
(a)
Interpretation:
For the given organic structures IUPAC name should be identified.
Concept Introduction
Any organic molecule can be named by using certain rules given by IUPAC (International Union for Pure and applied chemistry). IUPAC name consists of three parts in major namely Prefix suffix and root word.
Prefix represents the substituent present in the molecule and its position in the root name.
Suffix denotes the presence of
For
Root word represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton of the organic molecule.
When a molecule consists of cyclic structure, the root word of the molecule is prefixed with cyclo, if it is two cyclic structure combined then prefixed with bicyclo.
Two stereoisomers are there for an alkene molecule. It depends upon the location of bulky group (or high molecular weight) on the double bonded carbon atoms. If the bulky groups are in same side then it is cis-isomer. If the bulky groups are in opposite side then it is trans-isomer.
(a)
Answer to Problem 47PP
The systematic name for the molecule (a) is trans-3,4,5,5-tetramethyl-3-heptene.
Explanation of Solution
To identify: The systematic name for the given structure (a).
Draw the given molecule (a) and find the longest parent carbon chain or carbon skeleton and the substituents for naming the compound.
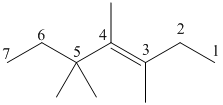
trans-3,4,5,5-tetramethyl-3-heptene
The given molecule is drawn. The parent carbon skeleton is the longest continuous carbon chain that should contain more number of carbons. In the given molecule the parent carbon skeleton is the chain which contains 7 carbons. Hence the root name of the molecule is hept. Since it is an alkene with 7 carbons then heptene will be the parent carbon chain name.
The substituents present in the molecule are methyl groups on 3, 4 and 5. Therefore on numbering the three methyl groups are present at 3, 4 and 5, 5 positions is 3, 4, 5, 5-tetramethyl.
The bulky groups attached on the opposite sides of double bonded carbon atoms, so the given alkene molecule is ‘trans’.
Hence the systematic name for the molecule (a) is trans-3, 4, 5, 5-tetramethyl-3-heptene.
(b)
Interpretation:
For the given organic structures IUPAC name should be identified.
Concept Introduction
Any organic molecule can be named by using certain rules given by IUPAC (International Union for Pure and applied chemistry). IUPAC name consists of three parts in major namely Prefix suffix and root word.
Prefix represents the substituent present in the molecule and its position in the root name.
Suffix denotes the presence of functional group if any in the molecule. It can be an alkene, alkyne, alcohol, carboxylic acid, alcohol etc...
For alkenes, suffix will be ‘ene’.
Root word represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton of the organic molecule.
When a molecule consists of cyclic structure, the root word of the molecule is prefixed with cyclo, if it is two cyclic structure combined then prefixed with bicyclo.
Two stereoisomers are there for an alkene molecule. It depends upon the location of bulky group (or high molecular weight) on the double bonded carbon atoms. If the bulky groups are in same side then it is cis-isomer. If the bulky groups are in opposite side then it is trans-isomer.
(b)
Answer to Problem 47PP
The systemic name for the molecule (b) is 1-ethylcyclohexene.
Explanation of Solution
To identify: The systematic name for the given structure (b).
Draw the given molecule (b) and find the longest parent carbon chain or carbon skeleton and the substituents.
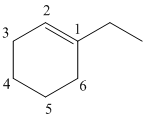
1-ethylcyclohexene
The given molecule is drawn. The parent carbon skeleton is the longest continuous carbon chain that should contain more number of carbons. In the given molecule the parent carbon skeleton is cyclic in nature which consists of 6 carbons so the root word for the molecule is cyclohexane. The suffix ‘ene’ is used since it is an alkene.
The substituent present in the molecule are 1 ethyl group. Therefore it named as 1-ethyl in suffix.
Hence the systematic name for the molecule (b) is 1-ethylcyclohexene.
(c)
Interpretation:
For the given organic structures IUPAC name should be identified.
Concept Introduction
Any organic molecule can be named by using certain rules given by IUPAC (International Union for Pure and applied chemistry). IUPAC name consists of three parts in major namely Prefix suffix and root word.
Prefix represents the substituent present in the molecule and its position in the root name.
Suffix denotes the presence of functional group if any in the molecule. It can be an alkene, alkyne, alcohol, carboxylic acid, alcohol etc...
For alkenes, suffix will be ‘ene’.
Root word represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton of the organic molecule.
When a molecule consists of cyclic structure, the root word of the molecule is prefixed with cyclo, if it is two cyclic structure combined then prefixed with bicyclo.
Two stereoisomers are there for an alkene molecule. It depends upon the location of bulky group (or high molecular weight) on the double bonded carbon atoms. If the bulky groups are in same side then it is cis-isomer. If the bulky groups are in opposite side then it is trans-isomer.
(c)
Answer to Problem 47PP
The systematic name for molecule (c) is 2–methyl bicyclo [2 2 2] oct-2-ene.
Explanation of Solution
To identify: The systematic name for the given structure (c).
Draw the given molecule (d) and find the longest parent carbon chain or carbon skeleton and the substituents.
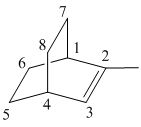
2–methylbicyclo [2 2 2] oct-2-ene
The given molecule is drawn. The parent carbon skeleton is the longest continuous carbon chain that should contain more number of carbons. In the given molecule the parent carbon skeleton is bicyclic in nature which consists of 8 carbons so the root word for the molecule is bicyclooctane. The suffix ‘ene’ is used since it is an alkene.
The given molecule is bicyclo fused alkene, number of carbons at the bridge and bridge head is counted and it is found that there are 2 carbons each at bridge head and 2 carbons at bridge.
The substituents present in the molecule are 1 methyl group. Therefore it named as 1-methyl in suffix.
Hence the systematic name for the molecule (c) is 2–methylbicyclo [2 2 2] oct-2-ene.
The systematic name for the given molecule is given by using the IUPAC rules.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 2-SEMESTER-ACCESS
- What is the name of the following compound? SiMe3arrow_forwardK Draw the starting structure that would lead to the major product shown under the provided conditions. Drawing 1. NaNH2 2. PhCH2Br 4 57°F Sunny Q Searcharrow_forward7 Draw the starting alkyl bromide that would produce this alkyne under these conditions. F Drawing 1. NaNH2, A 2. H3O+ £ 4 Temps to rise Tomorrow Q Search H2arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





