
Concept explainers
(a)
To determine: The lewis structure for
(a)
Answer to Problem 8.88QP
Solution
The lewis structure for
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
Number of valence electrons in hydrogen is
Carbon is bonded to three hydrogen atoms and nitrogen atom by single bond. With one oxygen, nitrogen is bonded by single bond while with other oxygen, it is bonded by double bond. Lone pairs of electrons present on oxygen atoms are delocalized which results in the formation of another lewis structure. Hence the lewis structure of
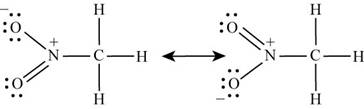
Figure 1
(b)
To determine: The lewis structure for.
(b)
Answer to Problem 8.88QP
Solution
The lewis structures for.
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
The two given possible skeletal for
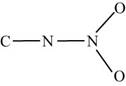
Figure 2
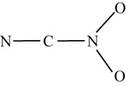
Figure 3
In the first skeletal, the nitrogen of
Number of valence electrons in carbon is
With one oxygen atom, nitrogen is bonded by single bond while with other oxygen; it is bonded by double bond. Lone pairs of electrons present on oxygen atoms are delocalized which results in the formation of another lewis structure. Hence the lewis structure of
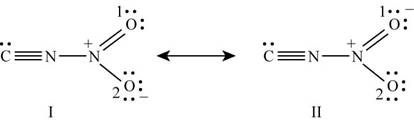
Figure 4
The formal charge on each atom of resonating structure (I) of
Formal charge is calculated as,
Number of valence electrons in first nitrogen is
Number of lone pair electrons in first nitrogen is
Number of bond pair electrons in first nitrogen is
To calculate the formal charge on first nitrogen, substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair electrons and bond pair electrons in the equation (1).
Number of valence electrons in carbon is
Number of lone pair electrons in carbon is
Number of bond pair electrons in carbon is
To calculate the formal charge on carbon, substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair electrons and bond pair electrons in the equation (1).
Number of valence electrons in second nitrogen is
Number of lone pair electrons in second nitrogen is
Number of bond pair electrons in second nitrogen is
To calculate the formal charge on second nitrogen, substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair electrons and bond pair electrons in the equation (1).
Number of valence electrons in oxygen (1) is
Number of lone pair electrons in oxygen (1) is
Number of bond pair electrons in oxygen (1) is
To calculate the formal charge on oxygen (1), substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair electrons and bond pair electrons in the equation (1).
Number of valence electrons in oxygen (2) is
Number of lone pair electrons in oxygen (2) is
Number of bond pair electrons in oxygen (2) is
To calculate the formal charge on oxygen (2), substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair electrons and bond pair electrons in the equation (1).
The formal charge on each atom of resonating structure (II) of
Number of valence electrons in first nitrogen is
Number of lone pair electrons in first nitrogen is
Number of bond pair electrons in first nitrogen is
To calculate the formal charge on first nitrogen, substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair electrons and bond pair electrons in the equation (1).
Number of valence electrons in carbon is
Number of lone pair electrons in carbon is
Number of bond pair electrons in carbon is
To calculate the formal charge on carbon, substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair electrons and bond pair electrons in the equation (1).
Number of valence electrons in second nitrogen is
Number of lone pair electrons in second nitrogen is
Number of bond pair electrons in second nitrogen is
To calculate the formal charge on second nitrogen, substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair electrons and bond pair electrons in the equation (1).
Number of valence electrons in oxygen (1) is
Number of lone pair electrons in oxygen (1) is
Number of bond pair electrons in oxygen (1) is
To calculate the formal charge on oxygen (1), substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair electrons and bond pair electrons in the equation (1).
Number of valence electrons in oxygen (2) is
Number of lone pair electrons in oxygen (2) is
Number of bond pair electrons in oxygen (2) is
To calculate the formal charge on oxygen (2), substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair electrons and bond pair electrons in the equation (1).
Number of valence electrons in carbon is
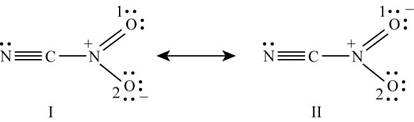
Figure 5
The formal charge on each atom of resonating structure (I) of
Number of valence electrons in first nitrogen is
Number of lone pair electrons in first nitrogen is
Number of bond pair electrons in first nitrogen is
To calculate the formal charge on first nitrogen, substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair electrons and bond pair electrons in the equation (1).
Number of valence electrons in carbon is
Number of lone pair electrons in carbon is
Number of bond pair electrons in carbon is
To calculate the formal charge on carbon, substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair electrons and bond pair electrons in the equation (1).
Number of valence electrons in second nitrogen is
Number of lone pair electrons in second nitrogen is
Number of bond pair electrons in second nitrogen is
To calculate the formal charge on second nitrogen, substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair electrons and bond pair electrons in the equation (1).
Number of valence electrons in oxygen (1) is
Number of lone pair electrons in oxygen (1) is
Number of bond pair electrons in oxygen (1) is
To calculate the formal charge on oxygen (1), substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair electrons and bond pair electrons in the equation (1).
Number of valence electrons in oxygen (2) is
Number of lone pair electrons in oxygen (2) is
Number of bond pair electrons in oxygen (2) is
To calculate the formal charge on oxygen (2), substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair electrons and bond pair electrons in the equation (1).
