
The decimal values of A, B, C, D and E.
Answer to Problem 7A
A
B
C
D
E
Given information:
A scale is given as below.
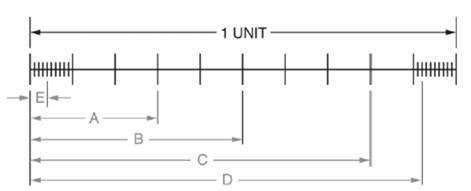
Calculation:
We have been given a scale as below.
From above scale we observe that length of scale is
Distance A is equal to
i.e. Distance A
i.e. Distance A
Hence, A
Similarly,
Distance B is equal to
i.e. Distance B
i.e. Distance B
Hence, B
Again,
Distance C is equal to
i.e. Distance C
i.e. Distance C
Hence, C
Further distance D is equal to
i.e. Distance D
i.e. Distance D
Hence, D
Also, distance E is equal to
i.e. Distance E
Hence, E
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
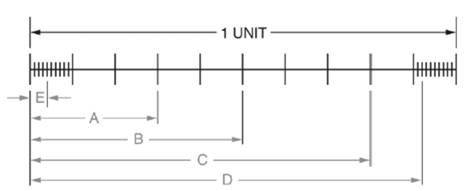
A scale is given as below.

Calculation:
We have been given a scale as below.

From above scale we observe that length of scale is
Distance A is equal to
i.e. Distance A
i.e. Distance A
Hence, A
Similarly,
Distance B is equal to
i.e. Distance B
i.e. Distance B
Hence, B
Again,
Distance C is equal to
i.e. Distance C
i.e. Distance C
Hence, C
Further distance D is equal to
i.e. Distance D
i.e. Distance D
Hence, D
Also, distance E is equal to
i.e. Distance E
Hence, E
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
EBK MATHEMATICS FOR MACHINE TECHNOLOGY
- 30.3. Find and classify the isolated singularities of the following func- tions: (a). 23+1 22(2-1) (b). ²e¹/, (c). sin 3z (d). COS 2arrow_forward3. Consider the polynomial equation 6-iz+7z2-iz³ +z = 0 for which the roots are 3i, -2i, -i, and i. (a) Verify the relations between this roots and the coefficients of the polynomial. (b) Find the annulus region in which the roots lie.arrow_forwardDetermine the set of odd primes p for which 23 is a quadratic residue.arrow_forward
- Q/ Find and classify the singularities of the functions- = 52+3 (1-2) sin² Z a fcz) b f(z) = tanz Z © f(2)= [z (e²-1)]arrow_forwardA linear programming computer package is needed. As part of the settlement for a class action lawsuit, Hoxworth Corporation must provide sufficient cash to make the following annual payments (in thousands of dollars). Year 1 2 2 3 4 5 6 Payment 210 235 260 305 335 480 The annual payments must be made at the beginning of each year. The judge will approve an amount that, along with earnings on its investment, will cover the annual payments. Investment of the funds will be limited to savings (at 4% annually) and government securities, at prices and rates currently quoted in The Wall Street Journal. Hoxworth wants to develop a plan for making the annual payments by investing in the following securities (par value = $1,000). Funds not invested in these securities will be placed in savings. Security Current Price Rate (%) Years to Maturity 1 2 $1,055 $1,000 6.750 5.125 3 4 Assume that interest is paid annually. The plan will be submitted to the judge and, if approved, Hoxworth will be…arrow_forwardA linear programming computer package is needed. Hanson Inn is a 96-room hotel located near the airport and convention center in Louisville, Kentucky. When a convention or a special event is in town, Hanson increases its normal room rates and takes reservations based on a revenue management system. A large professional organization has scheduled its annual convention in Louisville for the first weekend in June. Hanson Inn agreed to make at least 50% of its rooms available for convention attendees at a special convention rate in order to be listed as a recommended hotel for the convention. Although the majority of attendees at the annual meeting typically request a Friday and Saturday two-night package, some attendees may select a Friday night only or a Saturday night only reservation. Customers not attending the convention may also request a Friday and Saturday two-night package, or make a Friday night only or Saturday night only reservation. Thus, six types of reservations are…arrow_forward
- A linear programming computer package is needed. Epsilon Airlines services predominately the eastern and southeastern United States. A vast majority of Epsilon's customers make reservations through Epsilon's website, but a small percentage of customers make reservations via phone. Epsilon employs call-center personnel to handle these reservations along with any problems with the website reservation system and for the rebooking of flights for customers if their plans change or their travel is disrupted. Staffing the call center appropriately is a challenge for Epsilon's management team. Having too many employees on hand is a waste of money, but having too few results in very poor customer service and the potential loss of customers. Epsilon analysts have estimated the minimum number of call-center employees needed by day of week for the upcoming vacation season (June, July, and the first two weeks of August). These estimates are given in the following table. Day Minimum Number of…arrow_forwardind Original: 100-200 = 20,000 200400=20,000 80 602=3600 694761 =4 4x1.3225-6.29 4761/3600 = 1-3225 5.29-1058msy 6). The dose to the body was 200 mSv. Find the dose to the lung in mrem? W 200ms 20 2.15 and 8) A technique of 20 mAs, 40 kV produces a f4 Sy Find the dose to the Thyroid inarrow_forwardoriginal ssD 400x (100) 2 400 x (14)=100 34 10or (2)² = 100 × (0-85) = 100 x = 72.25 100x 40 72.25 =36.13 500 36.13 13.84 O. 7225 12x13.84≈ 166.08mAs 10) The dose of a radiograph was 100 mSv with a technique of: 10 mAs, 180 kV at 200 cm and tabletop. If the technique is changed to: 20 mAs, 153 kV at 100 cm using a 5:1 grid then find the new dose in rem to the Lungs. 11) A radiographic technique produces an exposure index of EI= 300 and TEI=600 at a source- to-image receptor distance (SID) of 200 cm, 100 kV, 5:1 grid using 10 mAs. If the technique is changed to 100 cm and 85 kV and 5 mAs with table top find the new exposure index? What is the value of DI? 10arrow_forward
- 0. 75 and 34 KV arved fromise to 75 halfed NAME Genesis Ward 0 mAs is 40 #2). A technique involves 150 mAs, 40 kV and produces an intensity of 2 R. are gone down KV C15%! In = 200% Find the new intensity in mGya, using 300 mAs and 46 kV? =100 206a 150mAS 40KV 2R kv 150 is so divide 00 mA, 200 alue of 100. Boomts 46KY 4). A technique is taken with 100 mA, 200 ms, 60 kV and produces 200 mSv.arrow_forwardFi is 2 O 2 ms, #3). A technique is taken with 100 mA, 200 60 kV and produces an EI value of 100. Find the EI value when this technique is changed to 200 mA, 100 ms, 69 kV? 4) m 2arrow_forward11) A radiographic technique produces an exposure index of EI= 300 and TEI=600 at a source- to-image receptor distance (SID) of 200 cm, 100 kV, 5:1 grid using 10 mAs. If the technique is changed to 100 cm and 85 kV and 5 mAs with table top find the new exposure index? What is the value of DI?arrow_forward
- Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
 College AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305115545Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
College AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305115545Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305071742Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305071742Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning  Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal Littell
Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal Littell Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL





