
(a)
Interpretation:
The major product obtained in the given reaction has to be identified.
Concept Introduction:
Hydro-halogenation reaction: In this reaction, hydrogen halide added across the unsaturated bond (
Markovnikov’s rule: An unsymmetrical alkene reacts with hydrogen halide in which halide ions goes to the more substitution position of carbon-carbon double bond which provides

Anti-Markovnikov’s rule: An unsymmetrical alkene reacts with hydrogen halide in which halide ions goes to the less substitution position of carbon-carbon double bond which provides alkyl halides.
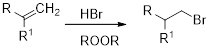
(b)
Interpretation:
The major product obtained in the given reaction has to be identified.
Concept Introduction:
Hydro-halogenation reaction: In this reaction, hydrogen halide added across the unsaturated bond (alkene).
Markovnikov’s rule: An unsymmetrical alkene reacts with hydrogen halide in which halide ions goes to the more substitution position of carbon-carbon double bond which provides alkyl halides.

Anti-Markovnikov’s rule: An unsymmetrical alkene reacts with hydrogen halide in which halide ions goes to the less substitution position of carbon-carbon double bond which provides alkyl halides.
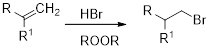
(c)
Interpretation:
The major product obtained in the given reaction has to be identified.
Concept Introduction:
Hydro-halogenation reaction: In this reaction, hydrogen halide added across the unsaturated bond (alkene).
Markovnikov’s rule: An unsymmetrical alkene reacts with hydrogen halide in which halide ions goes to the more substitution position of carbon-carbon double bond which provides alkyl halides.

Anti-Markovnikov’s rule: An unsymmetrical alkene reacts with hydrogen halide in which halide ions goes to the less substitution position of carbon-carbon double bond which provides alkyl halides.
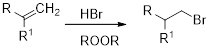
(d)
Interpretation:
The major product obtained in the given reaction has to be identified.
Concept Introduction:
Hydro-halogenation reaction: In this reaction, hydrogen halide added across the unsaturated bond (alkene).
Markovnikov’s rule: An unsymmetrical alkene reacts with hydrogen halide in which halide ions goes to the more substitution position of carbon-carbon double bond which provides alkyl halides.

Anti-Markovnikov’s rule: An unsymmetrical alkene reacts with hydrogen halide in which halide ions goes to the less substitution position of carbon-carbon double bond which provides alkyl halides.
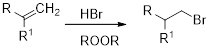
(e)
Interpretation:
The major product obtained in the given reaction has to be identified.
Concept Introduction:
Hydro-halogenation reaction: In this reaction, hydrogen halide added across the unsaturated bond (alkene).
Markovnikov’s rule: An unsymmetrical alkene reacts with hydrogen halide in which halide ions goes to the more substitution position of carbon-carbon double bond which provides alkyl halides.

Anti-Markovnikov’s rule: An unsymmetrical alkene reacts with hydrogen halide in which halide ions goes to the less substitution position of carbon-carbon double bond which provides alkyl halides.
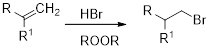
(f)
Interpretation:
The major product obtained in the given reaction has to be identified.
Concept Introduction:
Hydro-halogenation reaction: In this reaction, hydrogen halide added across the unsaturated bond (alkene).
Markovnikov’s rule: An unsymmetrical alkene reacts with hydrogen halide in which halide ions goes to the more substitution position of carbon-carbon double bond which provides alkyl halides.

Anti-Markovnikov’s rule: An unsymmetrical alkene reacts with hydrogen halide in which halide ions goes to the less substitution position of carbon-carbon double bond which provides alkyl halides.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 8 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY (LL) >CUSTOM PACKAGE<
- 6.15PM Sun Mar 30 K Draw the major product of this reaction. Include any relevant stereochemistry. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Problem 1 of O H [PhзPCH2CH3]*C|¯ NaH Drawing > Q Atoms, Bonds and Draw or tap a nearrow_forward8:17 PM Sun Mar 30 Draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. HSCH2CH2CH2SH, BF3 Probler Drawing Ato Bonds Clarrow_forwardpresented by Mr L How the coprion. (Il Done in no wraction, dew the starting redential) доarrow_forward
- 8:16 PM Sun Mar 30 K Draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Proble 1. CH3MgBr 2. H3O+ F Drawingarrow_forwardо но оarrow_forwardName the major organic product of the following action of 4-chloro-4-methyl-1-pentanol in neutral pollution 10+ Now the product. The product has a molecular formula f b. In a singly hain, the starting, material again converts into a secule with the molecular kormula CIO. but with comply Draw the major organic structure inhalationarrow_forward
- Macmillan Learning Alcohols can be oxidized by chromic acid derivatives. One such reagent is pyridinium chlorochromate, (C,H,NH*)(CICTO3), commonly known as PCC. Draw the proposed (neutral) intermediate and the organic product in the oxidation of 1-butanol by PCC when carried out in an anhydrous solvent such as CH₂C₁₂. PCC Intermediate OH CH2Cl2 Draw the intermediate. Select Draw Templates More с H Cr о Product Draw the product. Erase Select Draw Templates More H о Erasearrow_forwardIf I have 1-bromopropene, to obtain compound A, I have to add NaOH and another compound. Indicate which compound that would be. A C6H5 CH3arrow_forwardProvide the reagents for the following reactions.arrow_forward
- If I have 1-bromopropene, to obtain compound Z, I have to add two compounds A1 and A2. Indicate which compounds are needed. P(C6H5)3arrow_forwardDraw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Assume that the water side product is continuously removed to drive the reaction toward products. O CH3CH2NH2, TSOH Select to Draw >arrow_forwardPredict the major organic product(s) for the following reaction.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





