
Engineering Electromagnetics
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781260029963
Author: Hayt
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 8, Problem 8.19P
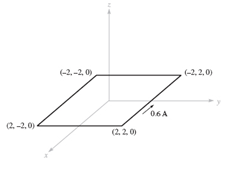
Given a material for which ℵK = 3.1 and within which B = 0.4yaz -T, find (a) H; (b) p; (c) u? ;(d) M; (e) J; (f) JB; (g) JT.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Q2.
a) Two three-phase transformers, designated A and B, have the following
secondary equivalent circuit parameters per phase:
R₁ = 0.002 Q, XA = 0.03 Q, RB = 0.004 Q, X = 0.012 Q
Transformer A is 250 kVA and transformer B is 450 kVA. Calculate how
they share a load of 650 KVA when connected in parallel (assume the
voltage ratios are equal)
b) A step-up transformer is being specified for the beginning of a 3-phase, 4
wire high voltage transmission line. Discuss your recommendation for the
configuration of the transformer connections on both the primary and
secondary side of the transformer.
c)
Define power system protection and describe its fundamental purpose.
Discuss the following key concepts including discrimination, stability,
speed of operation, sensitivity, and reliability in the context of the power
system protection components and schemes.
Q3.
a) Given the unsymmetrical phasors for a three-phase system, they can be
represented in terms of their symmetrical components as follows:
[Fa]
[1 1
Fb = 1 a²
[Fc.
11[Fao]
a Fai
1 a a2F a2-
where F stands for any three-phase quantity. Conversely, the sequence
components can be derived from the unsymmetrical phasors as:
[11 1] [Fal
Faol
Fa1 =
1 a a² F
1 a²
a
a2.
Given the unbalanced three-phase voltages:
V₁ = 120/10° V, V₂ = 200/110° V, V = 240/200° V
Calculate in polar form the sequence components of the voltage.
Complete the table of values for this circuit:
Chapter 8 Solutions
Engineering Electromagnetics
Ch. 8 - A point charge, Q = - 0.3 /C and m = 3 Ă— -10-16...Ch. 8 - Prob. 8.2PCh. 8 - Prob. 8.3PCh. 8 - Show that a charged particle in a uniform magnetic...Ch. 8 - Prob. 8.5PCh. 8 - Show that the differential work in moving a...Ch. 8 - A conducting strip of infinite length lies in the...Ch. 8 - Two conducting strips, having infinite length in...Ch. 8 - A current of-100az A/m flows on the conducting...Ch. 8 - A planar transmission line consists of two...
Ch. 8 - Prob. 8.11PCh. 8 - Two circular wire rings are parallel to each...Ch. 8 - An infinitely long current filament is oriented...Ch. 8 - A solenoid is 25 era long, 3 cm in diameter, and...Ch. 8 - Prob. 8.15PCh. 8 - Prob. 8.16PCh. 8 - Prob. 8.17PCh. 8 - Prob. 8.18PCh. 8 - Given a material for which ℵK = 3.1 and within...Ch. 8 - Find H in a material where (a) fir = 4.2, there...Ch. 8 - Prob. 8.21PCh. 8 - Prob. 8.22PCh. 8 - Calculate values for HO,B0, and M0 at p = c for a...Ch. 8 - Two current sheets, K0,ay, A/m at z = 0 and -K0,ay...Ch. 8 - Prob. 8.25PCh. 8 - Prob. 8.26PCh. 8 - Let đ�œ‡rj = 2 in region 1, defined by 2x + 3y —...Ch. 8 - For values of B below the knee on the...Ch. 8 - Prob. 8.29PCh. 8 - Prob. 8.30PCh. 8 - A toroid is constructed of a magnetic material...Ch. 8 - Prob. 8.32PCh. 8 - Prob. 8.33PCh. 8 - Determine the energy stored per unit length in the...Ch. 8 - Prob. 8.35PCh. 8 - Prob. 8.36PCh. 8 - A Toroid has known, reluctance R. Two windings...Ch. 8 - Prob. 8.38PCh. 8 - Conducting planes in air at Z = 0 and z = d carry...Ch. 8 - Prob. 8.40PCh. 8 - Prob. 8.41PCh. 8 - Find the mutual inductance between two filaments...Ch. 8 - Prob. 8.43PCh. 8 - Prob. 8.44PCh. 8 - Beginning with the definition, of the scalar...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
How does a computers main memory differ from its auxiliary memory?
