
Sub part (a):
Steady state level of output.
Sub part (a):
Explanation of Solution
The steady state level of output is calculated as follows:
The steady state level of output is 200 units.
Concept introduction:
Sub part (b):
Solow diagram to show short run impact.
Sub part (b):
Explanation of Solution
Figure 1 depicts Solow diagram which shows the short run impact of a 21% increase in the amount of labor available.
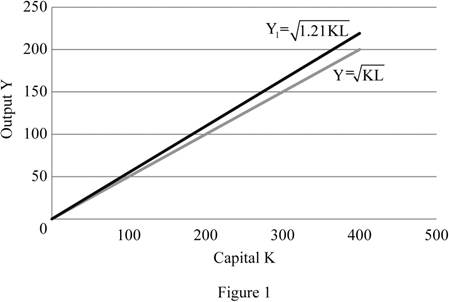
In figure 1, the horizontal axis represents the capital (K) and the vertical axis represents the output (Y). The initial production function
Concept introduction:
Economic growth: The economic growth is the increase in the overall goods and services produced per head in the economy over a specific period of time.
Solow growth rate The Solow growth rate is the rate of economic growth with given flexible price, and the existing real factors of capita, labor and knowledge. The Solow growth rate is an economy’s potential growth rate.
Sub part (c):
Steady state level of output.
Sub part (c):
Explanation of Solution
The new steady state level of output is calculated as follows:
The new steady state level of output is 220 units.
Concept introduction:
Economic growth: The economic growth is the increase in the overall goods and services produced per head in the economy over a specific period of time.
Sub part (d):
The new steady state level of output in the diagram.
Sub part (d):
Explanation of Solution
The new steady state level of output is 220 units which is depicted in the figure 1.
Sub part (e):
Action to gain long lasting benefits from the increase in capital stock.
Sub part (e):
Explanation of Solution
The initial production function is algebraically represented as follows:
Squaring both sides,
And solving for K, we get
Substitute K into the steady-state condition
And solve for Y by multiplying L and dividing by
Similarly, the new production function can be algebraically represented as follows:
Substitute K into the steady-state condition
And solve for Y by multiplying L and dividing by
Equating (1) in (2) we get
Substituting the values in equation (3) we get
Further, the percentage change in the output is depicted as follows:
This implies the steady-state level of output will grow by 21% per cent in the long run.
Concept introduction:
Production function: It is the relationship between the inputs employed by a firm and the maximum output the firm can produce with those inputs.
Sub part (f):
Output per worker.
Sub part (f):
Explanation of Solution
The output per worker in the initial steady state is calculated as follows:
The output per worker in the initial steady state is 2 units per labor.
The output per worker in the short run is calculated as follows:
The output per worker in short run is 1.82 units per labor.
The output per worker in the initial steady state is calculated as follows:
The output per worker in the long run is 2 units per labor.
Sub part (g):
New immigration policy and its effect.
Sub part (g):
Explanation of Solution
The citizens of the country are neither made worse off nor better off in the long run by a new immigration policy. This is because the new long-run level of output per worker compare with the initial level of output per worker remains unchanged which is 2 units per labor. This is unlike the short run effect which has lower output per worker. In the long run, the steady output level is determined largely by the
Concept introduction:
Depreciation: Depreciation is the process of decreasing the value of an asset over time especially due to wear and tear.
Investment: The investment is the money invests in terms of assets and building by the individual for the future consumption and profit making.
Sub part (h):
New steady state level of capital.
Sub part (h):
Explanation of Solution
The new steady state level of capital is calculated as follows
We know
Also
Equating all these we get,
Substituting the values we get
Thus the new steady state level of capital is 484, so that
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
EBK MODERN PRINCIPLES OF MACROECONOMICS
- After the ban is imposed, Joe’s firm switches to the more expensive biodegradable disposable cups. This increases the cost associated with each cup of coffee it produces. Which cost curve(s) will be impacted by the use of the more expensive biodegradable disposable cups? Why? Which cost curve(s) will not shift, and why not? Please use the table below to answer this question. For the second column (“Impacted? If so, how?”), please use one of the following three choices: No shift; Shifts up (i.e., increases: at nearly any given quantity, the cost goes up); or Shifts down (i.e., decreases: at nearly any given quantity, the cost goes down). $ Cost Curve Impacted? If so, how? Explanation of the Shift: Why or Why Not AFC No shift. Fix costs stay the same, regardless of quantity. Fixed cost is calculated as Fixed Cost/Quantity. Since fixed costs remain unchanged, AFC stays the same for each quantity. MC Shifts up. Since the biodegradable cups are more expensive, the…arrow_forwardStyrofoam is non-biodegradable and is not easily recyclable. Many cities and at least one state have enacted laws that ban the use of polystyrene containers. These locales understand that banning these containers will force many businesses to turn to other more expensive forms of packaging and cups, but argue the ban is environmentally important. Shane owns a firm with a conventional production function resulting in U-shaped ATC, AVC, and MC curves. Shane's business sells takeout food and drinks that are currently packaged in styrofoam containers and cups. Graph the short-run AFC0, AVC0, ATC0, and MC0 curves for Shane's firm before the ban on using styrofoam containers.arrow_forwardd-farrow_forward
- a-c pleasearrow_forwardd-farrow_forwardPART II: Multipart Problems wood or solem of triflussd aidi 1. Assume that a society has a polluting industry comprising two firms, where the industry-level marginal abatement cost curve is given by: MAC = 24 - ()E and the marginal damage function is given by: MDF = 2E. What is the efficient level of emissions? b. What constant per-unit emissions tax could achieve the efficient emissions level? points) c. What is the net benefit to society of moving from the unregulated emissions level to the efficient level? In response to industry complaints about the costs of the tax, a cap-and-trade program is proposed. The marginal abatement cost curves for the two firms are given by: MAC=24-E and MAC2 = 24-2E2. d. How could a cap-and-trade program that achieves the same level of emissions as the tax be designed to reduce the costs of regulation to the two firms?arrow_forward
- Only #4 please, Use a graph please if needed to help provearrow_forwarda-carrow_forwardFor these questions, you must state "true," "false," or "uncertain" and argue your case (roughly 3 to 5 sentences). When appropriate, the use of graphs will make for stronger answers. Credit will depend entirely on the quality of your explanation. 1. If the industry facing regulation for its pollutant emissions has a lot of political capital, direct regulatory intervention will be more viable than an emissions tax to address this market failure. 2. A stated-preference method will provide a measure of the value of Komodo dragons that is more accurate than the value estimated through application of the travel cost model to visitation data for Komodo National Park in Indonesia. 3. A correlation between community demographics and the present location of polluting facilities is sufficient to claim a violation of distributive justice. olsvrc Q 4. When the damages from pollution are uncertain, a price-based mechanism is best equipped to manage the costs of the regulator's imperfect…arrow_forward
- For environmental economics, question number 2 only please-- thank you!arrow_forwardFor these questions, you must state "true," "false," or "uncertain" and argue your case (roughly 3 to 5 sentences). When appropriate, the use of graphs will make for stronger answers. Credit will depend entirely on the quality of your explanation. 1. If the industry facing regulation for its pollutant emissions has a lot of political capital, direct regulatory intervention will be more viable than an emissions tax to address this market failure. cullog iba linevoz ve bubivorearrow_forwardExercise 3 The production function of a firm is described by the following equation Q=10,000-3L2 where L stands for the units of labour. a) Draw a graph for this equation. Use the quantity produced in the y-axis, and the units of labour in the x-axis. b) What is the maximum production level? c) How many units of labour are needed at that point? d) Provide one reference with you answer.arrow_forward

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





