
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of the given compound has to be written.
Concept Introduction:
Isomers: Compounds that have same molecular formula but different structural formula.
Constitutional isomers: Compounds that have same molecular formula but different connectivity (arrangement of atoms are different).
Nomenclature of organic compounds:
The naming of the organic compound is given by IUPAC (International Union for pure and applied chemistry). In the IUPAC names consist of certain rules for giving chemical names they are,
- The longer number of Carbon chain of a compound is identified is called parent of the compound.
- In the cyclic compounds the number of carbon involving in ring formation is called parent of the compound.
- The compound have more than one parent chains means the larger number of substitutions present in the chain is consider as a parent chain.
- The names of all substituents are arranged by alphabets to starts with lowest numbering.
- In the complex substituent having compounds the substituent name is assigned by a name each of them based on numbers going away from the parent.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Compound (a):
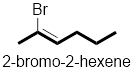
In the given compound, the longest carbon chain (highlighted with bold lines) contains six carbons and while numbering the parent chain, substituents should get the least possible number.
The presence of double bond at C-2 makes parent name as 2-hexene. The substituents Bromine atom at C-2; are arranged in alphabetical order followed by the parent name.
Therefore, the systematic name of the given compounds is ‘2-bromo-2-hexene’.
(b)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name and configuration of the given compound has to be written.
Concept Introduction:
Nomenclature of organic compounds:
The naming of the organic compound is given by IUPAC (International Union for pure and applied chemistry). In the IUPAC names consist of certain rules for giving chemical names they are,
- The longer number of Carbon chain of a compound is identified this is called parent of the compound.
- In the cyclic compounds the number of carbon involving in ring formation is called parent of the compound.
- The compound have more than one parent chains means the larger number of substitutions present in the chain is consider as a parent chain.
- The names of all substituents are arranged by alphabets to starts with lowest numbering.
- In the complex substituent having compounds the substituent name is assigned by a name each of them based on numbers going away from the parent.
R and S nomenclature:
It is used to assign the molecule using CIP rules.
The CIP rules are as follows:
- Select the chiral carbon and assign the numbers according to the decreasing
atomic mass of atoms attached to it. - If the numbering follows clockwise direction then the atom is termed as R and if it follows anti-clockwise direction then atom is termed as S.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Compound (b):
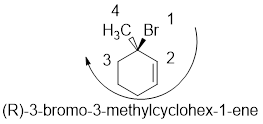
In the given compound, the longest carbon ring (highlighted with bold lines) contains six carbons and while numbering the parent chain, substituents should get the least possible number.
The presence of double bond at C-1 makes parent name is hex-1-ene. The substituents methyl located at C-3 and bromine atom at C-3; are arranged in alphabetical order followed by the parent name.
The chiral carbon and assign the numbers according to the decreasing atomic mass of atoms attached to it, follows clockwise direction then the atom is termed as R
Therefore, the systematic name of the given compounds is ‘3-bromo-3-methylcyclohex-1-ene’.
(c)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name and configuration of the given compound has to be written.
Concept Introduction:
Nomenclature of organic compounds:
The naming of the organic compound is given by IUPAC (International Union for pure and applied chemistry). In the IUPAC names consist of certain rules for giving chemical names they are,
- The longer number of Carbon chain of a compound is identified this is called parent of the compound.
- In the cyclic compounds the number of carbon involving in ring formation is called parent of the compound.
- The compound have more than one parent chains means the larger number of substitutions present in the chain is consider as a parent chain.
- The names of all substituents are arranged by alphabets to starts with lowest numbering.
- In the complex substituent having compounds the substituent name is assigned by a name each of them based on numbers going away from the parent.
In a cis isomer, groups are attached on the same side of the ring.
In a trans isomer, groups are attached on the opposite side of the ring.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
Compound (c):

In the given compound, the longest carbon ring (highlighted with bold lines) contains six carbons and while numbering the parent chain, substituents should get the least possible number.
The parent name is CYCLOHEXANE. The substituents bromine atoms are at C-1and C-4; are arranged in alphabetical order followed by the parent name. Here, bromine atoms are attached on the opposite side of the ring thus ‘trans’.
