
JRL’s financial statements contain the following information:
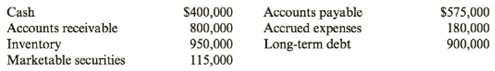
Required:
1. What is its
2. What is its quick ratio?
3. What is its cash ratio?
4. Discuss JRL’s liquidity using these ratios.
Concept introduction:
Current Ratio:
Current Ratio is measure of the company’s ability to pay off its current liabilities using its current assets. It is calculated by dividing the total current assets by total current liabilities. The formula of the current ratio is as follows:
Acid test ratio:
Acid test ration is also called Quick ratio. This ratio is calculated by dividing the quick assets (Cash, Cash equivalents, Short term investments and current receivables) by total current liabilities for the year. The formula for Acid test ratio is as follows:
Cash ratio:
Cash ratio is calculated by dividing and cash and cash equivalents by the total current liabilities. The formula for Cash ratio is as follows:
Cash Ratio = Cash and cash equivalents/ Current liabilities
Requirement 1:
To calculate:
The Current Ratio.
Answer to Problem 58BE
The Current Ratio is 3.
Explanation of Solution
The Current Ratio is calculated as follows:
| Cash | $ 400,000 |
| Marketable Securities | $ 115,000 |
| Accounts Receivables | $ 800,000 |
| Inventory | $ 950,000 |
| Total Current Assets (A) | $ 2,265,000 |
| Accounts Payable | $ 575,000 |
| Accrued Expenses | $ 180,000 |
| Total Current Liabilities (B) | $ 755,000 |
| Current Ratio (A/B) | 3.00 |
Concept introduction:
Current Ratio:
Current Ratio is measure of the company’s ability to pay off its current liabilities using its current assets. It is calculated by dividing the total current assets by total current liabilities. The formula of the current ratio is as follows:
Acid test ratio:
Acid test ration is also called Quick ratio. This ratio is calculated by dividing the quick assets (Cash, Cash equivalents, Short term investments and current receivables) by total current liabilities for the year. The formula for Acid test ratio is as follows:
Cash ratio:
Cash ratio is calculated by dividing and cash and cash equivalents by the total current liabilities. The formula for Cash ratio is as follows:
Cash Ratio = Cash and cash equivalents/ Current liabilities
Requirement 2:
To calculate:
The Quick Ratio.
Answer to Problem 58BE
The Quick Ratio is 1.74.
Explanation of Solution
The Quick Ratio is calculated as follows:
| Cash | $ 400,000 |
| Marketable Securities | $ 115,000 |
| Accounts Receivables | $ 800,000 |
| Total Quick Assets (A) | $ 1,315,000 |
| Accounts Payable | $ 575,000 |
| Accrued Expenses | $ 180,000 |
| Total Current Liabilities (B) | $ 755,000 |
| Quick Ratio (A/B) | 1.74 |
Concept introduction:
Current Ratio:
Current Ratio is measure of the company’s ability to pay off its current liabilities using its current assets. It is calculated by dividing the total current assets by total current liabilities. The formula of the current ratio is as follows:
Acid test ratio:
Acid test ration is also called Quick ratio. This ratio is calculated by dividing the quick assets (Cash, Cash equivalents, Short term investments and current receivables) by total current liabilities for the year. The formula for Acid test ratio is as follows:
Cash ratio:
Cash ratio is calculated by dividing and cash and cash equivalents by the total current liabilities. The formula for Cash ratio is as follows:
Cash Ratio = Cash and cash equivalents/ Current liabilities
Requirement 3:
To calculate:
The Cash Ratio.
Answer to Problem 58BE
The Cash Ratio is 0.68.
Explanation of Solution
The Cash Ratio is calculated as follows:
| Cash | $ 400,000 |
| Marketable Securities | $ 115,000 |
| Cash and Cash Equivalents (A) | $ 515,000 |
| Accounts Payable | $ 575,000 |
| Accrued Expenses | $ 180,000 |
| Total Current Liabilities (B) | $ 755,000 |
| Cash Ratio (A/B) | 0.68 |
Concept introduction:
Current Ratio:
Current Ratio is measure of the company’s ability to pay off its current liabilities using its current assets. It is calculated by dividing the total current assets by total current liabilities. The formula of the current ratio is as follows:
Acid test ratio:
Acid test ration is also called Quick ratio. This ratio is calculated by dividing the quick assets (Cash, Cash equivalents, Short term investments and current receivables) by total current liabilities for the year. The formula for Acid test ratio is as follows:
Cash ratio:
Cash ratio is calculated by dividing and cash and cash equivalents by the total current liabilities. The formula for Cash ratio is as follows:
Cash Ratio = Cash and cash equivalents/ Current liabilities
Requirement 4:
To discuss:
Liquidity of the company.
Answer to Problem 58BE
The Cash ratio shows that company does not have a good liquidity position.
Explanation of Solution
The Current, Quick and Cash ratio shows liquidity position as follows:
| Cash | $ 400,000 |
| Marketable Securities | $ 115,000 |
| Accounts Receivables | $ 800,000 |
| Inventory | $ 950,000 |
| Total Current Assets (A) | $ 2,265,000 |
| Accounts Payable | $ 575,000 |
| Accrued Expenses | $ 180,000 |
| Total Current Liabilities (B) | $ 755,000 |
| Current Ratio (A/B) | 3.00 |
| Cash | $ 400,000 |
| Marketable Securities | $ 115,000 |
| Accounts Receivables | $ 800,000 |
| Total Quick Assets (A) | $ 1,315,000 |
| Accounts Payable | $ 575,000 |
| Accrued Expenses | $ 180,000 |
| Total Current Liabilities (B) | $ 755,000 |
| Quick Ratio (A/B) | 1.74 |
| Cash | $ 400,000 |
| Marketable Securities | $ 115,000 |
| Cash and Cash Equivalents (A) | $ 515,000 |
| Accounts Payable | $ 575,000 |
| Accrued Expenses | $ 180,000 |
| Total Current Liabilities (B) | $ 755,000 |
| Cash Ratio (A/B) | 0.68 |
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Cornerstones of Financial Accounting
- Please provide the correct answer to this general accounting problem using accurate calculations.arrow_forwardI need help finding the correct solution to this financial accounting problem with valid methods.arrow_forwardCan you solve this financial accounting question with the appropriate financial analysis techniques?arrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning



