
Concept explainers
To express:
A binary number into a hexadecimal number.
Answer to Problem 18A
Hexadecimal number is 749.A4416.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
A binary number 11101001001.10100100012.
Calculation:
Binary number system uses the number 2 as its base. Therefore, it has 2 symbols: The numbers are 0 and 1.
And a hexadecimal number system uses the number 16 as its base i.e. it has 16 symbols, hexadecimal digits are 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, A, B, C, D, E and F.
Binary numbers are represented as from hexadecimal number
| Binary | 0000 | 0001 | 0010 | 0011 | 0100 | 0101 | 0110 | 0111 |
| Decimal | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| Hexadecimal | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| Binary | 1000 | 1001 | 1010 | 1011 | 1100 | 1101 | 1110 | 1111 |
| Decimal | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| Hexadecimal | 8 | 9 | A | B | C | D | E | F |
Each hexadecimal digit consists of 4 binary digits.
For example, hexadecimal number 9 is equal to binary number 1001.
For converting integer part of binary number into hexadecimal number, write down the binary number and represent four binary digits from right by its hexadecimal digit from the table.
Then combine all the digits together.
For converting fractional part of binary number into hexadecimal number, write down the binary number and represent four binary digits from left by its hexadecimal digit from the table.
Then combine all the digits together.
Finally, hexadecimal number is combination of both integer and fractional part.
Hexadecimal digits are equal to the summation of 2n where n = 0, 1, 2 and 3 (position from right).
For example, 9 = 23+20. In this example, 21 and 22are not there. So, at position 1 and 2, binary digit is zero, and at position 0 and 3, binary digit is one. Therefore, hexadecimal of binary 1001 is
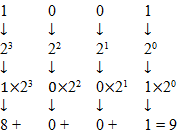
The hexadecimal number is equal to the summation of binary digits dn × 2n
Divide the binary number into block of four digits. If four digits are not there, then add additional zero in binary number. For example, 11 is written as 0011 and .11 is written as .1100.
Hexadecimal of binary number 1100100101001011.10010010012 is (Starting from right for integer part and starting from left for fractional part)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 85 Solutions
EBK MATHEMATICS FOR MACHINE TECHNOLOGY
- Q/solve the equation Laplac transforms:- x>0, to 43 1 иху u cx,α) = f(x) и a Cort ) = • lim u(x,t) = 0 8700 و X>0 , toarrow_forwardPlease conduct a step by step of these statistical tests on separate sheets of Microsoft Excel. If the calculations in Microsoft Excel are incorrect, the null and alternative hypotheses, as well as the conclusions drawn from them, will be meaningless and will not receive any points. The data for the following questions is provided in Microsoft Excel file on 4 separate sheets. Please conduct these statistical tests on separate sheets of Microsoft Excel. If the calculations in Microsoft Excel are incorrect, the null and alternative hypotheses, as well as the conclusions drawn from them, will be meaningless and will not receive any points. 1. One Sample T-Test: Determine whether the average satisfaction rating of customers for a product is significantly different from a hypothetical mean of 75. (Hints: The null can be about maintaining status-quo or no difference; If your alternative hypothesis is non-directional (e.g., μ≠75), you should use the two-tailed p-value from excel file to…arrow_forwardExplain how the answer could be 2 or 1.8 WITHOUT changing the questionarrow_forward
- +21 Rsts = R₁ (R+R) Calculate the total system relibility using the given formula including an explantion of how this formula was discvered.arrow_forward3. Use Laplace transforms to solve the semi-infinite wave problem a) utt = c²urr, x>0,t> 0, u(x, 0) = u(x, 0) = 0, u(0,t) = f(t), lim u(x,t) = 0. PIXarrow_forwarda/ Solved by de Alembert utt = c²uxx u(x, 0) = f(x) ut (x, 0) = g(x) f and y are given by where CI C = 1 f(x) = 3 e-x² ,д (x)=0 2 C=3 و f(x)=0 9 9CX = Xe-Xarrow_forward
 Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
