
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780137605521
Author: HIBBELER
Publisher: RENT PEARS
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 8.2, Problem 46P
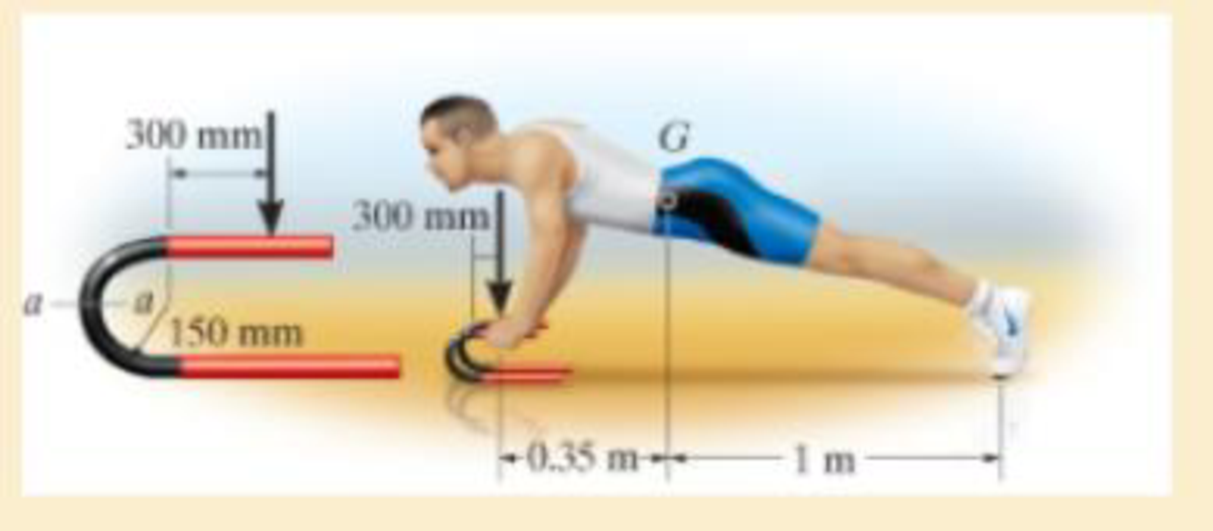
He is supported uniformly by two bars, each having a diameter of 25 mm. Assume the floor is smooth. Use the curved-beam formula to calculate the bending stress.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
A laminated spring Im long is built in 100 mm x 10 mm plates. If the spring is to carry a load
of 10 kN at its centre, determine the number of plates required for the spring. Take allowable
bending stress as 150 MPa.
The beam is supported by a pin at point A and a roller at
kN
point B. A distributed load of W₁ = 8 - and an applied
m
force of F₁ = 12 kN are applied to the beam. The beam has
an allowable bending stress of allow = 6 MPa. Neglect the
weight and thickness of the beam.
Take the origin for all functions to be at A., i.e. start at the
left and go right. Must use positive sign convention for V and
M.
d3
1
d3
d1
W1
d1
B
O
h
d2
F₁
Values for the figure are given in the following table. Note
the figure may not be to scale.
Dimensions for the whole beam
Variable
Value
d₁
4 m
d₂
2 m
Given the section is subjected to a moment of 500 N-m, calculate the normal stress in MPa at
the bottom of the section. Use positive for tension and negative for compression.
10 mm
30 mm
10 mm
30 mm
Chapter 8 Solutions
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
Ch. 8.1 - If it is subjected to an internal pressure of p =...Ch. 8.1 - If it is subjected to an internal pressure of p =...Ch. 8.1 - The thin-walled cylinder can be supported in one...Ch. 8.1 - If the inner diameter of the tank is 22 in., and...Ch. 8.1 - Prob. 5PCh. 8.1 - 88. The steel water pipe has an inner diameter of...Ch. 8.1 - The steel water pipe has an inner diameter of 12...Ch. 8.2 - Fundamental Problems F81. Determine the normal...Ch. 8.2 - Show the results in a differential element at the...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the state of stress at point A on the...
