
(a)
Interpretation:
For the given organic structures IUPAC name should be identified.
Concept Introduction
Any organic molecule can be named by using certain rules given by IUPAC (International Union for Pure and applied chemistry). IUPAC name consists of three parts in major namely Prefix suffix and root word.
Prefix represents the substituent present in the molecule and its position in the root name.
Suffix denotes the presence of
For
Root word represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton of the organic molecule.
When a molecule consists of cyclic structure, the root word of the molecule is prefixed with cyclo, if it is two cyclic structure combined then prefixed with bicyclo.
Two stereoisomers are there for an alkene molecule. It depends upon the location of bulky group (or high molecular weight) on the double bonded carbon atoms. If the bulky groups are in same side then it is cis-isomer. If the bulky groups are in opposite side then it is trans-isomer.
(a)
Answer to Problem 47PP
The systematic name for the molecule (a) is trans-3,4,5,5-tetramethyl-3-heptene.
Explanation of Solution
To identify: The systematic name for the given structure (a).
Draw the given molecule (a) and find the longest parent carbon chain or carbon skeleton and the substituents for naming the compound.
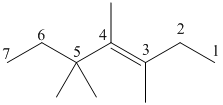
trans-3,4,5,5-tetramethyl-3-heptene
The given molecule is drawn. The parent carbon skeleton is the longest continuous carbon chain that should contain more number of carbons. In the given molecule the parent carbon skeleton is the chain which contains 7 carbons. Hence the root name of the molecule is hept. Since it is an alkene with 7 carbons then heptene will be the parent carbon chain name.
The substituents present in the molecule are methyl groups on 3, 4 and 5. Therefore on numbering the three methyl groups are present at 3, 4 and 5, 5 positions is 3, 4, 5, 5-tetramethyl.
The bulky groups attached on the opposite sides of double bonded carbon atoms, so the given alkene molecule is ‘trans’.
Hence the systematic name for the molecule (a) is trans-3, 4, 5, 5-tetramethyl-3-heptene.
(b)
Interpretation:
For the given organic structures IUPAC name should be identified.
Concept Introduction
Any organic molecule can be named by using certain rules given by IUPAC (International Union for Pure and applied chemistry). IUPAC name consists of three parts in major namely Prefix suffix and root word.
Prefix represents the substituent present in the molecule and its position in the root name.
Suffix denotes the presence of functional group if any in the molecule. It can be an alkene, alkyne, alcohol, carboxylic acid, alcohol etc...
For alkenes, suffix will be ‘ene’.
Root word represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton of the organic molecule.
When a molecule consists of cyclic structure, the root word of the molecule is prefixed with cyclo, if it is two cyclic structure combined then prefixed with bicyclo.
Two stereoisomers are there for an alkene molecule. It depends upon the location of bulky group (or high molecular weight) on the double bonded carbon atoms. If the bulky groups are in same side then it is cis-isomer. If the bulky groups are in opposite side then it is trans-isomer.
(b)
Answer to Problem 47PP
The systemic name for the molecule (b) is 1-ethylcyclohexene.
Explanation of Solution
To identify: The systematic name for the given structure (b).
Draw the given molecule (b) and find the longest parent carbon chain or carbon skeleton and the substituents.
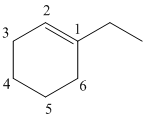
1-ethylcyclohexene
The given molecule is drawn. The parent carbon skeleton is the longest continuous carbon chain that should contain more number of carbons. In the given molecule the parent carbon skeleton is cyclic in nature which consists of 6 carbons so the root word for the molecule is cyclohexane. The suffix ‘ene’ is used since it is an alkene.
The substituent present in the molecule are 1 ethyl group. Therefore it named as 1-ethyl in suffix.
Hence the systematic name for the molecule (b) is 1-ethylcyclohexene.
(c)
Interpretation:
For the given organic structures IUPAC name should be identified.
Concept Introduction
Any organic molecule can be named by using certain rules given by IUPAC (International Union for Pure and applied chemistry). IUPAC name consists of three parts in major namely Prefix suffix and root word.
Prefix represents the substituent present in the molecule and its position in the root name.
Suffix denotes the presence of functional group if any in the molecule. It can be an alkene, alkyne, alcohol, carboxylic acid, alcohol etc...
For alkenes, suffix will be ‘ene’.
Root word represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton of the organic molecule.
When a molecule consists of cyclic structure, the root word of the molecule is prefixed with cyclo, if it is two cyclic structure combined then prefixed with bicyclo.
Two stereoisomers are there for an alkene molecule. It depends upon the location of bulky group (or high molecular weight) on the double bonded carbon atoms. If the bulky groups are in same side then it is cis-isomer. If the bulky groups are in opposite side then it is trans-isomer.
(c)
Answer to Problem 47PP
The systematic name for molecule (c) is 2–methyl bicyclo [2 2 2] oct-2-ene.
Explanation of Solution
To identify: The systematic name for the given structure (c).
Draw the given molecule (d) and find the longest parent carbon chain or carbon skeleton and the substituents.
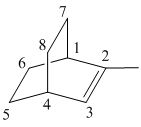
2–methylbicyclo [2 2 2] oct-2-ene
The given molecule is drawn. The parent carbon skeleton is the longest continuous carbon chain that should contain more number of carbons. In the given molecule the parent carbon skeleton is bicyclic in nature which consists of 8 carbons so the root word for the molecule is bicyclooctane. The suffix ‘ene’ is used since it is an alkene.
The given molecule is bicyclo fused alkene, number of carbons at the bridge and bridge head is counted and it is found that there are 2 carbons each at bridge head and 2 carbons at bridge.
The substituents present in the molecule are 1 methyl group. Therefore it named as 1-methyl in suffix.
Hence the systematic name for the molecule (c) is 2–methylbicyclo [2 2 2] oct-2-ene.
The systematic name for the given molecule is given by using the IUPAC rules.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEM PRINT STUDY GDE & SSM
- Devise a synthesis of each compound from the indicated starting material. You may also use any organic compounds with one or two carbons and any needed inorganic reagents. a. Brarrow_forwardPlease help me with #2b & #3 using the data.arrow_forwardHeparin is used as an anti-coagulant. A risk of heparin use is thrombocytopenia, or low platelet count. This risk is minimized with the use of low molecular weight heparins (LMWH), therefore it is desirable to separate LMWH from higher molecular weight heparins. The method of choice to do this is molecular exclusion chromatography. Below is a chromatogram from a molecular exclusion chromatographic run. Peaks ranging from A to J are clearly distinguishable. The heparin mixture that was analyzed had anywhere from 6 to 30 repeat units of monomer (where the heparin with 30 repeat units would be roughly five times the size of the heparin with six repeat units). a. Which letter most likely represents the peak with 6 repeat units given these heparin polymers were separated with molecular exclusion chromatography? b. Explain your reasoning describing the mechanism of retention in molecular exclusion chromatography. 100 80 60 60 Relative Abundance 40 40 E GH 20 20 B A 36 38 40 42 44 46 48 50 50…arrow_forward
- HELP NOW PLEASE ! ASAP! URGENT!arrow_forwardHELP NOW PLEASE ! ASAP! URGENT!arrow_forwardDraw a Newman projection for the molecule below from the perspective indicated. Which of the groups (letters A-H) are methyl groups? CH3 H H H A H B ☑ >> H. ABCDEFG I H -H CH3 G D CH F E Numeric 4 points How many gauche interactions exist in the conformation shown in the previous problem? 1arrow_forward
- HELP NOW PLEASE ! ASAP! URGENT!arrow_forwardHELP NOW PLEASE ! ASAP! URGENT!arrow_forwardWould the following organic synthesis occur in one step? Add any missing products, required catalysts, inorganic reagents, and other important conditions. Please include a detailed explanation and drawings showing how the reaction may occur in one step.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





