability. Hence, debit the state unemployment taxes payable by $77.76.
- Cash is an asset and there is a decrease the value of an asset. Hence, credit the cash by $5,245.66.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Connect Access Card For Financial Accounting Fundamentals
- Jeel Corporation projected current year sales of 45,000 units at a unit sale price of $32.00. Actual current year sales were 48,500 units at $34.50 per unit. Actual variable costs, budgeted at $22.50 per unit, totaled $21.75 per unit. Budgeted fixed costs totaled $375,000, while actual fixed costs amounted to $392,000. What is the sales volume variance for total revenue?arrow_forwardCan you help me solve this general accounting question using valid accounting techniques?arrow_forwardPlease provide the accurate solution to this financial accounting question using valid calculations.arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





