
Concept explainers
(a)
To determine: The lewis structure for
(a)
Answer to Problem 8.88QP
Solution
The lewis structure for
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
Number of valence electrons in hydrogen is
Carbon is bonded to three hydrogen atoms and nitrogen atom by single bond. With one oxygen, nitrogen is bonded by single bond while with other oxygen, it is bonded by double bond. Lone pairs of electrons present on oxygen atoms are delocalized which results in the formation of another lewis structure. Hence the lewis structure of
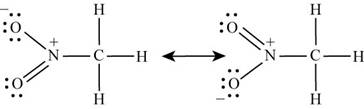
Figure 1
(b)
To determine: The lewis structure for.
(b)
Answer to Problem 8.88QP
Solution
The lewis structures for.
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
The two given possible skeletal for
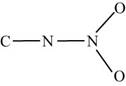
Figure 2
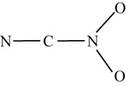
Figure 3
In the first skeletal, the nitrogen of
Number of valence electrons in carbon is
With one oxygen atom, nitrogen is bonded by single bond while with other oxygen; it is bonded by double bond. Lone pairs of electrons present on oxygen atoms are delocalized which results in the formation of another lewis structure. Hence the lewis structure of
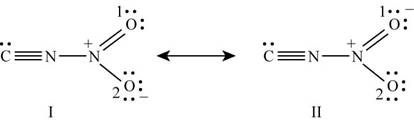
Figure 4
The formal charge on each atom of resonating structure (I) of
Formal charge is calculated as,
Number of valence electrons in first nitrogen is
Number of lone pair electrons in first nitrogen is
Number of bond pair electrons in first nitrogen is
To calculate the formal charge on first nitrogen, substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair electrons and bond pair electrons in the equation (1).
Number of valence electrons in carbon is
Number of lone pair electrons in carbon is
Number of bond pair electrons in carbon is
To calculate the formal charge on carbon, substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair electrons and bond pair electrons in the equation (1).
Number of valence electrons in second nitrogen is
Number of lone pair electrons in second nitrogen is
Number of bond pair electrons in second nitrogen is
To calculate the formal charge on second nitrogen, substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair electrons and bond pair electrons in the equation (1).
Number of valence electrons in oxygen (1) is
Number of lone pair electrons in oxygen (1) is
Number of bond pair electrons in oxygen (1) is
To calculate the formal charge on oxygen (1), substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair electrons and bond pair electrons in the equation (1).
Number of valence electrons in oxygen (2) is
Number of lone pair electrons in oxygen (2) is
Number of bond pair electrons in oxygen (2) is
To calculate the formal charge on oxygen (2), substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair electrons and bond pair electrons in the equation (1).
The formal charge on each atom of resonating structure (II) of
Number of valence electrons in first nitrogen is
Number of lone pair electrons in first nitrogen is
Number of bond pair electrons in first nitrogen is
To calculate the formal charge on first nitrogen, substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair electrons and bond pair electrons in the equation (1).
Number of valence electrons in carbon is
Number of lone pair electrons in carbon is
Number of bond pair electrons in carbon is
To calculate the formal charge on carbon, substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair electrons and bond pair electrons in the equation (1).
Number of valence electrons in second nitrogen is
Number of lone pair electrons in second nitrogen is
Number of bond pair electrons in second nitrogen is
To calculate the formal charge on second nitrogen, substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair electrons and bond pair electrons in the equation (1).
Number of valence electrons in oxygen (1) is
Number of lone pair electrons in oxygen (1) is
Number of bond pair electrons in oxygen (1) is
To calculate the formal charge on oxygen (1), substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair electrons and bond pair electrons in the equation (1).
Number of valence electrons in oxygen (2) is
Number of lone pair electrons in oxygen (2) is
Number of bond pair electrons in oxygen (2) is
To calculate the formal charge on oxygen (2), substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair electrons and bond pair electrons in the equation (1).
Number of valence electrons in carbon is
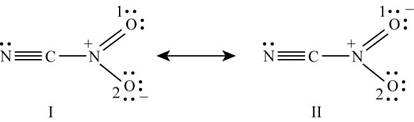
Figure 5
The formal charge on each atom of resonating structure (I) of
Number of valence electrons in first nitrogen is
Number of lone pair electrons in first nitrogen is
Number of bond pair electrons in first nitrogen is
To calculate the formal charge on first nitrogen, substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair electrons and bond pair electrons in the equation (1).
Number of valence electrons in carbon is
Number of lone pair electrons in carbon is
Number of bond pair electrons in carbon is
To calculate the formal charge on carbon, substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair electrons and bond pair electrons in the equation (1).
Number of valence electrons in second nitrogen is
Number of lone pair electrons in second nitrogen is
Number of bond pair electrons in second nitrogen is
To calculate the formal charge on second nitrogen, substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair electrons and bond pair electrons in the equation (1).
Number of valence electrons in oxygen (1) is
Number of lone pair electrons in oxygen (1) is
Number of bond pair electrons in oxygen (1) is
To calculate the formal charge on oxygen (1), substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair electrons and bond pair electrons in the equation (1).
Number of valence electrons in oxygen (2) is
Number of lone pair electrons in oxygen (2) is
Number of bond pair electrons in oxygen (2) is
To calculate the formal charge on oxygen (2), substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair electrons and bond pair electrons in the equation (1).
The formal charge on each atom of resonating structure (II) of
Number of valence electrons in first nitrogen is
Number of lone pair electrons in first nitrogen is
Number of bond pair electrons in first nitrogen is
To calculate the formal charge on first nitrogen, substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair electrons and bond pair electrons in the equation (1).
