
Concept explainers
Programs DYNACAM and MATRIX may be used to solve these problems or to check your solution where appropriate.
Figure P8-1 shows the cam and follower from Problem 6-65. Using graphical methods, find and sketch the equivalent fourbar linkage for this position of the cam and follower.
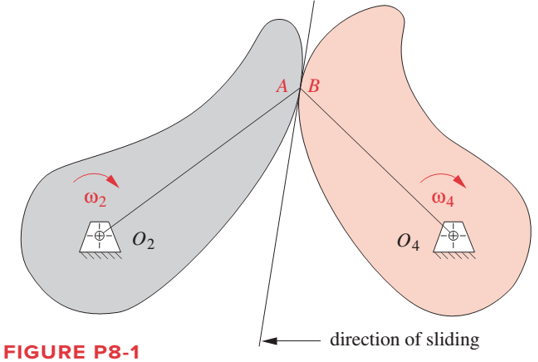
To sketch: The equivalent four bar linkage of thecam follower.
Explanation of Solution
Cams are rotated by cam pair at A and B. For an equivalent four bar linkage of cam and follower mechanism, the cam pair is converted into two turning pair by an imaginary link AB. Length of the link will be equal to the center of curvature distances between two cams. Also the two cam is replaced by a two links O2A and O2B. O2A is the distance between center of curvature of left cam at A and center of rotation of left cam at O2. Similarly O2B is distance between the center of curvature of right cam at B and center of rotation of right cam at O4.
Graphical method for four bar mechanism:-
- Take O2 and O4 as a fix link.
- Mark A and B as a center of curvature of the left and right cam respectively.
- Draw O2A and O2B and join A and B as AB.
Drawing the equivalent four bar linkage as shown below:
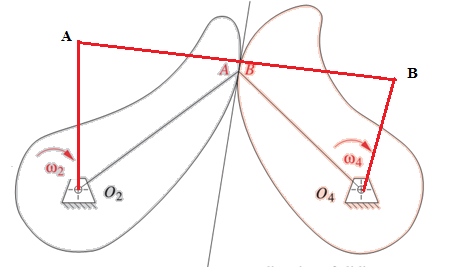
O2ABO4is the equivalent 4 bar linkage of two sliding cam mechanism. The angular velocity of left and right cam will be equal to the angular velocity of link O2A and O2B respectively.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
DESIGN OF MACHINERY
- Liquid water enters the boiler at 60 bar. Steam exits the boiler at 60 bar, 540°C and undergoes a throttling process to 40 bar before entering the turbine. Steam expands adiabatically through the turbine to 5 bar, 240°C, and then undergoes a throttling process to 1 bar before entering the condenser. Kinetic and potential energy effects can be ignored. Draw a Temperature-Entropy diagram and mark each of the states 2-5 on this diagram. Determine the power generated by the turbine, in kJ per kg of steam flowing. For the valves and the turbine, evaluate the rate of entropy production, each in kJ/K per kg of steam flowing.arrow_forwardFind the componenets of reactions at pins of A, B and D please show the detailed process and instructions for learning draw out all diagrams please and thank youarrow_forwardA cast iron cylinder of 200 mm inner diameter and 12.5 mm thick is closely wound with a layer of 4 mm diameter steel wire under a tensile stress of 55 MN/m². Determine the stresses set up in the cylinder and steel wire if water under a pressure of 3 MN/m² is admitted in the cylinder. Take E= 100 GN/m², E = 200 GN/m² and Poisson's ratio = 0.25.arrow_forward
- What is the effect of a clogged fuel injector?arrow_forwardYou are asked to design a unit to condense ammonia. The required condensation rate is 0.09kg/s. Saturated ammonia at 30 o C is passed over a vertical plate (10 cm high and 25 cm wide).The properties of ammonia at the saturation temperature of 30°C are hfg = 1144 ́10^3 J/kg andrho_v = 9.055 kg/m 3 . Use the properties of liquid ammonia at the film temperature of 20°C (Ts =10 o C):Pr = 1.463 rho_l= 610.2 kf/m^3 liquid viscosity= 1.519*10^-4 kg/ ms kinematic viscosity= 2.489*10^-7 m^2/s Cpl= 4745 J/kg C kl=0.4927 W/m C hfg*=hfg+0.68Cpl(Tsat-Given Ts) a) Instead of one plate you want to use small plates and install many of them. Calculate the requiredsurface temperature to achieve the desired condensation rate (0.09 kg/s) if you install 36vertical plates (with the same dimension as above: 10 cm high and 25 