
Concept explainers
Find the hydraulic uplift force at the base of the hydraulic structure per meter length.
Answer to Problem 8.5P
The hydraulic uplift force at the base of the hydraulic structure per meter length is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The hydraulic conductivity of the permeable soil layer k is
The head difference between the upstream and downstream H is 10 m.
The height of the water level
The depth of permeable layer up to the tip of the hydraulic structure D is 1.67 m.
The depth of permeable layer
Calculation:
Draw the free body diagram of the flow net for the given values as in Figure 1.
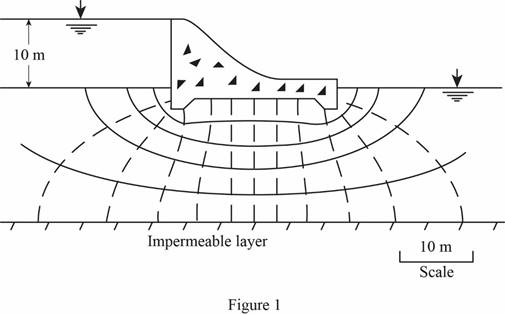
Determine the head loss for each drop using the relation.
Here,
Refer Figure 1.
The number of potential drop
Substitute 10 m for H and 12 for
Determine the pressure head at D using the relation.
Here, flow dis is the flow net distance.
Substitute 10 m for H, 3.34 m for
Determine the pressure head at E using the relation.
Substitute 10 m for H, 3.34 m for
Determine the pressure head at F using the relation.
Substitute 10 m for H, 1.67 m for D, 3.5 m for flow dis, and 0.833 for
Determine the pressure head at G using the relation.
Substitute 10 m for H, 1.67 m for D, 8.5 m for flow dis, and 0.833 for
Determine the pressure head at H using the relation.
Substitute 10 m for H, 3.34 m for
Determine the pressure head at I using the relation.
Substitute 10 m for H, 3.34 m for
Determine the hydraulic uplift force at the base of the hydraulic structure per meter length using the relation.
Here,
Take unit weight of water
Substitute
Draw the pressure head diagram as in Figure 2.
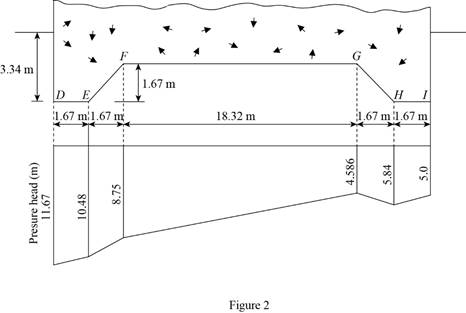
Therefore, the hydraulic uplift force at the base of the hydraulic structure per meter length is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap Course List)
- A 2.0 m wide strip foundation carries a wall load of 350 kN/m in a clayey soil where y = 17 kN/m³, c' = 5.0 kN/m² and 23°. The foundation depth is 1.5 m. For o' = 23°: Nc = 18.05; N = 8.66; N = 8.20. Determine the factor of safety using the equation below. 1 qu = c' NcFcs Fed Fci +qNqFqs FqdFqi + ½ BN F√s 1 2 (Enter your answer to three significant figures.) s Fyd Fi FS =arrow_forward1.2 m BX B 70 kN.m y = 16 kN/m³ c' = 0 6'-30° Water table Ysat 19 kN/m³ c' 0 &' = 30° A square foundation is shown in the figure above. Use FS = 6, and determine the size of the foundation. Use the Prakash and Saran theory (see equation and figures below). Suppose that F = 450 kN. Qu = BL BL[c′Nc(e)Fcs(e) + qNg(e)Fcs(e) + · 1 YBN(e) F 2 7(e) Fra(e)] (Enter your answer to two significant figures.) B: m Na(e) 60 40- 20- e/B=0 0.1 0.2 0.3 .0.4 0 0 10 20 30 40 Friction angle, ' (deg) Figure 1 Variation of Na(e) with o' Ny(e) 60 40 20 e/B=0 0.3 0.1 0.2 0.4 0 0 10 20 30 40 Friction angle, ' (deg) Figure 2 Variation of Nye) with o'arrow_forwardK/S 46. (O المهمات الجديدة 0 المنتهية 12 المغـ ۱۱:۰۹ search ليس لديك اي مهمات ☐ ○ ☑arrow_forward
- I need help setti if this problem up and solving. I keep doing something wrong.arrow_forward1.0 m (Eccentricity in one direction only)=0.15 m Call 1.5 m x 1.5m Centerline An eccentrically loaded foundation is shown in the figure above. Use FS of 4 and determine the maximum allowable load that the foundation can carry if y = 18 kN/m³ and ' = 35°. Use Meyerhof's effective area method. For '=35°, N = 33.30 and Ny = 48.03. (Enter your answer to three significant figures.) Qall = kNarrow_forwardWhat are some advantages and disadvantages of using prefabrication in construction to improve efficiency and cut down on delays?arrow_forward
- PROBLEM:7–23. Determine the maximum shear stress acting in the beam at the critical section where the internal shear force is maximum. 3 kip/ft ΑΟ 6 ft DiC 0.75 in. 6 ft 6 in. 1 in. F [ 4 in. C 4 in. D 6 in. Fig of prob:7-23 1 in. 6 ft Barrow_forward7.60 This abrupt expansion is to be used to dissipate the high-energy flow of water in the 5-ft-diameter penstock. Assume α = 1.0 at all locations. a. What power (in horsepower) is lost through the expansion? b. If the pressure at section 1 is 5 psig, what is the pressure at section 2? c. What force is needed to hold the expansion in place? 5 ft V = 25 ft/s Problem 7.60 (2) 10 ftarrow_forward7.69 Assume that the head loss in the pipe is given by h₁ = 0.014(L/D) (V²/2g), where L is the length of pipe and D is the pipe diameter. Assume α = 1.0 at all locations. a. Determine the discharge of water through this system. b. Draw the HGL and the EGL for the system. c. Locate the point of maximum pressure. d. Locate the point of minimum pressure. e. Calculate the maximum and minimum pressures in the system. Elevation 100 m Water T = 10°C L = 100 m D = 60 cm Elevation 95 m Elevation 100 m L = 400 m D = 60 cm Elevation = 30 m Nozzle 30 cm diameter jet Problem 7.69arrow_forward
- A rectangular flume of planed timber (n=0.012) slopes 0.5 ft per 1000 ft. (i)Compute the discharge if the width is 7 ft and the depth of water is 3.5 ft. (ii) What would be thedischarge if the width were 3.5 ft and depth of water is 7 ft? (iii) Which of the two forms wouldhave greater capacity and which would require less lumber?arrow_forwardFigure shows a tunnel section on the Colorado River Aqueduct. The area of the water cross section is 191 ft 2 , and the wetted perimeter is 39.1 ft. The flow is 1600 cfs. If n=0.013 for the concrete lining, find the slope.arrow_forward7.48 An engineer is making an estimate for a home owner. This owner has a small stream (Q= 1.4 cfs, T = 40°F) that is located at an elevation H = 34 ft above the owner's residence. The owner is proposing to dam the stream, diverting the flow through a pipe (penstock). This flow will spin a hydraulic turbine, which in turn will drive a generator to produce electrical power. Estimate the maximum power in kilowatts that can be generated if there is no head loss and both the turbine and generator are 100% efficient. Also, estimate the power if the head loss is 5.5 ft, the turbine is 70% efficient, and the generator is 90% efficient. Penstock Turbine and generator Problem 7.48arrow_forward
 Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning



