
To write:
The complete and balanced
a) 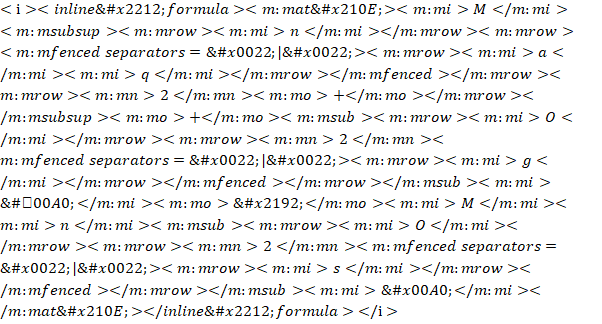 (basic solution)
(basic solution)
b)  (acidic solution)
(acidic solution)
c)
Answer to Problem 8.96QA
Solution:
Complete and balanced redox reaction is
a)
b)
c)
Explanation of Solution
1) Concept:
To balance a redox reaction, first we have to assign oxidation numbers to each of the elements in the compound and decide which element is going to be reduced and oxidized. Oxidation is loss of electrons or increase in oxidation number while reduction is gain of electrons or decrease in oxidation number.
2) Given:
i)
ii)  (acidic solution)
(acidic solution)
iii)
3) Calculations:
a)
i) The following preliminary expression relates the known reactant and products:
There are equal number of
ii) We perform an
As
iii) To balance these
iv) The ionic charge on the reactant is
v) Taking an inventory of atoms on both sides of the reaction arrow, we find that the left side has four more
Now the reaction is balanced.
b)
i) The following preliminary expression relates the known reactant and products:
There are equal numbers of  on both product and reactant sides, but there are unequal numbers of
on both product and reactant sides, but there are unequal numbers of
ii) We perform an
The
The change in the oxidation number is the same for oxidation and reduction.
iii) The ionic charge on the reactant is
iv) Taking an inventory of atoms on both sides of the reaction arrow, we find that the left side has four more
Now the reaction is balanced
c)
i) The following preliminary expression relates the known reactant and products:
There are unequal numbers of
ii) We perform an
The
The
The change in the oxidation number is the same for oxidation and reduction.
Also there are same number of charges on the reactant and product sides, so the reaction is balanced.
Conclusion:
In a redox reaction, substances either gain electrons or thereby undergo reduction, or they lose electrons and undergo oxidation. The given reaction is redox as the oxidation number of elements in the reactants changes during the reaction.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Chemistry: An Atoms-Focused Approach (Second Edition)
- What is the organic molecule X of the following acetal hydrolysis? Please draw a skeletal line structure and include a detailed explanation and drawing of how the mechanism proceeds. Please include any relevant information that is needed to understand the process of acetal hydrolysis.arrow_forwardWhat are is the organic molecule X and product Y of the following acetal hydrolysis? Please draw a skeletal line structure and include a detailed explanation and drawing of how the mechanism proceeds. Please include any relevant information that is needed to understand the process of acetal hydrolysis.arrow_forwardAt 300 K, in the decomposition reaction of a reactant R into products, several measurements of the concentration of R over time have been made (see table). Without using graphs, calculate the order of the reaction. t/s [R]/(mol L-1) 0 0,5 171 0,16 720 0,05 1400 0,027arrow_forward
- Predict the organic products that form in the reaction below, and draw the skeletal ("line") structures of the missing organic products. Please include all steps & drawings & explanations.arrow_forwardWhat are the missing reagents for the spots labeled 1 and 3? Please give a detailed explanation and include the drawings and show how the synthesis proceeds with the reagents.arrow_forwardWhat are the products of the following acetal hydrolysis? Please draw a skeletal line structure and include a detailed explanation and drawing of how the mechanism proceeds. Please include any relevant information that is needed to understand the process of acetal hydrolysis.arrow_forward
- What would happen if you added the HCI to the Grignard reagent before adding benzophenone? Draw a reaction mechanism to support your answer.arrow_forwardAt 300 K, in the decomposition reaction of a reactant R into products, several measurements of the concentration of R over time have been made (see table). Calculate the order of the reaction. t/s [R]/ (mol L-1) 0 0,5 171 0,16 720 0,05 1400 0,027arrow_forwardWrite the correct IUPAC names of the molecules in the picturearrow_forward
- How many grams of solid NaCN have to be added to 1.5L of water to dissolve 0.18 mol of Fe(OH)3 in the form Fe(CN)63 - ? ( For simplicity, ignore the reaction of CN - ion with water) Ksp for Fe(OH)3 is 2.8E -39, and Kform for Fe(CN)63 - is 1.0E31arrow_forwardDraw the most stable chair conformation of 1-ethyl-1-methylcyclohexane, clearly showing the axial and equatorial substituents. [4] Draw structures corresponding to the following IUPAC name for each of the following compounds; [5] i) 4-Isopropyl-2,4,5-trimethylheptane ii) trans-1-tert-butyl-4-ethylcyclohexane iii) Cyclobutylcycloheptane iv) cis-1,4-di-isopropylcyclohexane (chair conformation) v) 3-Ethyl-5-isobutylnonanearrow_forwardDraw and name molecules that meet the following descriptions; [4] a) An organic molecule containing 2 sp2 hybridised carbon and 1 sp-hybridised carbon atom. b) A cycloalkene, C7H12, with a tetrasubstituted double bond. Also answer question 2 from the imagearrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





