
Concept explainers
To calculate: The rate of crossover for two projects.
Introduction:
The
Answer to Problem 13QP
The crossover rate for the two projects is 11.19%. The NPV profiles show that both the projects have higher NPV for rate of discount below 11.19% and have lower NPV for the rate above 11.19%.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The details of two projects are provided. The cash flows of project X for year 1, year 2, and year 3, are $8,850, $9,100, and $8,800 respectively. The initial investment is $20,000. The cash flows of project Y for 3 years are $10,100, $7,800, $8,700 respectively, and the initial investment is $20,000.
Note:
- NPV is the difference between the present values of the cash inflows and the present values of cash outflows.
- The IRR is a rate of interest, which makes a project’s NPV equals zero. Hence, using the available information, assume that NPV is equal to zero and form an equation to compute the IRR.
Equation of NPV to compute IRR assuming that NPV is equal to zero:
Compute IRR for project X using a spreadsheet:
Step 1:
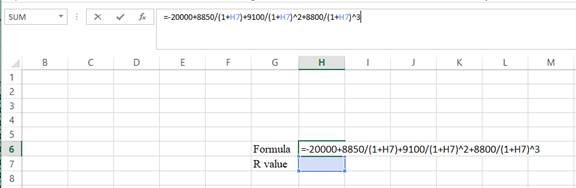
- Type the equation of NPV in H6 in the spreadsheet and consider the IRR value as H7.
Step 2:
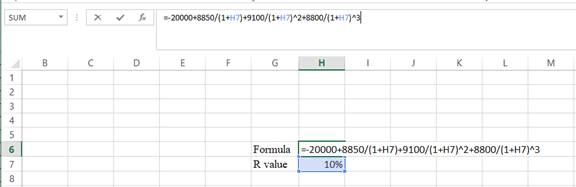
- Assume the IRR value as 10%.
Step 3:
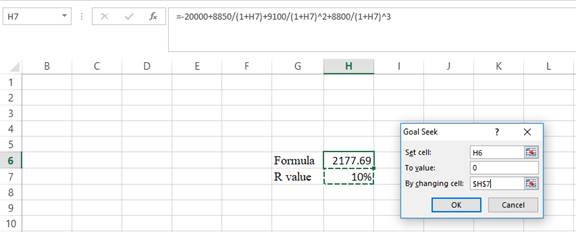
- In the spreadsheet, go to data and select What-if analysis.
- In What-if analysis, select Goal Seek.
- In “Set cell”, select H6 (the formula).
- The “To value” is considered as 0 (the assumption value for NPV).
- The H7 cell is selected for “By changing cell”.
Step 4:
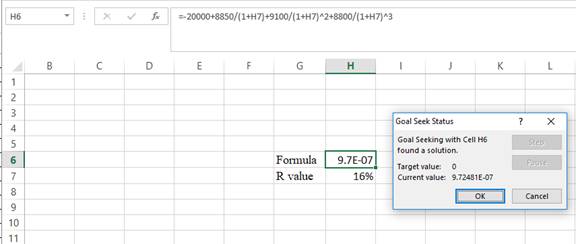
- Following the previous step, click OK in the Goal Seek Status. The Goal Seek Status appears with the IRR value.
Step 5:
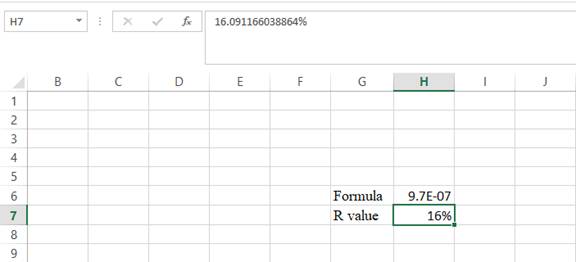
- The value appears to be 16.091166038864%.
Hence, the IRR value is 16.09%.
Compute IRR for project Y using a spreadsheet:
Step 1:
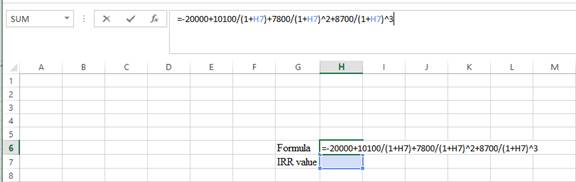
- Type the equation of NPV in H6 in the spreadsheet and consider the IRR value as H7.
Step 2:
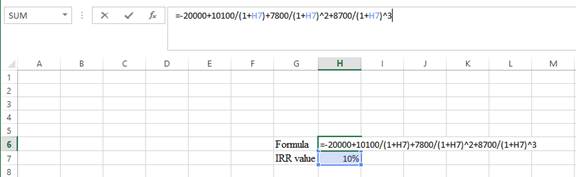
- Assume the IRR value as 10%.