Java: An Introduction to Problem Solving and Programming (8th Edition)
Why is the study of database technology important?
Database Concepts (8th Edition)
Assume a telephone signal travels through a cable at two-thirds the speed of light. How long does it take the s...
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
17–1C A high-speed aircraft is cruising in still air. How does the temperature of air at the nose of the aircra...
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
How are relationships between tables expressed in a relational database?
Modern Database Management
Comprehension Check 7-14
The power absorbed by a resistor can be given by P = I2R, where P is power in units of...
Thinking Like an Engineer: An Active Learning Approach (4th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- *P2.58. Solve for the node voltages shown in Figure P2.58. - 10 Ω w + 10 Ω 15 Ω w w '+' 5 Ω 20x 1 A Figure P2.58 w V2 502 12Aarrow_forwardAn 18.65 kW, 4-pole, 50 Hz, 3-phase induction motor has friction and windage losses of 2.5% of the output. The full-load slip is 4%. Find for full-load (i) the rotor cu loss (ii) the rotor input power (iii) the output torque.arrow_forwardQ1: Consider the finite state machine logic implementation in Fig. shown below: a. b. Construct the state diagram. Repeat the circuit design using j-k flip flop. C'lk A D 10 Clk Q D 32 Cik O 31 Please solve the question on a sheet of paper by hand and explain everything related to the question step by step.arrow_forward
- Anot ined sove in peaper S PU +96 An 18.65 kW, 4-pole, 50 Hz, 3-phase induction motor has friction and windage losses of 2.5% of the output. The full-load slip is 4 %. Find for full-load (i) the rotor cu loss (ii) the rotor input power (iii) the output torque. 750 1 T el Marrow_forwardAlternator has star-connected,4-pole, 50 Hz as the following data: Flux per pole-0.12 Wb; No. of slot/pole/phase=4; conductor/slot=4; Each coil spans 150° (electrical degree) pitches Find (i) number of turns per phase (ii) distribution factor (iii) pitch factor (iv) no-load phase voltage (v) no-load line voltage.arrow_forwardAlternator has star-connected,4-pole, 50 Hz as the following data: Flux per pole-0.12 Wb; No. of slot/pole/phase=4; conductor/slot=4; Each coil spans 150° (electrical degree) pitches Find (i) number of turns per phase (ii) distribution factor (iii) pitch factor (iv) no-load phase voltage (v) no-load line voltage.arrow_forward
- A) Suppose you were desiging a circuit that required two LEDs for "power on" indication. The power supply voltage is 5 volts, and each LED is rated at 1.6 volts and 20 mA. Calculate the dropping resistor sizes and power ratings: B) After doing this, a co-worker looks at your circuit and suggests a modification. Why not use a single dropping resistor for both LEDs, economizing the number of components necessary? Re-calculate the dropping resistor ratings (resistance and power) for the new design. Include the total power consumed by the circuit and the power delivered by the source.arrow_forwardS A L ined sove in peaper ۳/۱ 16852 Alternator has star-connected,4-pole, 50 Hz as the following data: Flux per pole-0.12 Wb; No. of slot/pole/phase-4; conductor/slot-4; Each coil spans 150° (electrical degree) pitches Find (i) number of turns per phase (ii) distribution factor (iii) pitch factor (iv) no-load phase voltage (v) no-load line voltage. 2ci25 750 r 2.01 ४arrow_forwardA) Complete the table of values for this circuit: B) Draw the schematic include polarityarrow_forward
- (choose R1, R2, R3, R4, R5 and assume that 300 β = , all resistors must be greater than zero) such that the following specifications are met: • Minimum open loop gain, Aol, 40dB (can be more, this is the minimum requirement) • Input current (at input terminals) <1uA • Power dissipation DC P ≤20mW • VCC=10V, VEE=0VI NEED HELP, I WANT ONLY TO CALCULATE THE RESISTORSarrow_forward80 V 300 Ω t = 0 500 i(t) Vc(t) 40 nF 2,5 mH -arrow_forwardProblem 1: Two-Force Equilibrium A 12 kg traffic light is suspended by two cables attached to a ceiling. Determine the force in Cable 1 (AB) and Cable 2 (AC). In other words, determine the tension in each cable, assuming the system is in static equilibrium. Barrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Diodes Explained - The basics how diodes work working principle pn junction; Author: The Engineering Mindset;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Fwj_d3uO5g8;License: Standard Youtube License