
EBK PHYSICS
5th Edition
ISBN: 9780134051796
Author: Walker
Publisher: YUZU
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 8, Problem 73GP
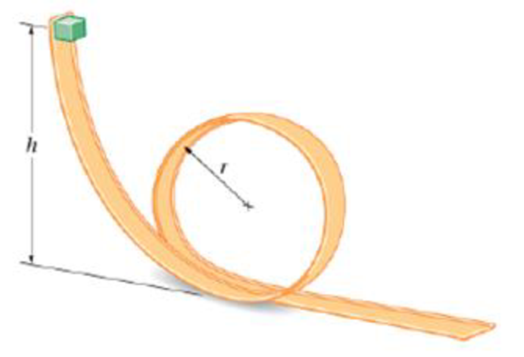
Predict/Calculate Loop-the-Loop (a) A block of mass m slides from rest on a frictionless top-the-loop track, as shown in Figure 8-44. What is the minimum release height, h, required for the block to maintain contact with the track at all times? Give your answer in terms of the radius of the loop, r. (b) Explain why the release height obtained in part (a) is independent of the block’s mass.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Two complex values are z1=8 + 8i, z2=15 + 7 i. z1∗ and z2∗ are the complex conjugate values.
Any complex value can be expessed in the form of a+bi=reiθ. Find r and θ for (z1-z∗2)/z1+z2∗. Find r and θ for (z1−z2∗)z1z2∗ Please show all steps
An electromagnetic wave is traveling through vacuum in the positive x direction. Its electric field vector is given by E=E0sin(kx−ωt)j^,where j^ is the unit vector in the y direction. If B0 is the amplitude of the magnetic field vector, find the complete expression for the magnetic field vector B→ of the wave.
What is the Poynting vector S(x,t), that is, the power per unit area associated with the electromagnetic wave described in the problem introduction?
Give your answer in terms of some or all of the variables E0, B0, k, x, ω, t, and μ0. Specify the direction of the Poynting vector using the unit vectors i^, j^, and k^ as appropriate. Please explain all steps
Another worker is performing a task with an RWL of only 9 kg and is lifting 18 kg, giving him an LI of 2.0 (high risk).
Questions:What is the primary issue according to NIOSH?Name two factors of the RWL that could be improved to reduce risk.If the horizontal distance is reduced from 50 cm to 30 cm, how does the HM change and what effect would it have?
Chapter 8 Solutions
EBK PHYSICS
Ch. 8.1 - 1. In Figure 8-8, the work done by a conservative...Ch. 8.2 - 1. The work done by a conservative force on a...Ch. 8.3 - A system with only conservative forces acting on...Ch. 8.4 - 4. A system is acted on by more than one force,...Ch. 8.5 - A system consists of an object moving along the x...Ch. 8 - Is it possible for the kinetic energy of an object...Ch. 8 - If the stretch of a spring is doubled, the force...Ch. 8 - When a mass is placed on top of a vertical spring,...Ch. 8 - If a spring is stretched so far that it is...Ch. 8 - An object is thrown upward to a person on a roof....
