
A 1.2-m plank with a mass of 3 kg rests on two joists. Knowing that the coefficient of static friction between the plank and the joists is 0.30, determine the magnitude of the horizontal force required to move the plank when (a) a = 750 mm, (b) a = 900 mm.
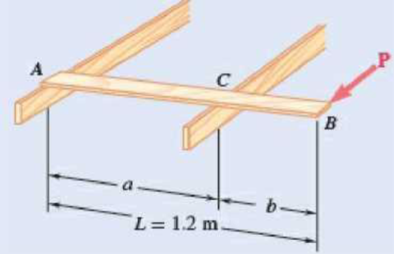
Fig. P8.37
(a)
Find the magnitude of the horizontal force required to move the plank.
Answer to Problem 8.37P
The magnitude of the horizontal force required to move the plank is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The length of the plank is
The mass of each plank is
The coefficient of static friction between the plank and the joists is
The distance between the points A and C in the plank is
Calculation:
Find the friction force (F) using the relation.
Show the free-body diagram of the member AB is vertical plane as in Figure 1.
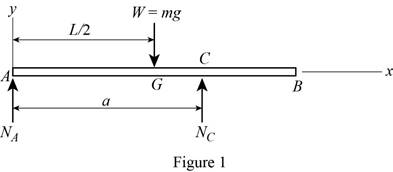
Take moment about point A.
Resolve the vertical component of forces.
Show the free-body diagram of the member AB is horizontal plane as in Figure 2.
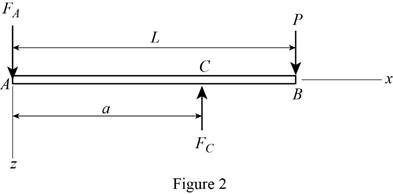
Take moment about point A.
Resolve the vertical component of forces.
Find the weight of the plank (W) using the relation.
Here, the acceleration due to gravity is g.
Consider the acceleration due to gravity is
Substitute 3 kg for m and
Substitute 29.43 N for W, 1.2 m for L, and 750 mm for a in Equation (1).
Substitute 29.43 N for W, 1.2 m for L, and 750 mm for a in Equation (2).
Substitute 1.2 m for L, and 750 mm for a in Equation (3).
Substitute 1.2 m for L, and 750 mm for a in Equation (4).
At point A, the plank to slip;
Find the horizontal force P using the relation.
Substitute 0.6P for
At point C, the plank to slip;
Find the horizontal force P using the relation.
Substitute 1.6P for
The smallest value of P will slip the plank. The plank will slip at A.
Therefore, the magnitude of the horizontal force required is
(b)
Find the magnitude of the horizontal force required to move the plank.
Answer to Problem 8.37P
The magnitude of the horizontal force required is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The length of the plank is
The mass of each plank is
The coefficient of static friction between the plank and the joists is
The distance between the points A and C in the plank is
Calculation:
Refer part (a) for calculation.
Substitute 29.43 N for W, 1.2 m for L, and 900 mm for a in Equation (1).
Substitute 29.43 N for W, 1.2 m for L, and 900 mm for a in Equation (2).
Substitute 1.2 m for L, and 900 mm for a in Equation (3).
Substitute 1.2 m for L, and 900 mm for a in Equation (4).
At point A, the plank to slip;
Find the horizontal force P using the relation.
Substitute 0.3333P for
At point C, the plank to slip;
Find the horizontal force P using the relation.
Substitute 1.3333P for
The smallest value of P will slip the plank. The plank will slip at C.
Therefore, the magnitude of the horizontal force required is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
EBK VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS: STA
- Access Pearson Mastering Engineering Back to my courses Course Home Course Home Scoresarrow_forwardAccess Pearson Mastering Engineering Back to my courses Course Home Course Home Scores Review Next >arrow_forwardAccess Pearson Course Home Scoresarrow_forwardCan you answer this question?arrow_forwardCan you answer this question?arrow_forwardA gear has a gear wheel with 16 teeth. The gear should be dimensioned for the highest and lowest gear ratio. Looking for output power, torque, speed?nin= 2000 rpmmin = 30Nmn=0,9a max= 450 mmModule 4Gear limitsz1 z213 13-1614 14-2615 15-4516 16-10117 17-131418 18-…..I have calculate but I can’t get the right answers…..√16 =459x60/56x57=1.1 lowest59x60/13x13=20,94 highestnut=2000/1.1= 1818rpmnut=2000/20.94=95.5 rpmMut=1.1x30=33 NmMut=20.94x30=628,2 Nm(Right answer)LowestZ=13, M=24,4Nm, n=2462 rpmHighestZ=92, M=172,5Nm, n=347,8 rpmP=5655W on botharrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