The formal charge on each atom of resonating structure (II) of
Number of valence electrons in first nitrogen is
Number of lone pair electrons in first nitrogen is
Number of bond pair electrons in first nitrogen is
To calculate the formal charge on first nitrogen, substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair electrons and bond pair electrons in the equation (1).
Number of valence electrons in carbon is
Number of lone pair electrons in carbon is
Number of bond pair electrons in carbon is
To calculate the formal charge on carbon, substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair electrons and bond pair electrons in the equation (1).
Number of valence electrons in second nitrogen is
Number of lone pair electrons in second nitrogen is
Number of bond pair electrons in second nitrogen is
To calculate the formal charge on second nitrogen, substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair electrons and bond pair electrons in the equation (1).
Number of valence electrons in oxygen (1) is
Number of lone pair electrons in oxygen (1) is
Number of bond pair electrons in oxygen (1) is
To calculate the formal charge on oxygen (1), substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair electrons and bond pair electrons in the equation (1).
Number of valence electrons in oxygen (2) is
Number of lone pair electrons in oxygen (2) is
Number of bond pair electrons in oxygen (2) is
To calculate the formal charge on oxygen (2), substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair electrons and bond pair electrons in the equation (1).
The resonating structure which possesses zero or minimum formal charge is preferred. The distribution of formal charges on both the molecules
(c)
To determine: Whether the given two structures of
(c)
Answer to Problem 8.88QP
Solution
The two structures of
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
In the resonating forms, the postion of atoms remains same. But in the two structures of
Conclusion
The two structures of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
EBK CHEMISTRY: THE SCIENCE IN CONTEXT,
- Draw the titration curve of (i) weak acid vs. strong base; (ii) weak acid vs. weakbase; (iii) diprotic acid with strong base (iii) triprotic acid with strong base.arrow_forwardComplete the reaction in the drawing area below by adding the major products to the right-hand side. If there won't be any products, because nothing will happen under these reaction conditions, check the box under the drawing area instead. Note: if the products contain one or more pairs of enantiomers, don't worry about drawing each enantiomer with dash and wedge bonds. Just draw one molecule to represent each pair of enantiomers, using line bonds at the chiral center. More... No reaction. my ㄖˋ + 1. Na O Me Click and drag to start drawing a structure. 2. H +arrow_forwardPredict the intermediate 1 and final product 2 of this organic reaction: NaOMe H+ + 1 2 H H work up You can draw 1 and 2 in any arrangement you like. Note: if either 1 or 2 consists of a pair of enantiomers, just draw one structure using line bonds instead of 3D (dash and wedge) bonds at the chiral center. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. X $ dmarrow_forward
- Predict the major products of this organic reaction: 1. NaH (20°C) 2. CH3Br ? Some notes: • Draw only the major product, or products. You can draw them in any arrangement you like. • Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds where necessary, for example to distinguish between major products that are enantiomers. • If there are no products, just check the box under the drawing area. No reaction. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. G Crarrow_forwardPredict the major products of this organic reaction: 1. LDA (-78°C) ? 2. Br Some notes: • Draw only the major product, or products. You can draw them in any arrangement you like. . • Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds where necessary, for example to distinguish between major products that are enantiomers. • If there are no products, just check the box under the drawing area. No reaction. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Xarrow_forwardPlease draw the structuresarrow_forward
- Draw the missing intermediates 1 and 2, plus the final product 3, of this synthesis: 0 1. Eto 1. Eto- 1 2 2. MeBr 2. EtBr H3O+ A 3 You can draw the three structures in any arrangement you like. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forwardDraw the missing intermediate 1 and final product 2 of this synthesis: 1. MeO- H3O+ 1 2 2. PrBr Δ You can draw the two structures in any arrangement you like. Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forwardWhat is the differences between: Glyceride and phosphoglyceride Wax and Fat Soap and Fatty acid HDL and LDL cholesterol Phospho lipids and sphingosine What are the types of lipids? What are the main lipid components of membrane structures? How could lipids play important rules as signaling molecules and building units? The structure variety of lipids makes them to play significant rules in our body, conclude breifly on this statement.arrow_forward
- What is the differences between DNA and RNA for the following: - structure - function - type What is the meaning of: - replication - transcription - translation show the base pair connection(hydrogen bond) in DNA and RNAarrow_forwardWhat is the IP for a amino acid- give an example what are the types of amino acids What are the structures of proteins The N-Terminal analysis by the Edman method shows saralasin contains sarcosine at the N-terminus. Partial hydrolysis of saralasin with dilute hydrochloric acid yields the following fragments: Try-Val-His Sar-Arg-Val His-Pro-Ala Val- Tyr- Val Arg-Val-Tyr What is the structure of saralasin?arrow_forwardWhat is the IP for a amino acid- give an example what are the types of amino acids What are the structures of proteins The N-Terminal analysis by the Edman method shows saralasin contains sarcosine at the N-terminus. Partial hydrolysis of saralasin with dilute hydrochloric acid yields the following fragments: Try-Val-His Sar-Arg-Val His-Pro-Ala Val- Tyr- Val Arg-Val-Tyr What is the structure of saralasin?arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