Ch. 8 - It is a law of nature that the total energy of the...Ch. 8 - Discuss the venous energy conversions that occur...Ch. 8 - Discuss the nature of the work done by the...Ch. 8 - It the force on an object is zero, does that mean...Ch. 8 - When a ball is thrown upward, its mechanical...Ch. 8 - When a ball is thrown upward, it spends the same...Ch. 8 - The work done by a conservative force is indicated...Ch. 8 - 2. Calculate the work done by gravity as a 3.2-kg...Ch. 8 - Calculate the work done by friction as a 37-kg box...Ch. 8 - Predict/Calculate A 2.8-kg block is attached to a...Ch. 8 - Predict/Calculate (a) Calculate the work done by...Ch. 8 - In the system shown in Figure 8-26, suppose the...Ch. 8 - Predict/Explain Ball 1 is thrown to the ground...Ch. 8 - A mass is attached to the bottom of a vertical...Ch. 8 - Find the gravitational potential energy of an...Ch. 8 - A student lifts a 1.42-kg book from her desk to a...Ch. 8 - At the local ski slope, an 82.0-kg skier rides a...Ch. 8 - BIO The Wing of the Hawkmoth Experiments performed...Ch. 8 - Predict/Calculate A vertical spring stores 0.962 J...Ch. 8 - Pushing on the pump of a soap dispenser compresses...Ch. 8 - BIO Mantis Shrimp Smasher A peacock mantis shrimp...Ch. 8 - Predict/Calculate The work required to stretch a...Ch. 8 - A 0.33-kg pendulum bob is attached to a string 1.2...Ch. 8 - Prob. 18PCECh. 8 - Prob. 19PCECh. 8 - For an object moving along the x axis, the...Ch. 8 - At an amusement park, a swimmer uses a water side...Ch. 8 - Prob. 22PCECh. 8 - A skateboarder at a skate park rides along the...Ch. 8 - Three balls are thrown upward with the same...Ch. 8 - A 0.21-kg apple falls from a tree to the ground,...Ch. 8 - Predict/Calculate A 2.9-kg block slides with a...Ch. 8 - A 0.26-kg rock is thrown vertically upward from...Ch. 8 - A 1 40-kg block sides with a speed of 0.950 m/s on...Ch. 8 - A 5.76-kg rock is dropped and allowed to fall...Ch. 8 - Predict/Calculate Suppose the pendulum bob m...Ch. 8 - The two masses in the Atwoods machine shown in...Ch. 8 - In the previous problem, suppose the masses have...Ch. 8 - Prob. 33PCECh. 8 - Catching a wave, a 77-kg surfer starts with a...Ch. 8 - At a playground, a 19-kg child plays on a slide...Ch. 8 - Starting at rest at the edge of a swimming pool, a...Ch. 8 - A 22,000-kg airplane lands with a speed of 64 m/s...Ch. 8 - A78-kg skateboarder grinds down a hubba ledge that...Ch. 8 - You ride your bicycle down a hill, maintaining a...Ch. 8 - A 111-kg seal at an amusement park slides from...Ch. 8 - A 1.9-kg rock is released from rest at the surface...Ch. 8 - A 1250-kg car drives up a hill that is 16.2 m...Ch. 8 - The Outlaw Run roller coaster in Branson,...Ch. 8 - A 1.80-kg block slides on a rough horizontal...Ch. 8 - Figure 8-34 shows a potential energy curve as a...Ch. 8 - An object moves along the x axis, subject to the...Ch. 8 - A 1.34-kg object moves along the x axis, subject...Ch. 8 - The potential energy of a particle moving along...Ch. 8 - A block of mass m = 0.88 kg is connected to a...Ch. 8 - A ball of mass m = 0.75 kg is thrown straight...Ch. 8 - Figure 8-35 depicts the potential energy of a...Ch. 8 - Figure 8-35 depicts the potential energy of a...Ch. 8 - CE You and a friend both solve a problem involving...Ch. 8 - CE A particle moves under the influence of a...Ch. 8 - A sled slides without friction down a small,...Ch. 8 - A 74 Kg skier encounters a dip in the snows...Ch. 8 - Running Shoes The soles of a popular make of...Ch. 8 - Nasal Strips The force required to flex a nasal...Ch. 8 - The water slide shown in Figure 8-37 ends at a...Ch. 8 - A skateboarder starts at point A in Figure 8-38...Ch. 8 - The Crash of Skylab NASAs Skylab, the largest...Ch. 8 - BIO Bird Tendons Several studies indicate that the...Ch. 8 - In the Atwoods machine of Problem 31, the mass m2...Ch. 8 - A 6.60-kg block slides with an initial speed of...Ch. 8 - Jeff of the Jungle swings on a 7.6-m vine that...Ch. 8 - A 1.9-kg block slides down a frictionless ramp, as...Ch. 8 - Suppose the ramp in Figure 8-40 is not motionless....Ch. 8 - BIO Compressing the Ground A running track at...Ch. 8 - BIO A Fleas Jump The resilin in the body of a flea...Ch. 8 - Predict/Calculate Tension at the Bottom A ball of...Ch. 8 - An ice cube is placed on top of an overturned...Ch. 8 - Predict/Calculate The two blocks shown in Figure...Ch. 8 - Predict/Calculate Loop-the-Loop (a) A block of...Ch. 8 - Figure 8-45 shows a 1.75-kg block at rest on a...Ch. 8 - In Figure 8-45 a 1.2-kg block is held at rest...Ch. 8 - BIO The Flight of the Dragonflies Of all the...Ch. 8 - BIO The Flight of the Dragonflies Of all the...Ch. 8 - BIO The Flight of the Dragonflies Of all the...Ch. 8 - BIO The Flight of the Dragonflies Of all the...Ch. 8 - Predict/Calculate Referring to Example 8-12...Ch. 8 - Referring to Example 8-12 Suppose the block is...Ch. 8 - Referring to Example 8-17 suppose we would like...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Fill in the blanks: The nose is to the mouth. The ankle is to the knee. The ring finger is to the inde...
