
Concept explainers
To determine:
The cellular structures are necessary for photosynthesis.
Answer to Problem S3.3BYB
Solution:
Chloroplast are necessary for photosynthesis,
Explanation of Solution
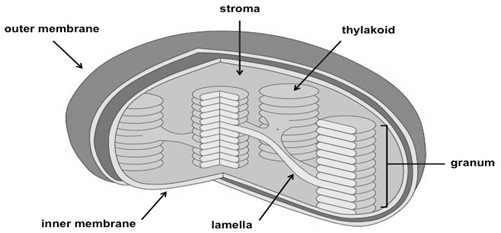
Photosynthesis is an important biological process. It’s only used by plants and other microorganisms to convert light energy into chemical energy that can later be released to energy the organisms.
Plastids
The plastids are cell organelles that are found in the plant cells only and some unicellular organisms (Euglena) of uncertain similarity. These can be classified into several types, depending upon the nature of the pigments they contain. Chloroplasts contain chlorophyll pigments, while chromoplasts contain pigments other than chlorophyll. The leucoplasts are devoid of any pigment. However, they have the capacity to develop pigments as and when necessary. Chlorophyll is the green colored pigment present in the chloroplast of the plant cell. It performs the function of trapping light energy and converts into chemical energy.
Different structures of chloroplast:
The chloroplasts are found in the leaves of green plants and are the most common and biologically important plastids.
Importance of Chloroplasts:
(i) Chloroplasts are able to trap solar energy and change it into chemical energy. All living organisms use this chemical energy to perform their life activities.
(ii) Chloroplasts fix up carbon dioxide and release oxygen during photosynthesis. This keeps the percentage of two gases balanced in the atmosphere.
(iii) They store starch either temporarily (e.g. in higher plants) or permanently (e.g. in several algae).
The chloroplast is cell organelle and it is equivalent to mitochondria because it possesses DNA, therefore, chloroplast is known as semiautonomous cell organelle. And chloroplasts may change into chromoplast to provide colors to many flowers and fruits to attract animals. Hence, Chloroplast cellular structures are necessary for photosynthesis.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
LSC TOMBALL BIOLOGY CONNECT ACCESS
- ✓ Details Draw a protein that is embedded in a membrane (a transmembrane protein), label the lipid bilayer and the protein. Identify the areas of the lipid bilayer that are hydrophobic and hydrophilic. Draw a membrane with two transporters: a proton pump transporter that uses ATP to generate a proton gradient, and a second transporter that moves glucose by secondary active transport (cartoon-like is ok). It will be important to show protons moving in the correct direction, and that the transporter that is powered by secondary active transport is logically related to the proton pump.arrow_forwarddrawing chemical structure of ATP. please draw in and label whats asked. Thank you.arrow_forwardOutline the negative feedback loop that allows us to maintain a healthy water concentration in our blood. You may use diagram if you wisharrow_forward
- Give examples of fat soluble and non-fat soluble hormonesarrow_forwardJust click view full document and register so you can see the whole document. how do i access this. following from the previous question; https://www.bartleby.com/questions-and-answers/hi-hi-with-this-unit-assessment-psy4406-tp4-report-assessment-material-case-stydu-ms-alecia-moore.-o/5e09906a-5101-4297-a8f7-49449b0bb5a7. on Google this image comes up and i have signed/ payed for the service and unable to access the full document. are you able to copy and past to this response. please see the screenshot from google page. unfortunality its not allowing me attch the image can you please show me the mathmetic calculation/ workout for the reult sectionarrow_forwardIn tabular form, differentiate between reversible and irreversible cell injury.arrow_forward
- 1.)What cross will result in half homozygous dominant offspring and half heterozygous offspring? 2.) What cross will result in all heterozygous offspring?arrow_forward1.Steroids like testosterone and estrogen are nonpolar and large (~18 carbons). Steroids diffuse through membranes without transporters. Compare and contrast the remaining substances and circle the three substances that can diffuse through a membrane the fastest, without a transporter. Put a square around the other substance that can also diffuse through a membrane (1000x slower but also without a transporter). Molecule Steroid H+ CO₂ Glucose (C6H12O6) H₂O Na+ N₂ Size (Small/Big) Big Nonpolar/Polar/ Nonpolar lonizedarrow_forwardwhat are the answer from the bookarrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





