
Concept explainers
To determine:
The cellular structures are necessary for photosynthesis.
Answer to Problem S3.3BYB
Solution:
Chloroplast are necessary for photosynthesis,
Explanation of Solution
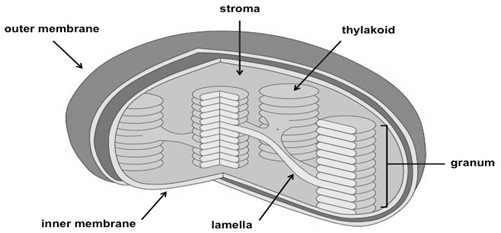
Photosynthesis is an important biological process. It’s only used by plants and other microorganisms to convert light energy into chemical energy that can later be released to energy the organisms.
Plastids
The plastids are cell organelles that are found in the plant cells only and some unicellular organisms (Euglena) of uncertain similarity. These can be classified into several types, depending upon the nature of the pigments they contain. Chloroplasts contain chlorophyll pigments, while chromoplasts contain pigments other than chlorophyll. The leucoplasts are devoid of any pigment. However, they have the capacity to develop pigments as and when necessary. Chlorophyll is the green colored pigment present in the chloroplast of the plant cell. It performs the function of trapping light energy and converts into chemical energy.
Different structures of chloroplast:
The chloroplasts are found in the leaves of green plants and are the most common and biologically important plastids.
Importance of Chloroplasts:
(i) Chloroplasts are able to trap solar energy and change it into chemical energy. All living organisms use this chemical energy to perform their life activities.
(ii) Chloroplasts fix up carbon dioxide and release oxygen during photosynthesis. This keeps the percentage of two gases balanced in the atmosphere.
(iii) They store starch either temporarily (e.g. in higher plants) or permanently (e.g. in several algae).
The chloroplast is cell organelle and it is equivalent to mitochondria because it possesses DNA, therefore, chloroplast is known as semiautonomous cell organelle. And chloroplasts may change into chromoplast to provide colors to many flowers and fruits to attract animals. Hence, Chloroplast cellular structures are necessary for photosynthesis.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
BIO 212 HUMAN BIOLOGY LAB NOTEBOOK
- In one paragraph show how atoms and they're structure are related to the structure of dna and proteins. Talk about what atoms are. what they're made of, why chemical bonding is important to DNA?arrow_forwardWhat are the structure and properties of atoms and chemical bonds (especially how they relate to DNA and proteins).arrow_forwardThe Sentinel Cell: Nature’s Answer to Cancer?arrow_forward
- Molecular Biology Question You are working to characterize a novel protein in mice. Analysis shows that high levels of the primary transcript that codes for this protein are found in tissue from the brain, muscle, liver, and pancreas. However, an antibody that recognizes the C-terminal portion of the protein indicates that the protein is present in brain, muscle, and liver, but not in the pancreas. What is the most likely explanation for this result?arrow_forwardMolecular Biology Explain/discuss how “slow stop” and “quick/fast stop” mutants wereused to identify different protein involved in DNA replication in E. coli.arrow_forwardMolecular Biology Question A gene that codes for a protein was removed from a eukaryotic cell and inserted into a prokaryotic cell. Although the gene was successfully transcribed and translated, it produced a different protein than it produced in the eukaryotic cell. What is the most likely explanation?arrow_forward
- Molecular Biology LIST three characteristics of origins of replicationarrow_forwardMolecular Biology Question Please help. Thank you For E coli DNA polymerase III, give the structure and function of the b-clamp sub-complex. Describe how the structure of this sub-complex is important for it’s function.arrow_forwardMolecular Biology LIST three characteristics of DNA Polymerasesarrow_forward
- Molecular Biology RNA polymerase core enzyme structure contains what subunits? To form holo enzyme, sigma factor is added to core. What is the name of the structure formed? Give the detailed structure of sigma factor and the function of eachdomain. Please help. Thank youarrow_forwardMolecular Biology You have a single bacterial cell whose DNA is labelled with radioactiveC14. After 5 rounds of cell division, how may cells will contain radioactive DNA? Please help. Thank youarrow_forward1. Explain the structure and properties of atoms and chemical bonds (especially how they relate to DNA and proteins). Also add some pictures.arrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