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
There are 25 individuals in population 1, all with genotype AA, and there are 40 individuals in population 2, a...
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
APPLY 1.2 Express the following quantities in scientific notation
using fundamental SI units of mass and lengt...
Chemistry (7th Edition)
Choose the best answer to each of the following. Explain your reasoning. Whats the best explanation for the loc...
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
1.1 Write a one-sentence definition for each of the following:
a. chemistry
b. chemical
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
18. SCIENTIFIC THINKING By measuring the fossil remains of Homo floresiensis, scientists have estimated its wei...
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Two complex values are z1=8 + 8i, z2=15 + 7 i. z1∗ and z2∗ are the complex conjugate values. Any complex value can be expessed in the form of a+bi=reiθ. Find r and θ for z1z2∗. Find r and θ for z1/z2∗? Find r and θ for (z1−z2)∗/z1+z2∗. Find r and θ for (z1−z2)∗/z1z2∗ Please explain all steps, Thank youarrow_forwardAn ac series circuit consists of a voltage source of frequency 60 Hz and voltage amplitude V, a 505-Ω resistor, and a capacitor of capacitance 7.2 μF. What must be the source voltage amplitude V for the average electrical power consumed in the resistor to be 236 W? There is no inductance in the circuit.arrow_forwardAn L−R−C series circuit has R= 280 Ω . At the frequency of the source, the inductor has reactance XLL= 905 Ω and the capacitor has reactance XC= 485 Ω . The amplitude of the voltage across the inductor is 445 V . What is the amplitude of the voltage across the resistor and the capacitor? What is the voltage amplitude of the source? What is the rate at which the source is delivering electrical energy to the circuit?arrow_forward
- A 0.185 H inductor is connected in series with a 98.5 Ω resistor and an ac source. The voltage across the inductor is vL=−(12.5V)sin[(476rad/s)t]vL. Derive an expression for the voltage vR across the resistor. Express your answer in terms of the variables L, R, VL (amplitude of the voltage across the inductor), ω, and t. What is vR at 2.13 ms ? Please explain all stepsarrow_forwardA worker lifts a box under the following conditions:Horizontal distance (H): 30 cmInitial height (V): 60 cmVertical travel (D): 50 cmTorso rotation (A): 30°Frequency: 3 times/minute for 1 hourGrip: Good Question:What is the RWL for this task?What does this value mean in terms of occupational safety?arrow_forwardCan someone helparrow_forward
- Can someone help mearrow_forward3. Four identical small masses are connected in a flat perfect square. Rank the relative rotational inertias (IA, IB, IC) about the three axes of rotation shown. Axes A and B are in the plane of the square, and axis C is perpendicular to the plane, through mass m1. ΙΑ IB m2 m1 m3 Ic m4 (a) IAarrow_forwardConsider the circuit shown in the figure below. (Assume L = 5.20 m and R2 = 440 Ω.) (a) When the switch is in position a, for what value of R1 will the circuit have a time constant of 15.4 µs? (b) What is the current in the inductor at the instant the switch is thrown to position b?arrow_forwardCan someone helparrow_forwardCan someone help mearrow_forwardA particle in a box between x=0 and x=6 has the wavefunction Psi(x)=A sin(2πx). How muchenergy is required for the electron to make a transition to Psi(x)= A’ sin(7π x/3). Draw anapproximate graph for the wavefunction. Find A and A'arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanical work done (GCSE Physics); Author: Dr de Bruin's Classroom;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OapgRhYDMvw;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY