
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: Statics, 4th Edition
4th Edition
ISBN: 9781305501607
Author: Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher: CENGAGE L
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 8, Problem 8.83P
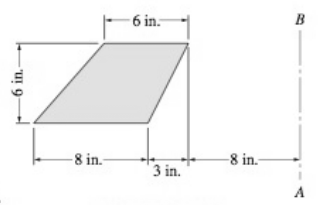
A solid is generated by rotating the plane area about the axis AB. Compute the volume of the solid.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
One thousand kg/h of a (50-50 wt%) acetone-in-water solution is to be extracted at 25C in a continuous,
countercurrent system with pure 1,1,2-trichloroethane to obtain a raffinate containing 10 wt% acetone. Using the
following equilibrium data, determine with an equilateral-triangle diagram:
a- the minimum flow rate of solvent;
b- the number of stages required for a solvent rate equal to 1.5 times minimum, and composition of each
streamleaving each stage.
c- Repeat the calculation of (a) and (b) if the solvent used has purity 93wt% (4wr% acetone, 3wt% water
impurities)
acetone water
1,1,2-trichloroethane
Raffinate. Weight
Extract. Weight
0.6
0.13
0.27
Fraction Acetone
Fraction Acetone
0.5
0.04
0.46
0.44
0.56
0.4
0.03
0.57
0.29
0.40
0.3
0.02
0.68
0.12
0.18
0.2
0.015
0.785
0.0
0.0
0.1
0.01
0.89
0.55
0.35
0.1
0.5
0.43
0.07
0.4
0.57
0.03
0.3
0.68
0.02
0.2
0.79
0.01
0.1
0.895
0.005
2500 kg/hr of (20-80) nicotine water solution is to be extracted with benzene containing 0.5% nicotine in
the 1st and 2ed stages while the 3rd stage is free of nicotine. Cross- current operation is used with different amounts
of solvent for each stages 2000kg/hr in the 1st stage, 2300 kg/hr in the 2nd stage, 2600 kg/hr in the 3rd,
determine: -
a- The final raffinate concentration and % extraction.
b-
b- The minimum amount of solvent required for counter-current operation if the minimum concentration
will be reduced to 5% in the outlet raffinate.
Equilibrium data
Wt % Nicotine in water
Wt % Nicotine in benzene
0
4
16
25
0
4
21
30
Quiz/An eccentrically loaded bracket is welded to the support as shown in Figure below. The load is static. The weld size
for weld w1 is h1=6mm, for w2 h2 5mm, and for w3 is h3 -5.5 mm. Determine the safety factor (S.f) for the welds.
F=22 kN. Use an AWS Electrode type (E90xx).
140
101.15
REDMI NOTE 8 PRO
AI QUAD CAMERA
F
Chapter 8 Solutions
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: Statics, 4th Edition
Ch. 8 - Use integration to determine the coordinates of...Ch. 8 - Use integration to determine the coordinates of...Ch. 8 - Use integration to determine the coordinates of...Ch. 8 - Use integration to determine the coordinates of...Ch. 8 - Use integration to determine the coordinates of...Ch. 8 - Use integration to determine the coordinates of...Ch. 8 - Using integration, locate the centroid of the area...Ch. 8 - Determine the y-coordinate of the centroid of the...Ch. 8 - Determine the y-coordinate 0f the centroid of the...Ch. 8 - Use integration to locate the centroid of the...