cm wide).arrow_forward11-19 designed in Problem The shaft shown in figure P11-4 was 10-19, for the data in the row(s) assigned from table PII-1, and the corresponding diameter of shaft found in Problem 10-19, design suitable bearings 5 E8 cycles at the load for at least State all assumptions. to support 1200rpm. (a) Using hydrodynamically lubricated bronze sleeve bearings with ON = 40, Lld = 0.8, and clearance ratio 0.0025. of a ← gear T gear Key figure PI-4 Given from the problem 10-19 we get d= 1.153 in from the table 11-1 we get a = 16 in b= 18in L= 20inarrow_forward
- In an irrigation system, the following characteristics of the pipe network are available.• 100 meters of 4" PVC pipe, 3 gate valves• 500 meters of 3" PVC pipe, 4 gate valves• 200 meters of 2" H.G. pipe, 2 globe valves• 50 litres per second circulate in the pipes:Calculate:1. Total energy losses in meters.2. Leaks in pipes.3. Losses in accessories.4. Calculate the equivalent pipe of that system assuming only pipes without fittings.Solve the problem without artificial intelligence, solve by one of the expertsarrow_forwardIn a series pipe, calculate the diameter 2 according to the following:• Ltotal: 325 m• L1: 52 m, D1: 3/4"• L2: 254 m, D2:?• L3: 19 m, D: 1-1/4".Indicate the nominal diameter. Solve without using artificial inteligence, solve by one of the expertsarrow_forwardWhat is the critical speed of the shaft in rad/s for one, two, and three elements?arrow_forward
- 2. Express the following complex numbers in rectangular form. (a) z₁ = 2еjл/6 (b) Z2=-3e-jπ/4 (c) Z3 = √√√3e-j³/4 (d) z4 = − j³arrow_forwardA prismatic beam is built into a structure. You can consider the boundary conditions at A and B to be fixed supports. The beam was originally designed to withstand a triangular distributed load, however, the loading condition has been revised and can be approximated by a cosine function as shown in the figure below. You have been tasked with analysing the structure. As the beam is prismatic, you can assume that the bending rigidity (El) is constant. wwo cos 2L x A B Figure 3: Built in beam with a varying distributed load In order to do this, you will: a. Solve the reaction forces and moments at point A and B. Hint: you may find it convenient to use the principal of superposition. (2%) b. Plot the shear force and bending moment diagrams and identify the maximum shear force and bending moment. (2%) c. Develop an expression for the vertical deflection. Clearly state your expression in terms of x. (1%)arrow_forwardQuestion 1: Beam Analysis Two beams (ABC and CD) are connected using a pin immediately to the left of Point C. The pin acts as a moment release, i.e. no moments are transferred through this pinned connection. Shear forces can be transferred through the pinned connection. Beam ABC has a pinned support at point A and a roller support at Point C. Beam CD has a roller support at Point D. A concentrated load, P, is applied to the mid span of beam CD, and acts at an angle as shown below. Two concentrated moments, MB and Mc act in the directions shown at Point B and Point C respectively. The magnitude of these moments is PL. Moment Release A B с ° MB = PL Mc= = PL -L/2- -L/2- → P D Figure 1: Two beam arrangement for question 1. To analyse this structure, you will: a) Construct the free body diagrams for the structure shown above. When constructing your FBD's you must make section cuts at point B and C. You can represent the structure as three separate beams. Following this, construct the…arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