Therefore, the systematic name of the given compounds is ‘trans 1,4-dibromocyclohexane’.
(d)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of the given compound has to be written.
Concept Introduction:
Nomenclature of organic compounds:
The naming of the organic compound is given by IUPAC (International Union for pure and applied chemistry). In the IUPAC names consist of certain rules for giving chemical names they are,
- The longer number of Carbon chain of a compound is identified this is called parent of the compound.
- In the cyclic compounds the number of carbon involving in ring formation is called parent of the compound.
- The compound have more than one parent chains means the larger number of substitutions present in the chain is consider as a parent chain.
- The names of all substituents are arranged by alphabets to starts with lowest numbering.
- In the complex substituent having compounds the substituent name is assigned by a name each of them based on numbers going away from the parent.
(d)
Explanation of Solution
Compound (d):

In the given compound, the longest carbon chain (highlighted with bold lines) contains four carbons and while numbering the parent chain, substituents should get the least possible number.
The parent name is butane. The substituents chlorine atom at C-1 and C-4; are arranged in alphabetical order followed by the parent name.
Therefore, the systematic name of the given compounds is ‘1,4-dichlorobutane’.
(e)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name and configuration of the given compound has to be written.
Concept Introduction:
Nomenclature of organic compounds:
The naming of the organic compound is given by IUPAC (International Union for pure and applied chemistry). In the IUPAC names consist of certain rules for giving chemical names they are,
- The longer number of Carbon chain of a compound is identified this is called parent of the compound.
- In the cyclic compounds the number of carbon involving in ring formation is called parent of the compound.
- The compound have more than one parent chains means the larger number of substitutions present in the chain is consider as a parent chain.
- The names of all substituents are arranged by alphabets to starts with lowest numbering.
- In the complex substituent having compounds the substituent name is assigned by a name each of them based on numbers going away from the parent.
R and S nomenclature:
It is used to assign the molecule using CIP rules.
The CIP rules are as follows:
- Select the chiral carbon and assign the numbers according to the decreasing atomic mass of atoms attached to it.
- If the numbering follows clockwise direction then the atom is termed as R and if it follows anti-clockwise direction then atom is termed as S.
(e)
Explanation of Solution
Compound (e):
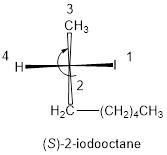
In the given compound, the longest carbon ring contains eight carbons and while numbering the parent chain, substituents should get the least possible number. The parent name is octane. The substituents iodine atom located at C-2; are arranged in alphabetical order followed by the parent name.
The numbering follows clockwise direction as shown above then it is termed as R. Least priority group is above the plane so the configuration is reversed.
Therefore, the systematic name of the given compounds is ‘(S)-2-iodooctane’.
(f)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name and configuration of the given compound has to be written.
Concept Introduction:
Nomenclature of organic compounds:
The naming of the organic compound is given by IUPAC (International Union for pure and applied chemistry). In the IUPAC names consist of certain rules for giving chemical names they are,
- The longer number of Carbon chain of a compound is identified this is called parent of the compound.
- In the cyclic compounds the number of carbon involving in ring formation is called parent of the compound.
- The compound have more than one parent chains means the larger number of substitutions present in the chain is consider as a parent chain.
- The names of all substituents are arranged by alphabets to starts with lowest numbering.
- In the complex substituent having compounds the substituent name is assigned by a name each of them based on numbers going away from the parent.
R and S nomenclature:
It is used to assign the molecule using CIP rules.
The CIP rules are as follows:
- Select the chiral carbon and assign the numbers according to the decreasing atomic mass of atoms attached to it.
- If the numbering follows clockwise direction then the atom is termed as R and if it follows anti-clockwise direction then atom is termed as S.
(f)
Explanation of Solution
Compound (f):
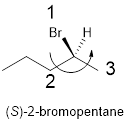
In the given compound, the longest carbon ring (highlighted with bold lines) contains five carbons and while numbering the parent chain, substituents should get the least possible number.
The parent name is hexane. The substituents bromine atom located at C-2; are arranged in alphabetical order followed by the parent name.
The chiral carbon and assign the numbers according to the decreasing atomic mass of atoms attached to it, follows anti-clockwise direction then atom is termed as S.
Therefore, the systematic name of the given compounds is ‘(S)-2-bromopentane’.
(g)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name and configuration of the given compound has to be written.
Concept Introduction:
Nomenclature of organic compounds:
The naming of the organic compound is given by IUPAC (International Union for pure and applied chemistry). In the IUPAC names consist of certain rules for giving chemical names they are,
- The longer number of Carbon chain of a compound is identified this is called parent of the compound.
- In the cyclic compounds the number of carbon involving in ring formation is called parent of the compound.
- The compound have more than one parent chains means the larger number of substitutions present in the chain is consider as a parent chain.
- The names of all substituents are arranged by alphabets to starts with lowest numbering.
- The complex substituent is built by a substituent on a substituent; so called complex substituent.
- In the complex substituent having compounds the substituent name is assigned by a name each of them based on numbers going away from the parent.
R and S nomenclature:
It is used to assign the molecule using CIP rules.
The CIP rules are as follows:
- Select the chiral carbon and assign the numbers according to the decreasing atomic mass of atoms attached to it.
- If the numbering follows clockwise direction then the atom is termed as R and if it follows anti-clockwise direction then atom is termed as S.
(g)
Explanation of Solution
Compound (g):
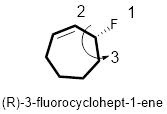
In the given compound, the longest carbon ring (highlighted with bold lines) contains seven carbons in a ring and while numbering the parent chain, substituents should get the least possible number.
The presence of double bond at C-1 on the ring makes parent name is cyclohept-1-ene. The substituents Fluorine atom located at C-3; are arranged in alphabetical order followed by the parent name.
The chiral carbon and assign the numbers according to the decreasing atomic mass of atoms attached to it, follows anti-clockwise direction then atom is termed as S. Least priority group is above the plane so the configuration is reversed. Hence, the configuration is (R).
Therefore, the systematic name of the given compounds is ‘(R)- 3-fluorocyclohept-1-ene’.
(h)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of the given compound has to be written.
Concept Introduction:
Nomenclature of organic compounds:
The naming of the organic compound is given by IUPAC (International Union for pure and applied chemistry). In the IUPAC names consist of certain rules for giving chemical names they are,
- The longer number of Carbon chain of a compound is identified this is called parent of the compound.
- In the cyclic compounds the number of carbon involving in ring formation is called parent of the compound.
- The compound have more than one parent chains means the larger number of substitutions present in the chain is consider as a parent chain.
- The names of all substituents are arranged by alphabets to starts with lowest numbering.
- The complex substituent is built by a substituent on a substituent; so called complex substituent.
- In the complex substituent having compounds the substituent name is assigned by a name each of them based on numbers going away from the parent.
(h)
Explanation of Solution
Compound (h):
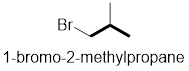
In the given compound, the longest carbon chain (highlighted with bold lines) contains three carbons and while numbering the parent chain, substituents should get the least possible number.
The parent name is Propane. The substituents methyl located at C-2 and bromine atom at C-1; are arranged in alphabetical order followed by the parent name.
Therefore, the systematic name of the given compounds is ‘1-bromo-2-methylpropane’.
(i)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC names and configuration of the given compound has to be written.
Concept Introduction:
Nomenclature of organic compounds:
The naming of the organic compound is given by IUPAC (International Union for pure and applied chemistry). In the IUPAC names consist of certain rules for giving chemical names they are,
- The longer number of Carbon chain of a compound is identified this is called parent of the compound.
- In the cyclic compounds the number of carbon involving in ring formation is called parent of the compound.
- The compound have more than one parent chains means the larger number of substitutions present in the chain is consider as a parent chain.
- The names of all substituents are arranged by alphabets to starts with lowest numbering.