Ch. 8.2 - Determine the magnitude of the load P that will...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the state of stress at point B. Show the...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the state of stress at point A on the...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the state of stress at point A on the...Ch. 8.2 - Show the results in a differential element at the...Ch. 8.2 - The plate has a thickness of 20 mm and P acts...Ch. 8.2 - Plot the distribution of normal stress acting...Ch. 8.2 - Also, plot the normal-stress distribution over the...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the stress components at point A on the...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the stress components at point B on the...Ch. 8.2 - If it is subjected to the force system shown,...Ch. 8.2 - Neglect the weight of the block.Ch. 8.2 - Neglect the weight of the block.Ch. 8.2 - He is supported uniformly by two bars, each having...Ch. 8.2 - Specify the region to which this load can be...Ch. 8.2 - The pins at C and D are at the same location as...Ch. 8.2 - If the force at the ram on the clamp at D is P= 8...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the maximum ram force P that can be...Ch. 8.2 - and an outer radius of 3.00 in. If the face of the...Ch. 8 - If it supports a cable loading of 800 lb,...Ch. 8 - Determine the state of stress at point E on the...Ch. 8 - Determine the state of stress at point F on the...Ch. 8 - The suspender arm AE has a square cross-sectional...Ch. 8 - If the cross section of the femur at section aa...Ch. 8 - If it has a mass of 5 kg/m, determine the largest...Ch. 8 - and is used to support the vertical reactions of...Ch. 8 - and is used to support the vertical reactions of...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Can you please answer the rest of the questionsarrow_forwardThe eye hook has the dimensions shown. If it supports a cable loading of 800 lb, determine the maximum normal stress at section a–a and sketch the stress distribution acting over the cross section. Use the curved-beam formula to calculate the bending stress.arrow_forwardDetermine the maximum stress produced by the loads and create the shear and moment diagram for the cantilever beam system using the method of superposition.arrow_forward
- Calculate shear force and bending moment at point c.arrow_forwardThe box beam is made by nailing four 2-in. by 8-in. plankstogether as shown. Given that w0 = 300 lb/ft, find the largestallowable force P if the bending stress is limited to 1400 psi.arrow_forwardThe simply supported joist is used in the construction of a floor for a building. In order to keep the floor low with respect to the sill beams C and D, the ends of the joist are notched as shown. If the allowable shear stress is tallow = 350 psi and the allowable bending stress is s allow = 1700 psi, determine the smallest height h so that the beam will support a load of P = 600 lb. Also, will the entire joist safely support the load? Neglect the stress concentration at the notch.arrow_forward
- a. the maximum tension bending stress at any location along the beam b. Determine the maximum compression bending stress at any location along the beamarrow_forwardThe beam is constructed of four boards, and is subjected to a moment of M=200 kip in, calculate the resultant force on the top board C. -1 in. 1 in. M-200 kip.in 13 in 80 T in. 8 in 1 in.arrow_forwarda. the maximum tension bending stress at any location along the beam b. Determine the maximum compression bending stress at any location along the beamarrow_forward
- The axle of the freight train is subjected to loadings as shown below. The diameter of the axle is 137.5 mm. If it is supported by two journal bearings at C and D, determine the maximum bending Stress. Include a FBD, SFD and BMD using either the section or graphical method. Draw a cross-section of the shaft and indicate the points of maximum tension and compression.arrow_forwardFor the next Beam in Cantiléver; Calculate the Maximum Compressive and Tensile Stresses Due to Bending The section of the beam is Rectangular with b = 150 mm and H = 300 mm 3 kN 1.0 kN/m kosm- .8 m-0.8 m- -1.6 m-arrow_forwardwith the drawingarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Everything About COMBINED LOADING in 10 Minutes! Mechanics of Materials; Author: Less Boring Lectures;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=N-PlI900hSg;License: Standard youtube license