Ch. 8 - Locate the centroid of the parabola by...Ch. 8 - Use integration to locate the centroid of the...Ch. 8 - The parametric equations of the plane curve known...Ch. 8 - Use the method of composite areas to calculate the...Ch. 8 - Use the method of composite areas to calculate the...Ch. 8 - Use the method of composite areas to calculate the...Ch. 8 - Use the method of composite areas to calculate the...Ch. 8 - Use the method of composite areas to calculate the...Ch. 8 - Use the method of composite areas to calculate the...Ch. 8 - Use the method of composite areas to calculate the...Ch. 8 - Use the method of composite areas to calculate the...Ch. 8 - The plane region is bounded by a semicircle of...Ch. 8 - The centroid of the plane region shown is at C....Ch. 8 - Compute the centroidal coordinates of the L-shaped...Ch. 8 - Find the centroidal coordinates of the plane...Ch. 8 - Using the method of composite areas, find the...Ch. 8 - Given that the centroid of the plane region is at...Ch. 8 - Using the method of composite curves, locate the...Ch. 8 - Using the method of composite curves, locate the...Ch. 8 - Using the method of composite curves, locate the...Ch. 8 - Using the method of composite curves, locate the...Ch. 8 - Using the method of composite curves, locate the...Ch. 8 - Using the method of composite curves, locate the...Ch. 8 - Determine the ratio a/b for which the centroid of...Ch. 8 - Use numerical integration to locate the centroid...Ch. 8 - Determine the centroidal coordinates of the plane...Ch. 8 - Compute the centroidal y-coordinate of the plane...Ch. 8 - The equation of the catenary shown is y = 100 cosh...Ch. 8 - Use integration to locate the centroid of the...Ch. 8 - By integration, find the centroid of the surface...Ch. 8 - Locate the centroid of the volume obtained by...Ch. 8 - Solve Prob. 8.41 assuming that the triangle is...Ch. 8 - Use integration to find the centroidal coordinates...Ch. 8 - Solve Prob. 8.43 assuming that the area is...Ch. 8 - Verify the centroidal z-coordinate of the pyramid...Ch. 8 - Use integration to compute the z-coordinate of the...Ch. 8 - Determine the centroidal z-coordinate of the...Ch. 8 - Prob. 8.48PCh. 8 - Locate the centroid of the volume between the...Ch. 8 - Prob. 8.50PCh. 8 - Prob. 8.51PCh. 8 - By the method of composite volumes, determine the...Ch. 8 - By the method of composite volumes, determine the...Ch. 8 - By the method of composite volumes, determine the...Ch. 8 - By the method of composite volumes, determine the...Ch. 8 - By the method of composite volumes, determine the...Ch. 8 - By the method of composite volumes, determine the...Ch. 8 - Use the method of composite volumes to determine...Ch. 8 - The cylindrical container will have maximum...Ch. 8 - Using the method of composite surfaces, locate the...Ch. 8 - Using the method of composite surfaces, locate the...Ch. 8 - Using the method of composite surfaces, locate the...Ch. 8 - Using the method of composite surfaces, locate the...Ch. 8 - Using the method of composite surfaces, locate the...Ch. 8 - Using the method of composite surfaces, locate the...Ch. 8 - The picture board and its triangular supporting...Ch. 8 - By the method of composite curves, locate the...Ch. 8 - By the method of composite curves, locate the...Ch. 8 - By the method of composite curves, locate the...Ch. 8 - Use numerical integration to find the centroid of...Ch. 8 - Prob. 8.71PCh. 8 - Locate the centroid of the volume generated by...Ch. 8 - Prob. 8.73PCh. 8 - Prob. 8.74PCh. 8 - Prob. 8.75PCh. 8 - A 6-in. diameter hole is drilled in the conical...Ch. 8 - A torus is formed by rotating the circle about the...Ch. 8 - A solid of revolution is formed by rotating the...Ch. 8 - Compute the volume of the spherical cap that is...Ch. 8 - Calculate the surface area of the truncated sphere...Ch. 8 - The rim of a steel V-belt pulley is formed by...Ch. 8 - Determine the volume of the machine part shown.Ch. 8 - A solid is generated by rotating the plane area...Ch. 8 - Prob. 8.84PCh. 8 - Find the surface area of the 90 duct elbow.Ch. 8 - Determine the volume of the concrete arch dam.Ch. 8 - (a) Find the volume of liquid contained in the...Ch. 8 - Compute the surface area of the axi-symmetric...Ch. 8 - The steel cylinder with a cylindrical hole is...Ch. 8 - The hemispherical glass bowl is filled with water....Ch. 8 - What is the ratio L/R for which the uniform wire...Ch. 8 - Small screws are used to fasten a piece of...Ch. 8 - Prob. 8.93PCh. 8 - 3.94 The aluminum cylinder is attached to the...Ch. 8 - Prob. 8.95PCh. 8 - Prob. 8.96PCh. 8 - Prob. 8.97PCh. 8 - Locate the center of gravity of the hammer if the...Ch. 8 - Prob. 8.99PCh. 8 - The cylindrical water tank with R = 10 ft and H =...Ch. 8 - Prob. 8.101PCh. 8 - Five 34-in. diameter holes are to be drilled in a...Ch. 8 - Wind pressure acting on a cylinder can be...Ch. 8 - Prob. 8.104PCh. 8 - The pressure acting on the square plate varies as...Ch. 8 - Prob. 8.106PCh. 8 - Prob. 8.107PCh. 8 - If the intensity of the line loading is...Ch. 8 - Prob. 8.109PCh. 8 - The intensity of the line loading acting on a...Ch. 8 - Determine the resultant force or resultant couple...Ch. 8 - The inside surface of each thin shell carries a...Ch. 8 - Calculate the resultant force caused by the water...Ch. 8 - Determine the resultant force acting on the elbow...Ch. 8 - Determine the smallest distance I) that would...Ch. 8 - Each of the three gates has a constant width 1:...Ch. 8 - The concrete dam shown in cross section holds back...Ch. 8 - A concrete seawater dam is shown in cross section....Ch. 8 - Determine the force F required to pull up the...Ch. 8 - The normal pressure acting on the triangular plate...Ch. 8 - One side of the container has a 03-m square door...Ch. 8 - The 12-ft wide quarter-circular gate AB is hinged...Ch. 8 - The center of gravity of the plane wire figure is...Ch. 8 - The 10-m wide gate restrains water at a depth of 6...Ch. 8 - Find the resultant of the line load shown.Ch. 8 - Prob. 8.126RPCh. 8 - Determine the centroidal coordinates of the volume...Ch. 8 - Prob. 8.128RPCh. 8 - Prob. 8.129RPCh. 8 - Prob. 8.130RPCh. 8 - Using the method of composite areas, find the...Ch. 8 - Find the centroid of the truncated parabolic...Ch. 8 - Prob. 8.133RPCh. 8 - A solid of revolution is formed by rotating the...Ch. 8 - Two hemispherical shells of inner diameter 1 m are...Ch. 8 - Calculate the area of the surface generated when...Ch. 8 - Determine the resultant of the line loading, given...Ch. 8 - Determine the centroidal coordinates of the plane...Ch. 8 - The sheet metal trough has a uniform wall...Ch. 8 - The trough is filled with water (=62.4lb/ft3)....Ch. 8 - The thin-walled cylindrical can with a spherical...Ch. 8 - Find the location of the centroid of the shaded...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- (read image)arrow_forwardProblem 3.30 A piston-cylinder device contains 0.85 kg of refrigerant- 134a at -10°C. The piston that is free to move has a mass of 12 kg and a diameter of 25 cm. The local atmospheric pressure is 100 kPa. Now, heat is transferred to refrigerant-134a until the temperature is 15°C. Determine (a) the final pressure, (b) the change in the volume of the refrigerant, and (c) the change in the enthalpy of the refrigerant-134a. please show Al work step by steparrow_forwardPart 1 The storage tank contains lubricating oil of specific gravity 0.86 In one inclined side of the tank, there is a 0.48 m diameter circular inspection door, mounted on a horizontal shaft along the centre line of the gate. The oil level in the tank rests 8.8 m above the mounted shaft. (Please refer table 01 for relevant SG, D and h values). Describe the hydrostatic force and centre of pressure with the aid of a free body diagram of the inspection door. Calculate the magnitude of the hydrostatic force and locate the centre of pressure. 45° Estimate the moment that would have to be applied to the shaft to open the gate. Stop B If the oil level raised by 2 m from the current level, calculate the new moment required to open the gate. Figure 01arrow_forward
- From thermodynamics please fill in the table show all work step by steparrow_forwardThe 150-lb skater passes point A with a speed of 6 ft/s. (Figure 1) Determine his speed when he reaches point B. Neglect friction. Determine the normal force exerted on him by the track at this point. 25 ft B = 4x A 20 ft xarrow_forwardA virtual experiment is designed to determine the effect of friction on the timing and speed of packages being delivered to a conveyor belt and the normal force applied to the tube. A package is held and then let go at the edge of a circular shaped tube of radius R = 5m. The particle at the bottom will transfer to the conveyor belt, as shown below. Run the simulations for μ = 0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6 and determine the time and speed at which the package is delivered to the conveyor belt. In addition, determine the maximum normal force and its location along the path as measured by angle 0. Submit in hardcopy form: (0) Free Body Diagram, equations underneath, derivations (a) Your MATLAB mfile (b) A table listing the values in 5 columns: μ, T (time of transfer), V (speed of transfer), 0 (angle of max N), Nmax (max N) (c) Based on your results, explain in one sentence what you think will happen to the package if the friction is increased even further, e.g. μ = 0.8. NOTE: The ODE is…arrow_forward
- Patm = 1 bar Piston m = 50 kg 5 g of Air T₁ = 600 K P₁ = 3 bar Stops A 9.75 x 10-3 m² FIGURE P3.88arrow_forwardAssume a Space Launch System (Figure 1(a)) that is approximated as a cantilever undamped single degree of freedom (SDOF) system with a mass at its free end (Figure 1(b)). The cantilever is assumed to be massless. Assume a wind load that is approximated with a concentrated harmonic forcing function p(t) = posin(ωt) acting on the mass. The known properties of the SDOF and the applied forcing function are given below. • Mass of SDOF: m =120 kip/g • Acceleration of gravity: g = 386 in/sec2 • Bending sectional stiffness of SDOF: EI = 1015 lbf×in2 • Height of SDOF: h = 2000 inches • Amplitude of forcing function: po = 6 kip • Forcing frequency: f = 8 Harrow_forwardAssume a Space Launch System (Figure 1(a)) that is approximated as a cantilever undamped single degree of freedom (SDOF) system with a mass at its free end (Figure 1(b)). The cantilever is assumed to be massless. Assume a wind load that is approximated with a concentrated harmonic forcing function p(t) = posin(ωt) acting on the mass. The known properties of the SDOF and the applied forcing function are given below. • Mass of SDOF: m =120 kip/g • Acceleration of gravity: g = 386 in/sec2 • Bending sectional stiffness of SDOF: EI = 1015 lbf×in2 • Height of SDOF: h = 2000 inches • Amplitude of forcing function: po = 6 kip • Forcing frequency: f = 8 Hz Figure 1: Single-degree-of-freedom system in Problem 1. Please compute the following considering the steady-state response of the SDOF system. Do not consider the transient response unless it is explicitly stated in the question. (a) The natural circular frequency and the natural period of the SDOF. (10 points) (b) The maximum displacement of…arrow_forward
- Assume a Space Launch System (Figure 1(a)) that is approximated as a cantilever undamped single degree of freedom (SDOF) system with a mass at its free end (Figure 1(b)). The cantilever is assumed to be massless. Assume a wind load that is approximated with a concentrated harmonic forcing function p(t) = posin(ωt) acting on the mass. The known properties of the SDOF and the applied forcing function are given below. • Mass of SDOF: m =120 kip/g • Acceleration of gravity: g = 386 in/sec2 • Bending sectional stiffness of SDOF: EI = 1015 lbf×in2 • Height of SDOF: h = 2000 inches • Amplitude of forcing function: po = 6 kip • Forcing frequency: f = 8 Hz Figure 1: Single-degree-of-freedom system in Problem 1. Please compute the following considering the steady-state response of the SDOF system. Do not consider the transient response unless it is explicitly stated in the question. (a) The natural circular frequency and the natural period of the SDOF. (10 points) (b) The maximum displacement of…arrow_forwardPlease solve 13 * √(2675.16)² + (63.72 + 2255,03)² = 175x106 can you explain the process for getting d seperate thank youarrow_forwardIf the 300-kg drum has a center of mass at point G, determine the horizontal and vertical components of force acting at pin A and the reactions on the smooth pads C and D. The grip at B on member DAB resists both horizontal and vertical components of force at the rim of the drum. P 60 mm; 60 mm: 600 mm A E 30° B C 390 mm 100 mm D Garrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:CENGAGE L
Lesson 2: Thermodynamic Properties; Author: The Thermo Sage;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qA-xwgliPAc;License: Standard Youtube License