- In the complex substituent having compounds the substituent name is assigned by a name each of them based on numbers going away from the parent.
(i)
Explanation of Solution
Compound (i):
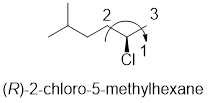
In the given compound, the longest carbon chain (highlighted with bold lines) contains six carbons and while numbering the parent chain, substituents should get the least possible number.
The parent name is hexane. The substituents methyl located at C-5 and chlorine atom at C-2; are arranged in alphabetical order followed by the parent name.
The chiral carbon and assign the numbers according to the decreasing atomic mass of atoms attached to it, follows clockwise direction then the atom is termed as R.
Therefore, the systematic name of the given compounds is ‘(R)-2-chloro-5-methylhexane’.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
OWLv2 with MindTap Reader, 1 term (6 months) Printed Access Card for Brown/Iverson/Anslyn/Foote's Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition
- Given a complex reaction with rate equation v = k1[A] + k2[A]2, what is the overall reaction order?arrow_forwardPlease draw the structure in the box that is consistent with all the spectral data and alphabetically label all of the equivalent protons in the structure (Ha, Hb, Hc....) in order to assign all the proton NMR peaks. The integrations are computer generated and approximate the number of equivalent protons. Molecular formula: C13H1802 14 13 12 11 10 11 (ppm) Structure with assigned H peaks 2.08 3.13arrow_forwardCHEMICAL KINETICS. One of the approximation methods for solving the rate equation is the steady-state approximation method. Explain what it consists of.arrow_forward
- CHEMICAL KINETICS. One of the approximation methods for solving the rate equation is the limiting or determining step approximation method. Explain what it consists of.arrow_forwardCHEMICAL KINETICS. Indicate the approximation methods for solving the rate equation.arrow_forwardTRANSMITTANCE เบบ Please identify the one structure below that is consistent with the 'H NMR and IR spectra shown and draw its complete structure in the box below with the protons alphabetically labeled as shown in the NMR spectrum and label the IR bands, including sp³C-H and sp2C-H stretch, indicated by the arrows. D 4000 OH LOH H₂C CH3 OH H₂C OCH3 CH3 OH 3000 2000 1500 HAVENUMBERI-11 1000 LOCH3 Draw your structure below and label its equivalent protons according to the peak labeling that is used in the NMR spectrum in order to assign the peaks. Integrals indicate number of equivalent protons. Splitting patterns are: s=singlet, d=doublet, m-multiplet 8 3Hb s m 1Hd s 3Hf m 2Hcd 2Had 1He 鄙视 m 7 7 6 5 4 3 22 500 T 1 0arrow_forward
- Relative Transmittance 0.995 0.99 0.985 0.98 Please draw the structure that is consistent with all the spectral data below in the box and alphabetically label the equivalent protons in the structure (Ha, Hb, Hc ....) in order to assign all the proton NMR peaks. Label the absorption bands in the IR spectrum indicated by the arrows. INFRARED SPECTRUM 1 0.975 3000 2000 Wavenumber (cm-1) 1000 Structure with assigned H peaks 1 3 180 160 140 120 100 f1 (ppm) 80 60 40 20 0 C-13 NMR note that there are 4 peaks between 120-140ppm Integral values equal the number of equivalent protons 10.0 9.0 8.0 7.0 6.0 5.0 4.0 3.0 2.0 1.0 0.0 fl (ppm)arrow_forwardCalculate the pH of 0.0025 M phenol.arrow_forwardIn the following reaction, the OH- acts as which of these? NO2-(aq) + H2O(l) ⇌ OH-(aq) + HNO2(aq)arrow_forward
- Using spectra attached, can the unknown be predicted? Draw the predicition. Please explain and provide steps. Molecular focrmula:C16H13ClOarrow_forwardCalculate the percent ionization for 0.0025 M phenol. Use the assumption to find [H3O+] first. K = 1.0 x 10-10arrow_forwardThe Ka for sodium dihydrogen phosphate is 6.32 x 10-8. Find the pH of a buffer made from 0.15 M H2PO4- and 0.25 M HPO42- .arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

