
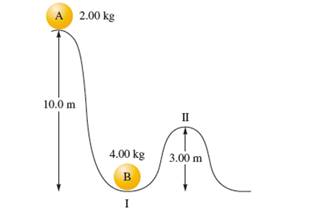
Interpretation: The kinetic energy and potential energy of ball B at the point II needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 9 Solutions
EBK WEBASSIGN FOR ZUMDAHL'S CHEMICAL PR
- ¿Qué the product is obtained from tetraethoxypropano and hidrazina?. Indicate the reason why the corresponding dial is used.arrow_forwardIf CH3COCH2CH(OCH3)2 is reacted with hydrazine, two isomeric products are formed. Indicate their structures and the major product.arrow_forwardIs it possible to obtain addition derivatives to nitrogen in position 2 of pyrazoles by reaction with electrophilic agents? Reason for this.arrow_forward
- Starting from 1,3-dicarbonyl derivatives to obtain isooxazoles and isothiazoles. Indicate whether synthetic methods exist.arrow_forwardIn the synthesis of benzotriazole, adding NaNO2 heats the solution. State the reason.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by treating benzotriazole with dimethyl sulfate or methyl iodide in a basic medium.arrow_forward
- What is the significance of selecting a "representative" sample for chemical analysis, and how does this practice ensure accurate and reliable results with respect to chemical analyses?arrow_forwardIdentify and provide an explanation of the differences between homogeneous and heterogeneous sampling in the context of sampling methods.arrow_forwardГ C-RSA CHROMATOPAC CH=1 DATA 1: @CHRM1.C00 ATTEN=10 SPEED= 10.0 0.0 b.092 0.797 1.088 1.813 C-RSA CHROMATOPAC CH=1 Report No. =13 ** CALCULATION REPORT ** DATA=1: @CHRM1.000 11/03/05 08:09:52 CH PKNO TIME 1 2 0.797 3 1.088 4 1.813 AREA 1508566 4625442 2180060 HEIGHT 207739 701206 V 287554 V MK IDNO CONC NAME 18.1447 55.6339 26.2213 TOTAL 8314067 1196500 100 C-R8A CHROMATOPAC CH=1 DATA 1: @CHRM1.C00 ATTEN=10 SPEED= 10.0 0. 0 087 337. 0.841 1.150 C-R8A CHROMATOPAC CH=1 Report No. =14 DATA=1: @CHRM1.000 11/03/05 08:12:40 ** CALCULATION REPORT ** CH PKNO TIME AREA 1 3 0.841 1099933 41.15 4039778 HEIGHT MK IDNO 170372 649997¯¯¯ CONC NAME 21.4007 78.5993 TOTAL 5139711 820369 100 3 C-R8A CHROMATOPAC CH=1 DATA 1: @CHRM1.C00 ATTEN=10 SPEED= 10.0 0.100 0:652 5.856 3 1.165 C-RSA CHROMATOPAC CH-1 Report No. =15 DATA=1: @CHRM1.000 11/03/05 08:15:26 ** CALCULATION REPORT ** CH PKNO TIME AREA HEIGHT MK IDNO CONC NAME 1 3 3 0.856 4 1.165 TOTAL 1253386 4838738 175481 708024 V 20.5739 79.4261 6092124…arrow_forward
 General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning





