
(a)
Interpretation: All constitutional isomers formed in the given
Concept introduction: The removal of halide and neighboring
Answer to Problem 8.33P
All constitutional isomers formed in the given
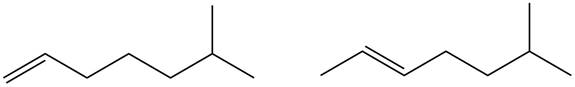
Figure 1
Disubstituted alkene is the major product of the reaction.
Explanation of Solution
The
In the given compound, two
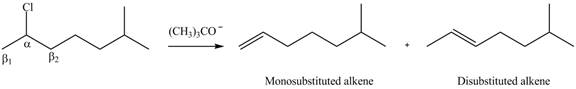
Figure 2
According to Zaitsev rule, more substituted alkene is obtained as a major product in
All constitutional isomers formed in the given
(b)
Interpretation: All constitutional isomers formed in the given
Concept introduction: The removal of halide and neighboring
Answer to Problem 8.33P
All constitutional isomers formed in the given
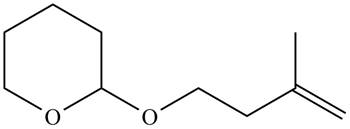
Figure 3
Monosubstituted alkene is the major product of the reaction.
Explanation of Solution
The
In the given compound, only one
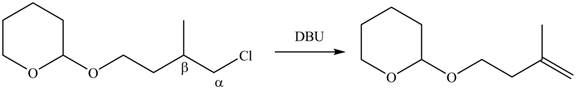
Figure 4
According to Zaitsev rule, more substituted alkene is obtained as a major product in
All constitutional isomers formed in the given
(c)
Interpretation: All constitutional isomers formed in the given
Concept introduction: The removal of halide and neighboring
Answer to Problem 8.33P
All constitutional isomers formed in the given
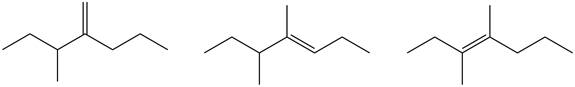
Figure 5
Tetrasubstituted alkene is the major product of the reaction.
Explanation of Solution
The
In the given compound, three
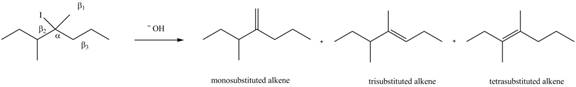
Figure 6
According to Zaitsev rule, more substituted alkene is obtained as a major product in
All constitutional isomers formed in the given
(d)
Interpretation: All constitutional isomers formed in the given
Concept introduction: The removal of halide and neighboring
Answer to Problem 8.33P
All constitutional isomers formed in the given
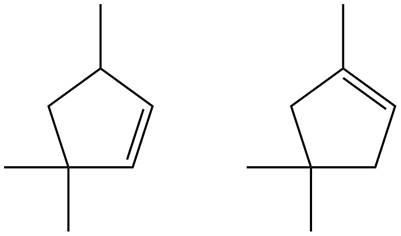
Figure 7
Trisubstituted alkene is the major product of the reaction.
Explanation of Solution
The
In the given compound, two
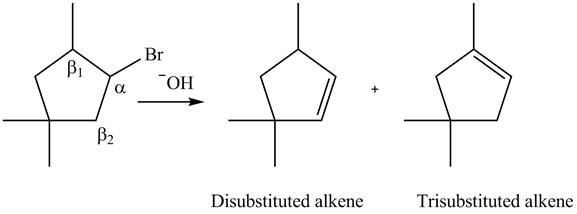
Figure 8
According to Zaitsev rule, more substituted alkene is obtained as a major product in
All constitutional isomers formed in the given
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- MnO2 acts as an oxidant in the chlorine synthesis reaction.arrow_forwardIn Potassium mu-dihydroxydicobaltate (III) tetraoxalate K4[Co2(C2O4)4(OH)2], indicate whether the OH ligand type is bidentate.arrow_forwardImagine an electrochemical cell based on these two half reactions with electrolyte concentrations as given below: Oxidation: Pb(s) → Pb2+(aq, 0.10 M) + 2 e– Reduction: MnO4–(aq, 1.50 M) + 4 H+(aq, 2.0 M) + 3 e– → MnO2(s) + 2 H2O(l) Calculate Ecell (assuming temperature is standard 25 °C).arrow_forward
- : ☐ + Draw the Fischer projection of the most common naturally-occurring form of aspartate, with the acid group at the top and the side chain at the bottom. Important: be sure your structure shows the molecule as it would exist at physiological pH. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. ✓arrow_forwardFor a silver-silver chloride electrode, the following potentials are observed: E°cell = 0.222 V and E(saturated KCl) = 0.197 V Use this information to find the [Cl–] (technically it’s the activity of Cl– that’s relevant here, but we’ll just call it “concentration” for simplicity) in saturated KCl.arrow_forwardA concentration cell consists of two Sn/Sn2+ half-cells. The cell has a potential of 0.10 V at 25 °C. What is the ratio of [Sn2+] (i.e., [Sn2+left-half] / [Sn2+right-half])?arrow_forward
- Electrochemical cell potentials can be used to determine equilibrium constants that would be otherwise difficult to determine because concentrations are small. What is Κ for the following balanced reaction if E˚ = +0.0218 V? 3 Zn(s) + 2 Cr3+(aq) → 3 Zn2+(aq) + Cr(s) E˚ = +0.0218 Varrow_forwardConsider the following half-reactions: Hg2+(aq) + 2e– → Hg(l) E°red = +0.854 V Cu2+(aq) + 2e– → Cu(s)E°red = +0.337 V Ni2+(aq) + 2e– → Ni(s) E°red = -0.250 V Fe2+(aq) + 2e– → Fe(s) E°red = -0.440 V Zn2+(aq) + 2e– → Zn(s) E°red = -0.763 V What is the best oxidizing agent shown above (i.e., the substance that is most likely to be reduced)?arrow_forwardCalculate the equilibrium constant, K, for MnO2(s) + 4 H+(aq) + Zn(s) → Mn2+(aq) + 2 H2O(l) + Zn2+(aq)arrow_forward
- In the drawing area below, draw the condensed structures of formic acid and ethyl formate. You can draw the two molecules in any arrangement you like, so long as they don't touch. Click anywhere to draw the first atom of your structure. A C narrow_forwardWrite the complete common (not IUPAC) name of each molecule below. Note: if a molecule is one of a pair of enantiomers, be sure you start its name with D- or L- so we know which enantiomer it is. molecule Ο C=O common name (not the IUPAC name) H ☐ H3N CH₂OH 0- C=O H NH3 CH₂SH H3N ☐ ☐ X Garrow_forward(Part A) Provide structures of the FGI products and missing reagents (dashed box) 1 eq Na* H* H -H B1 B4 R1 H2 (gas) Lindlar's catalyst A1 Br2 MeOH H2 (gas) Lindlar's catalyst MeO. OMe C6H1402 B2 B3 A1 Product carbons' origins Draw a box around product C's that came from A1. Draw a dashed box around product C's that came from B1.arrow_forward