Step 3:
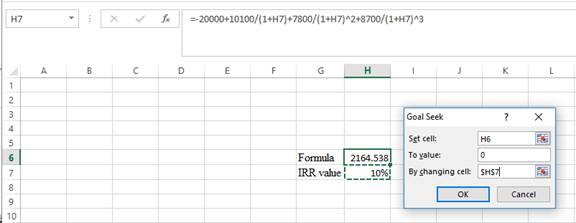
- In the spreadsheet, go to data and select What-if analysis.
- In What-if analysis, select Goal Seek.
- In “Set cell”, select H6 (the formula).
- The “To value” is considered as 0 (the assumption value for NPV).
- The H7 cell is selected for “By changing cell”.
Step 4:
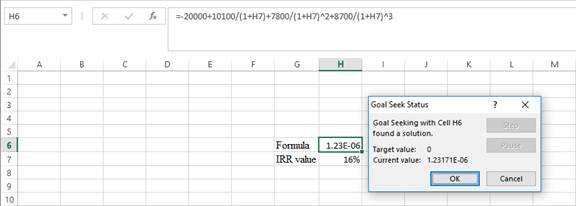
- Following the previous step, click OK in the Goal Seek Status. The Goal Seek Status appears with the IRR value.
Step 5:
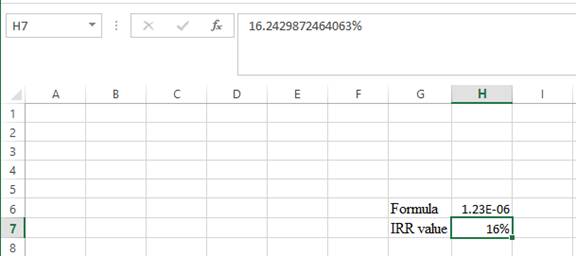
- The value appears to be 16.2429872464063%.
Hence, the IRR value is 16.24%.
Formula to compute the crossover rate:
Equation of crossover rate to compute R:
Where,
“R” denotes the crossover rate.
Compute R using a spreadsheet:
Step 1:
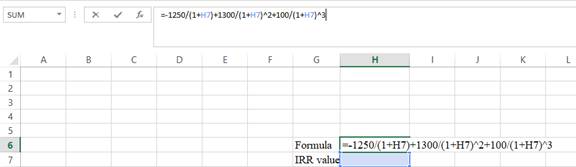
- Type the equation of NPV in H6 in the spreadsheet and consider the IRR value as H7.
Step 2:
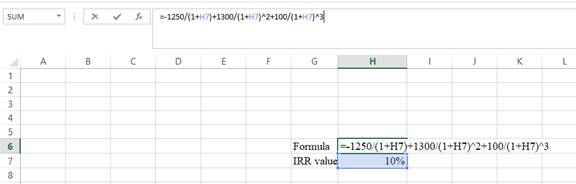
- Assume the IRR value as 10%.
Step 3:
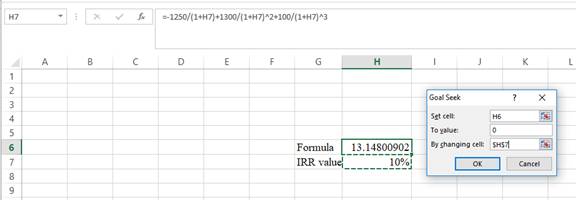
- In the spreadsheet, go to data and select What-if analysis.
- In What-if analysis, select Goal Seek.
- In “Set cell”, select H6 (the formula).
- The “To value” is considered as 0 (the assumption value for NPV).
- The H7 cell is selected for “By changing cell”.
Step 4:
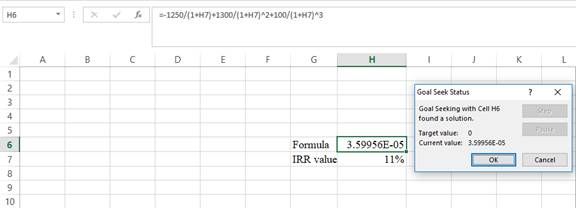
- Following the previous step, click OK in the Goal Seek Status. The Goal Seek Status appears with the IRR value.
Step 5:
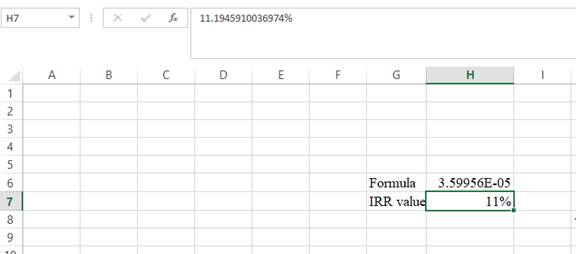
- The value appears to be 11.1945910036974%.
Hence, the R-value is 11.19%.
Formula to calculate the NPV:
Note: As the discount rate is over a range of 0% to 25%, calculate NPV for 0%, 5%, 10%, 15%, 20%, and 25%.
Compute the NPV with the discount rate of 0% for project X:
Compute the NPV with the discount rate of 0% for project Y:
Hence, the NPVs for projects X and Y @ 0% are $6,750 and $6,600 respectively.
Compute the NPV with the discount rate of 5% for project X:
Compute the NPV with the discount rate of 5% for project Y:
Hence, the NPVs for projects X and Y @ 5% are $4.284.31 and $4,209.26 respectively.
Compute the NPV with the discount rate of 10% for project X:
Compute the NPV with the discount rate of 10% for project Y:
Hence, the NPVs for projects X and Y @ 10% are $2,177.69 and $2,164.54 respectively.
Compute the NPV with the discount rate of 15% for project X:
Compute the NPV with the discount rate of 15% for project Y:
Hence, the NPVs for projects X and Y @ 15% are $362.70 and $400.92 respectively.
Compute the NPV with the discount rate of 20% for project X:
Compute the NPV with the discount rate of 20% for project Y:
Hence, the NPVs for projects X and Y @ 20% are -$1,212.96 and -$1,131.94 respectively.
Compute the NPV with the discount rate of 25% for project X:
Compute the NPV with the discount rate of 25% for project Y:
Hence, the NPVs for projects X and Y at 25% are -$2,590.4 and -$2,473.6 respectively.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Fundamentals Of Corporate Finance, Tenth Standard Edition
- What is the time value of money, and why is it important in financial decision-making?arrow_forwardPlease don't use chatgpt. The formula for calculating the present value of a future amount is:A) Future Value × (1 + r)^nB) Future Value ÷ (1 + r)^nC) Future Value × (1 - r)^nD) Future Value ÷ (1 - r)^n help in this question.arrow_forwardThe formula for calculating the present value of a future amount is:A) Future Value × (1 + r)^nB) Future Value ÷ (1 + r)^nC) Future Value × (1 - r)^nD) Future Value ÷ (1 - r)^n need help!arrow_forward
- no ai What is the primary purpose of diversification in investing?A) To maximize returnsB) To eliminate all riskC) To reduce unsystematic riskD) To ensure stable dividendsarrow_forwardno chatgpt Which of the following is a capital structure decision?A) Deciding how much to pay in dividendsB) Deciding how to allocate funds to various projectsC) Deciding the mix of debt and equity financingD) Deciding how much inventory to purchase need help!arrow_forwardWhich of the following is a capital structure decision?A) Deciding how much to pay in dividendsB) Deciding how to allocate funds to various projectsC) Deciding the mix of debt and equity financingD) Deciding how much inventory to purchasearrow_forward
- No chatgpt!! The weighted average cost of capital (WACC) is used to:A) Measure the profitability of a companyB) Determine the cost of debt financing onlyC) Calculate the company’s average cost of financing from debt and equityD) Estimate the future stock price need help.arrow_forwardNo AI The weighted average cost of capital (WACC) is used to:A) Measure the profitability of a companyB) Determine the cost of debt financing onlyC) Calculate the company’s average cost of financing from debt and equityD) Estimate the future stock pricearrow_forwardCost of Trade Credit A large retailer obtains merchandise under the credit terms of 3/20, net 35, but routinely takes 65 days to pay its bills. (Because the retailer is an important customer, suppliers allow the firm to stretch its credit terms.) What is the retailer's effective cost of trade credit? Assume a 365-day year. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to two decimal places. The answer is not 27.09 which is incorrect.arrow_forward
- You invest $1,000 a year for 10 years at 6 percent and then invest $2,000 a year for an additional 10 years at 6 percent. How much will you have accumulated at the end of the 20 years? Answer: $49,967 *Please include all work & formulasarrow_forwardNo ai please! What is the role of an underwriter in an IPO?A) To lend money to the companyB) To set the dividend policyC) To buy the securities and sell them to the publicD) To manage the company’s operations need hearrow_forwardNo ai tool What is the role of an underwriter in an IPO?A) To lend money to the companyB) To set the dividend policyC) To buy the securities and sell them to the publicD) To manage the company’s operationsarrow_forward
 Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

 Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson,
Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson, Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