Number of valence electrons in carbon is
Number of lone pair electrons in carbon is
Number of bond pair electrons in carbon is
To calculate the formal charge on carbon, substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair electrons and bond pair electrons in the equation (1).
Number of valence electrons in second nitrogen is
Number of lone pair electrons in second nitrogen is
Number of bond pair electrons in second nitrogen is
To calculate the formal charge on second nitrogen, substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair electrons and bond pair electrons in the equation (1).
Number of valence electrons in oxygen (1) is
Number of lone pair electrons in oxygen (1) is
Number of bond pair electrons in oxygen (1) is
To calculate the formal charge on oxygen (1), substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair electrons and bond pair electrons in the equation (1).
Number of valence electrons in oxygen (2) is
Number of lone pair electrons in oxygen (2) is
Number of bond pair electrons in oxygen (2) is
To calculate the formal charge on oxygen (2), substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair electrons and bond pair electrons in the equation (1).
The resonating structure which possesses zero or minimum formal charge is preferred. The distribution of formal charges on both the molecules
(c)
To determine: Whether the given two structures of
(c)
Answer to Problem 8.88QP
Solution
The two structures of
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
In the resonating forms, the postion of atoms remains same. But in the two structures of
Conclusion
The two structures of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
CHEMISTRY:SCI.IN CONTEXT (CL)-PACKAGE
- Li+ is a hard acid. With this in mind, which if the following compounds should be most soluble in water? Group of answer choices LiBr LiI LiF LiClarrow_forwardQ4: Write organic product(s) of the following reactions and show the curved-arrow mechanism of the reactions. Br MeOH OSO2CH3 MeOHarrow_forwardProvide the correct IUPAC name for the compound shown here. Reset cis- 5- trans- ☑ 4-6- 2- 1- 3- di iso tert- tri cyclo sec- oct but hept prop hex pent yl yne ene anearrow_forward
- Q6: Predict the major product(s) for the following reactions. Note the mechanism (SN1, SN2, E1 or E2) the reaction proceeds through. If no reaction takes place, indicate why. Pay attention to stereochemistry. NaCN DMF Br σ Ilm... Br H Br H H NaCN CH3OH KOtBu tBuOH NaBr H₂O LDA Et2O (CH3)2CHOH KCN DMSO NaOH H₂O, A LDA LDA Systemarrow_forwardQ7: For the following reactions, indicate the reaction conditions that would provide the indicated product in a high yield. Note the major reaction pathway that would take place (SN1, SN2, E1, or E2) Note: There may be other products that are not shown. There maybe more than one plausible pathway. Br H3C OH H3C CI ... H3C SCH2CH3 CI i SCH2CH3 ཨ་ Br System Settarrow_forwardQ2: Rank the compounds in each of the following groups in order of decreasing rate of solvolysis in aqueous acetone. OSO2CF3 OSO2CH3 OH a. b. CI Brarrow_forward
- ох 4-tert-butyl oxy cyclohex-1-ene Incorrect, 1 attempt remaining The systematic name of this compound classifies the -OR group as a substituent of the hydrocarbon, which is considered the principal functional group. The ether substituent is named with the suffix 'oxy'. The general format for the systematic name of a hydrocarbon is: [prefix/substituent] + [parent] + [functional group suffix] Substituents are listed in alphabetical order. Molecules with a chiral center will indicate the absolute configuration at the beginning of its name with the R and S notation.arrow_forward5. Compressibility (6 points total). The isothermal compressibility is a measure of how hard/easy it is to compress an object (how squishy is it?) at constant temperature. It is др defined as Br=-()=-(200²)T' (a) You might wonder why there is a negative sign in this formula. What does it mean when this quantity is positive and what does it mean when this quantity is negative? (b) Derive the formula for the isothermal compressibility of an ideal gas (it is very simple!) (c) Explain under what conditions for the ideal gas the compressibility is higher or lower, and why that makes sense.arrow_forward19. (3 pts) in Chapter 7 we will see a reaction of halocyclohexanes that requires that the halogen occupy an axial position with this in mind, would you expect cis-1-bromo-3-methylcyclohexane or trans-1-bromo-3-methylcyclohexane to be more reactive in this reaction? Briefly explain your choice using structures to support your answer. Mere-eries-cecleone) The tran-i-browse-3-methylcyclohexionearrow_forward
- Please help me calculate the undiluted samples ppm concentration. My calculations were 280.11 ppm. Please see if I did my math correctly using the following standard curve. Link: https://mnscu-my.sharepoint.com/:x:/g/personal/vi2163ss_go_minnstate_edu/EVSJL_W0qrxMkUjK2J3xMUEBHDu0UM1vPKQ-bc9HTcYXDQ?e=hVuPC4arrow_forwardProvide an IUPAC name for each of the compounds shown. (Specify (E)/(Z) stereochemistry, if relevant, for straight chain alkenes only. Pay attention to commas, dashes, etc.) H₁₂C C(CH3)3 C=C H3C CH3 CH3CH2CH CI CH3 Submit Answer Retry Entire Group 2 more group attempts remaining Previous Nextarrow_forwardArrange the following compounds / ions in increasing nucleophilicity (least to most nucleophilic) CH3NH2 CH3C=C: CH3COO 1 2 3 5 Multiple Choice 1 point 1, 2, 3 2, 1, 3 3, 1, 2 2, 3, 1 The other answers are not correct 0000arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





