
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of the given compound has to be written.
Concept Introduction:
Isomers: Compounds that have same molecular formula but different structural formula.
Constitutional isomers: Compounds that have same molecular formula but different connectivity (arrangement of atoms are different).
Nomenclature of organic compounds:
The naming of the organic compound is given by IUPAC (International Union for pure and applied chemistry). In the IUPAC names consist of certain rules for giving chemical names they are,
- The longer number of Carbon chain of a compound is identified is called parent of the compound.
- In the cyclic compounds the number of carbon involving in ring formation is called parent of the compound.
- The compound have more than one parent chains means the larger number of substitutions present in the chain is consider as a parent chain.
- The names of all substituents are arranged by alphabets to starts with lowest numbering.
- In the complex substituent having compounds the substituent name is assigned by a name each of them based on numbers going away from the parent.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Compound (a):
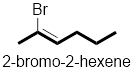
In the given compound, the longest carbon chain (highlighted with bold lines) contains six carbons and while numbering the parent chain, substituents should get the least possible number.
The presence of double bond at C-2 makes parent name as 2-hexene. The substituents Bromine atom at C-2; are arranged in alphabetical order followed by the parent name.
Therefore, the systematic name of the given compounds is ‘2-bromo-2-hexene’.
(b)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name and configuration of the given compound has to be written.
Concept Introduction:
Nomenclature of organic compounds:
The naming of the organic compound is given by IUPAC (International Union for pure and applied chemistry). In the IUPAC names consist of certain rules for giving chemical names they are,
- The longer number of Carbon chain of a compound is identified this is called parent of the compound.
- In the cyclic compounds the number of carbon involving in ring formation is called parent of the compound.
- The compound have more than one parent chains means the larger number of substitutions present in the chain is consider as a parent chain.
- The names of all substituents are arranged by alphabets to starts with lowest numbering.
- In the complex substituent having compounds the substituent name is assigned by a name each of them based on numbers going away from the parent.
R and S nomenclature:
It is used to assign the molecule using CIP rules.
The CIP rules are as follows:
- Select the chiral carbon and assign the numbers according to the decreasing
atomic mass of atoms attached to it. - If the numbering follows clockwise direction then the atom is termed as R and if it follows anti-clockwise direction then atom is termed as S.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Compound (b):
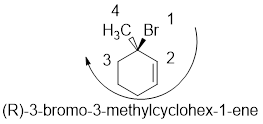
In the given compound, the longest carbon ring (highlighted with bold lines) contains six carbons and while numbering the parent chain, substituents should get the least possible number.
The presence of double bond at C-1 makes parent name is hex-1-ene. The substituents methyl located at C-3 and bromine atom at C-3; are arranged in alphabetical order followed by the parent name.
The chiral carbon and assign the numbers according to the decreasing atomic mass of atoms attached to it, follows clockwise direction then the atom is termed as R
Therefore, the systematic name of the given compounds is ‘3-bromo-3-methylcyclohex-1-ene’.
(c)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name and configuration of the given compound has to be written.
Concept Introduction:
Nomenclature of organic compounds:
The naming of the organic compound is given by IUPAC (International Union for pure and applied chemistry). In the IUPAC names consist of certain rules for giving chemical names they are,
- The longer number of Carbon chain of a compound is identified this is called parent of the compound.
- In the cyclic compounds the number of carbon involving in ring formation is called parent of the compound.
- The compound have more than one parent chains means the larger number of substitutions present in the chain is consider as a parent chain.
- The names of all substituents are arranged by alphabets to starts with lowest numbering.
- In the complex substituent having compounds the substituent name is assigned by a name each of them based on numbers going away from the parent.
In a cis isomer, groups are attached on the same side of the ring.
In a trans isomer, groups are attached on the opposite side of the ring.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
Compound (c):

In the given compound, the longest carbon ring (highlighted with bold lines) contains six carbons and while numbering the parent chain, substituents should get the least possible number.
The parent name is CYCLOHEXANE. The substituents bromine atoms are at C-1and C-4; are arranged in alphabetical order followed by the parent name. Here, bromine atoms are attached on the opposite side of the ring thus ‘trans’.
Therefore, the systematic name of the given compounds is ‘trans 1,4-dibromocyclohexane’.
(d)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of the given compound has to be written.
Concept Introduction:
Nomenclature of organic compounds:
The naming of the organic compound is given by IUPAC (International Union for pure and applied chemistry). In the IUPAC names consist of certain rules for giving chemical names they are,
- The longer number of Carbon chain of a compound is identified this is called parent of the compound.
- In the cyclic compounds the number of carbon involving in ring formation is called parent of the compound.
- The compound have more than one parent chains means the larger number of substitutions present in the chain is consider as a parent chain.
- The names of all substituents are arranged by alphabets to starts with lowest numbering.
- In the complex substituent having compounds the substituent name is assigned by a name each of them based on numbers going away from the parent.
(d)
Explanation of Solution
Compound (d):

In the given compound, the longest carbon chain (highlighted with bold lines) contains four carbons and while numbering the parent chain, substituents should get the least possible number.
The parent name is butane. The substituents chlorine atom at C-1 and C-4; are arranged in alphabetical order followed by the parent name.
Therefore, the systematic name of the given compounds is ‘1,4-dichlorobutane’.
(e)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name and configuration of the given compound has to be written.
Concept Introduction:
Nomenclature of organic compounds:
The naming of the organic compound is given by IUPAC (International Union for pure and applied chemistry). In the IUPAC names consist of certain rules for giving chemical names they are,
- The longer number of Carbon chain of a compound is identified this is called parent of the compound.
- In the cyclic compounds the number of carbon involving in ring formation is called parent of the compound.
- The compound have more than one parent chains means the larger number of substitutions present in the chain is consider as a parent chain.
- The names of all substituents are arranged by alphabets to starts with lowest numbering.
- In the complex substituent having compounds the substituent name is assigned by a name each of them based on numbers going away from the parent.
R and S nomenclature:
It is used to assign the molecule using CIP rules.
The CIP rules are as follows:
- Select the chiral carbon and assign the numbers according to the decreasing atomic mass of atoms attached to it.
- If the numbering follows clockwise direction then the atom is termed as R and if it follows anti-clockwise direction then atom is termed as S.
(e)
Explanation of Solution
Compound (e):
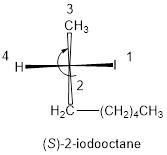
In the given compound, the longest carbon ring contains eight carbons and while numbering the parent chain, substituents should get the least possible number. The parent name is octane. The substituents iodine atom located at C-2; are arranged in alphabetical order followed by the parent name.
The numbering follows clockwise direction as shown above then it is termed as R. Least priority group is above the plane so the configuration is reversed.
Therefore, the systematic name of the given compounds is ‘(S)-2-iodooctane’.
(f)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name and configuration of the given compound has to be written.
Concept Introduction:
Nomenclature of organic compounds:
The naming of the organic compound is given by IUPAC (International Union for pure and applied chemistry). In the IUPAC names consist of certain rules for giving chemical names they are,
- The longer number of Carbon chain of a compound is identified this is called parent of the compound.
- In the cyclic compounds the number of carbon involving in ring formation is called parent of the compound.
- The compound have more than one parent chains means the larger number of substitutions present in the chain is consider as a parent chain.
- The names of all substituents are arranged by alphabets to starts with lowest numbering.
- In the complex substituent having compounds the substituent name is assigned by a name each of them based on numbers going away from the parent.
R and S nomenclature:
It is used to assign the molecule using CIP rules.
The CIP rules are as follows:
- Select the chiral carbon and assign the numbers according to the decreasing atomic mass of atoms attached to it.
- If the numbering follows clockwise direction then the atom is termed as R and if it follows anti-clockwise direction then atom is termed as S.
(f)
Explanation of Solution
Compound (f):
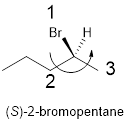
In the given compound, the longest carbon ring (highlighted with bold lines) contains five carbons and while numbering the parent chain, substituents should get the least possible number.
The parent name is hexane. The substituents bromine atom located at C-2; are arranged in alphabetical order followed by the parent name.
The chiral carbon and assign the numbers according to the decreasing atomic mass of atoms attached to it, follows anti-clockwise direction then atom is termed as S.
Therefore, the systematic name of the given compounds is ‘(S)-2-bromopentane’.
(g)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name and configuration of the given compound has to be written.
Concept Introduction:
Nomenclature of organic compounds:
The naming of the organic compound is given by IUPAC (International Union for pure and applied chemistry). In the IUPAC names consist of certain rules for giving chemical names they are,
- The longer number of Carbon chain of a compound is identified this is called parent of the compound.
- In the cyclic compounds the number of carbon involving in ring formation is called parent of the compound.
- The compound have more than one parent chains means the larger number of substitutions present in the chain is consider as a parent chain.
- The names of all substituents are arranged by alphabets to starts with lowest numbering.
- The complex substituent is built by a substituent on a substituent; so called complex substituent.
- In the complex substituent having compounds the substituent name is assigned by a name each of them based on numbers going away from the parent.
R and S nomenclature:
It is used to assign the molecule using CIP rules.
The CIP rules are as follows:
- Select the chiral carbon and assign the numbers according to the decreasing atomic mass of atoms attached to it.
- If the numbering follows clockwise direction then the atom is termed as R and if it follows anti-clockwise direction then atom is termed as S.
(g)
Explanation of Solution
Compound (g):
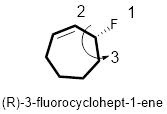
In the given compound, the longest carbon ring (highlighted with bold lines) contains seven carbons in a ring and while numbering the parent chain, substituents should get the least possible number.
The presence of double bond at C-1 on the ring makes parent name is cyclohept-1-ene. The substituents Fluorine atom located at C-3; are arranged in alphabetical order followed by the parent name.
The chiral carbon and assign the numbers according to the decreasing atomic mass of atoms attached to it, follows anti-clockwise direction then atom is termed as S. Least priority group is above the plane so the configuration is reversed. Hence, the configuration is (R).
Therefore, the systematic name of the given compounds is ‘(R)- 3-fluorocyclohept-1-ene’.
(h)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of the given compound has to be written.
Concept Introduction:
Nomenclature of organic compounds:
The naming of the organic compound is given by IUPAC (International Union for pure and applied chemistry). In the IUPAC names consist of certain rules for giving chemical names they are,
- The longer number of Carbon chain of a compound is identified this is called parent of the compound.
- In the cyclic compounds the number of carbon involving in ring formation is called parent of the compound.
- The compound have more than one parent chains means the larger number of substitutions present in the chain is consider as a parent chain.
- The names of all substituents are arranged by alphabets to starts with lowest numbering.
- The complex substituent is built by a substituent on a substituent; so called complex substituent.
- In the complex substituent having compounds the substituent name is assigned by a name each of them based on numbers going away from the parent.
(h)
Explanation of Solution
Compound (h):
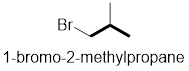
In the given compound, the longest carbon chain (highlighted with bold lines) contains three carbons and while numbering the parent chain, substituents should get the least possible number.
The parent name is Propane. The substituents methyl located at C-2 and bromine atom at C-1; are arranged in alphabetical order followed by the parent name.
Therefore, the systematic name of the given compounds is ‘1-bromo-2-methylpropane’.
(i)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC names and configuration of the given compound has to be written.
Concept Introduction:
Nomenclature of organic compounds:
The naming of the organic compound is given by IUPAC (International Union for pure and applied chemistry). In the IUPAC names consist of certain rules for giving chemical names they are,
- The longer number of Carbon chain of a compound is identified this is called parent of the compound.
- In the cyclic compounds the number of carbon involving in ring formation is called parent of the compound.
- The compound have more than one parent chains means the larger number of substitutions present in the chain is consider as a parent chain.
- The names of all substituents are arranged by alphabets to starts with lowest numbering.
- In the complex substituent having compounds the substituent name is assigned by a name each of them based on numbers going away from the parent.
(i)
Explanation of Solution
Compound (i):
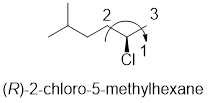
In the given compound, the longest carbon chain (highlighted with bold lines) contains six carbons and while numbering the parent chain, substituents should get the least possible number.
The parent name is hexane. The substituents methyl located at C-5 and chlorine atom at C-2; are arranged in alphabetical order followed by the parent name.
The chiral carbon and assign the numbers according to the decreasing atomic mass of atoms attached to it, follows clockwise direction then the atom is termed as R.
Therefore, the systematic name of the given compounds is ‘(R)-2-chloro-5-methylhexane’.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-OWL V2 ACCESS
- What is the reaction mechanism for this?arrow_forwardCurved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s). Be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond-making steps. + Drawing Arrows CH3ONA, CH3OH heat : Br:O Na → H H Br Na + H H H H H :0: .H + Undo Reset Done Q CH3 Drag To Pan +arrow_forwardWhat is the reaction mechanism for this?arrow_forward
- 20.19 Predict the structure of the major 1,2-addition product formed by reaction of one mole of Cl₂ with 3-methylenecyclohexene. Also predict the structure of the 1,4-addition product formed under these conditions. 20.20 Which of the two molecules shown do you expect to be the major product formed by 1,2-addition of HCI to cyclopentadiene? Explain. Cyclopentadiene + HC 3-Chlorocyclopentene (racemic) or 4-Chlorocyclopentene (racemic)arrow_forward20.35 Propose structural formulas for compounds A and B and specify the configuration of compound B. EtO₂C 250°C C14H2004 CO₂Et 1. Oso, then NaHSO3 2. HIO4 C14H2006 A Barrow_forward20.21 Predict the major product formed by 1,4-addition of HCI to cyclopentadiene. 20.22 Draw structural formulas for the two constitutional isomers with the molecular for- mula C₂H,Br, formed by adding one mole of Br, to cyclopentadiene.arrow_forward
- Add substituents to draw the conformer below (sighting down the indicated bond), then rotate the back carbon to provide the conformation that will be capable of an E2 elimination. R/S stereochemistry is graded. + I I H CH3 Ph Досн Br OCH 3 Drawing Q H Atoms, Bonds and Rings Charges Tap a node to see suggestions. H H H H H Undo Reset Remove Done Rotatearrow_forward20.17 Predict the structure of the major product formed by 1,2-addition of HBr to 3-methylenecyclohexene. 3-Methylenecyclohexene 20.18 Predict the major product formed by 1,4-addition of HBr to 3-methylenecyclohexene.arrow_forward+ Draw a vicinal alkyl bromide that would produce the following alkene in an E2 elimination. Use a dash or wedge bond to indicate stereochemistry on asymmetric centers, where applicable. Ignore any inorganic byproducts. Br Drawing Strong Base H Q Atoms, Bonds Charges and Rings Draw or tap a new bond to see suggestions. Remove Done 語 Reset Undo + Drag To Panarrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
