
(a)
Interpretation:
The mechanism for the given elimination reaction including carbocation rearrangement is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The
Answer to Problem 8.65P
The
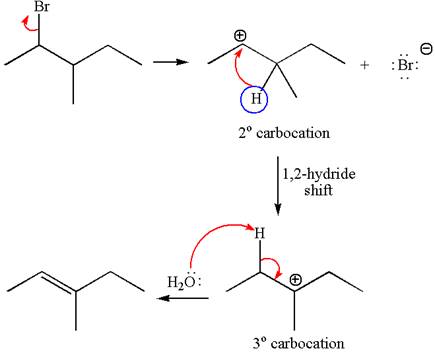
Explanation of Solution
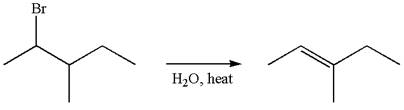
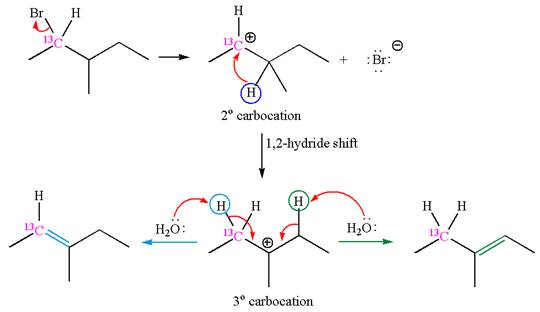
The given reaction equation is
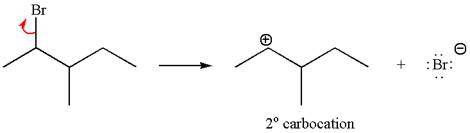
In first step, the leaving group
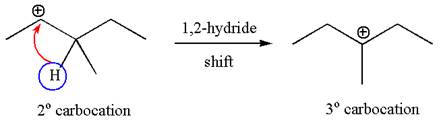
The carbocation formed is rearranged by
The water molecule acts as a base and abstracts a proton from the carbon adjacent to the carbocation, forming
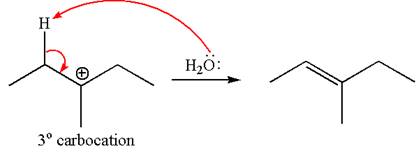
The mechanism for the given elimination reaction is drawn to show the carbocation rearrangement by
(b)
Interpretation:
The mechanism for the given elimination reaction without carbocation rearrangement is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The
Answer to Problem 8.65P
The
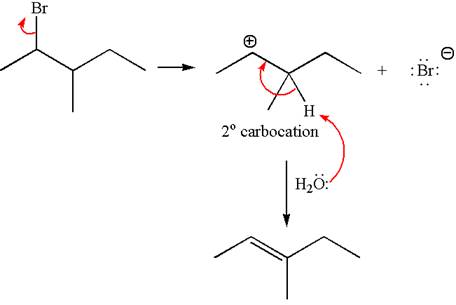
Explanation of Solution
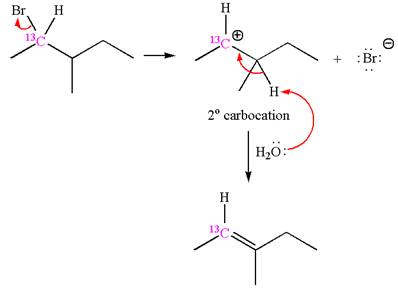
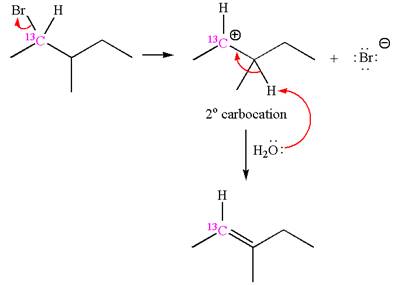
The given reaction equation is
In the first step, the leaving group
In the second step, without rearrangement, the proton is eliminated by the base
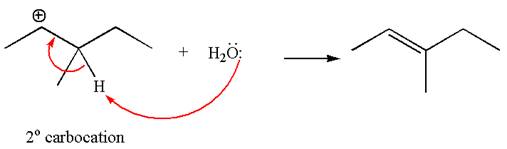
The mechanism for the given elimination reaction is drawn to without rearrangement step, indicating that the same product is formed with or without rearrangement.
(c)
Interpretation:
It is to be explained how the
Concept introduction:
The
Answer to Problem 8.65P
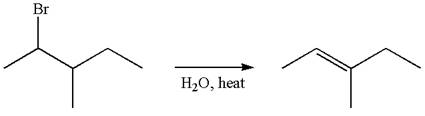
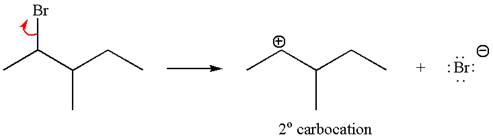
The reaction with carbocation rearrangement gave two products, and the reaction without carbocation rearrangement gave only one product, as shown below, indicating that the
Reaction with rearrangement:
Reaction without rearrangement:
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction equation is
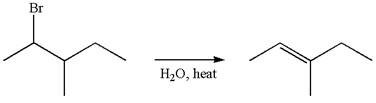
If the carbon bonded to the leaving group in the given substrate is labelled as
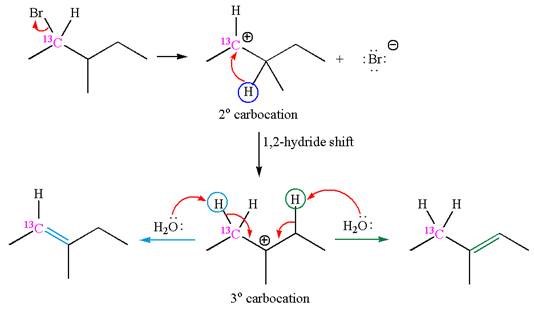
In one product, one of the double bonded carbon is
If the reaction proceeds without rearrangement, then only one product is formed where one of the double bonded carbon is
As the reaction with rearrangement of carbocation formed two products, and reaction without rearrangement formed only one product, it indicates that the E1 products depend on whether the rearrangement occurred.
It is explained that the E1 products depend on whether the reaction includes carbocation rearrangement occurring with
(d)
Interpretation:
How the deuterium isotope labeling is useful to determine whether the rearrangement is occurred in given
Concept introduction:
The
Answer to Problem 8.65P
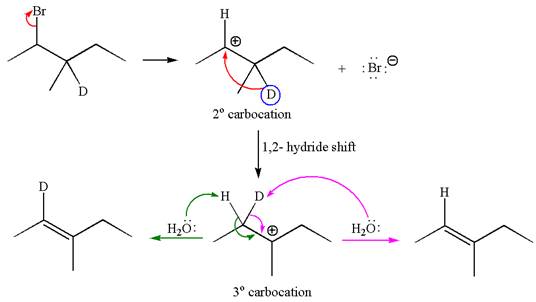
The reaction with carbocation rearrangement by migration of deuterium gave two products, and the reaction without carbocation rearrangement gave only one product as shown below, indicating that the deuterium isotope labeling is useful to determine whether the rearrangement occurred in the given
Reaction with rearrangement:
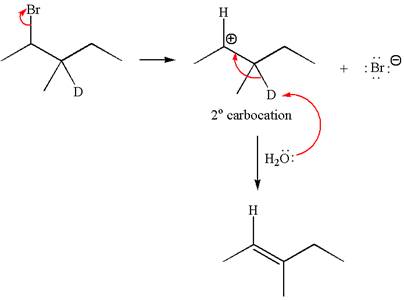
Reaction without rearrangement:
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction equation is
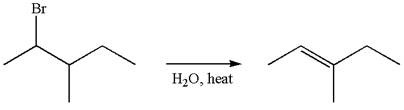
If the migrating hydrogen in the given substrate is replaced with deuterium, then two products are formed when the reaction occurred through carbocation rearrangement. The detailed mechanism is as follows:
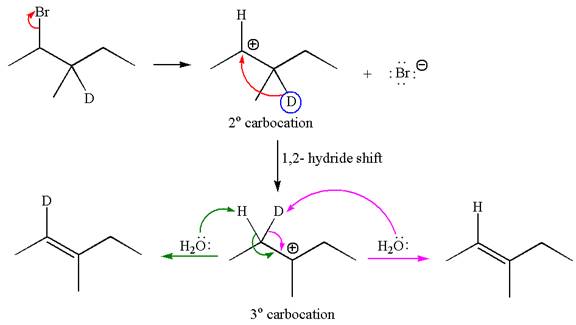
One product is formed by elimination of hydrogen atom and another by elimination of deuterium atom.
If the reaction proceeds without rearrangement, only one product is formed by elimination of deuterium atom. The detailed mechanism is as follows:
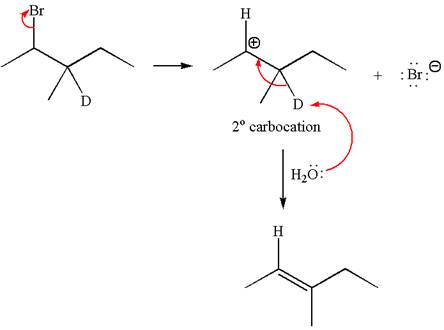
As the reaction with rearrangement of carbocation formed two products and reaction without rearrangement formed only one product, it indicates the E1 products depend on whether the rearrangement occurs.
It is explained on the basis of formation of different products that deuterium isotope labeling is useful to determine whether the rearrangement occurred in the given
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY: PRINCIPLES AND M
- Synthesize 2-Ethyl-3-methyloxirane from dimethyl(propyl)sulfonium iodide using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize 2-Hydroxy-2-phenylacetonitrile from phenylmethanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forward
- Synthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardIf possible, please provide the formula of the compound 3,3-dimethylbut-2-enal.arrow_forwardSynthesize 1,4-dibromobenzene from acetanilide (N-phenylacetamide) using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forward
- Indicate the products obtained by mixing (3-oxo-3-phenylpropyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide with sodium hydride.arrow_forwardWe mix N-ethyl-2-hexanamine with excess methyl iodide and followed by heating with aqueous Ag2O. Indicate the major products obtained.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing acetophenone with iodine and NaOH.arrow_forward
- Indicate the products obtained by mixing 2-Propanone and ethyllithium and performing a subsequent acid hydrolysis.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained if (E)-2-butenal and 3-oxo-butanenitrile are mixed with sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forwardQuestion 3 (4 points), Draw a full arrow-pushing mechanism for the following reaction Please draw all structures clearly. Note that this intramolecular cyclization is analogous to the mechanism for halohydrin formation. COH Br + HBr Brarrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
