
1.
Pass necessary journal entries to record the transactions.
1.
Explanation of Solution
Journal entry is a set of economic events which can be measured in monetary terms. These are recorded chronologically and systematically.
Accounting rules for Journal entries:
- To record increase balance of account: Debit assets, expenses, losses and credit liabilities, capital, revenue and gains.
- To record decrease balance of account: Credit assets, expenses, losses and debit liabilities, capital, revenue and gains.
Pass necessary journal entries to record the transactions.
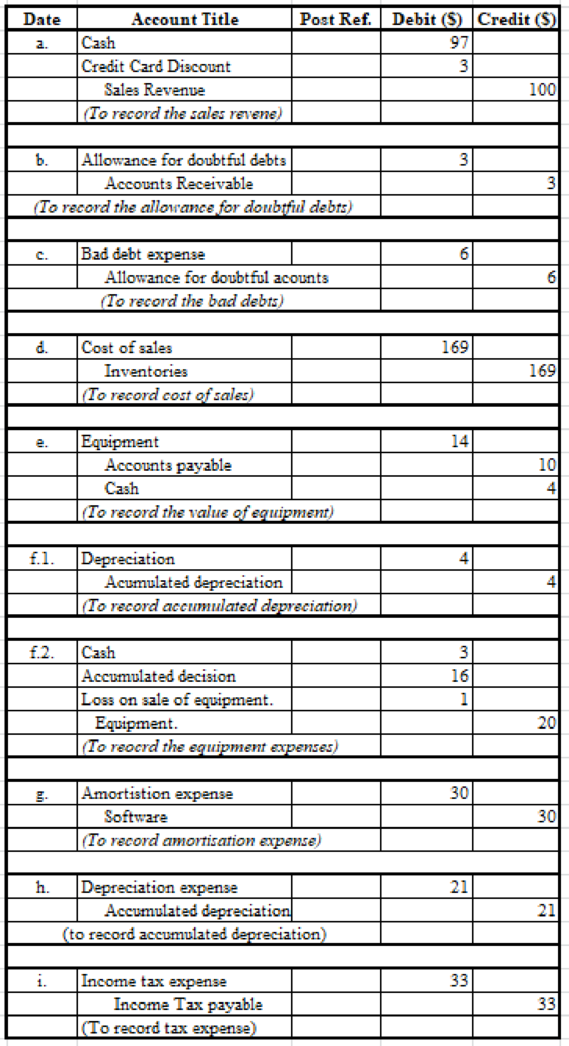
Table (2)
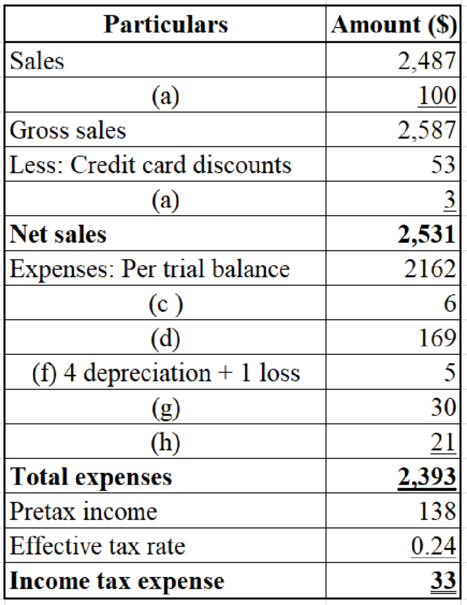
Table (2)
2.
Prepare T accounts using the
2.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare T accounts using the trial balance information and an adjusted trial balance.
| Cash | ||
| Beginning balance 570 | ||
| ||
| f.2 3 | e. 4 | |
| Ending balance 666 | ||
Table (3)
| Beginning balance 373 |
| |
| Ending balance 370 | ||
Table (3)
| Allowance for doubtful accounts | ||
| Balance 570 | ||
| b 3 | c 6 | |
| Balance 21 | ||
Table (3)
| Inventories | ||
| Beginning balance 539 |
| |
| Ending balance 370 | ||
Table (4)
| Prepaid Expenses | ||
| Beginning balance 59 | ||
| Ending balance 59 | ||
Table (5)
| Land | ||
| Beginning balance 22 | ||
| Ending balance 22 | ||
Table (6)
| Building | ||
| Beginning balance 189 | ||
| Ending balance 189 | ||
Table (7)
| Equipment | ||
|
Beginning balance 360
| f.2. 20 | |
| Ending balance 354 | ||
Table (8)
| Balance 222 | ||
| f.1. 4 | ||
| f.2 16 | h. 21 | |
| Balance 231 | ||
Table (9)
| Software | ||
| Beginning balance 90 |
| |
| Ending balance 60 | ||
Table (10)
| Patents | ||
| Beginning balance 1 | ||
| Ending balance 1 | ||
Table (11)
| Beginning balance 161 | ||
| Ending balance 161 | ||
Table (12)
| Accounts Payable | ||
| Balance 252 | ||
| e. 10 | ||
| Balance 262 | ||
Table (13)
| Accrued Liabilities | ||
| Balance 182 | ||
| Balance 182 | ||
Table (14)
| Income Tax Payable | ||
| Balance 16 | ||
| i. 33 | ||
| Balance 49 | ||
Table (15)
| Long term Debt | ||
| Balance 49 | ||
| Balance 49 | ||
Table (16)
| Common Stock | ||
| Balance 3 | ||
| Balance 3 | ||
Table (17)
| Additional paid in capital | ||
| Balance 243 | ||
| Balance 243 | ||
Table (18)
| Balance 1,107 | ||
| Balance 1,107 | ||
Table (19)
| Sales Revenue | ||
|
Balance 2,847 a. 100 | ||
| Balance 2,587 | ||
Table (20)
| Credit Card Discounts | ||
|
Beginning balance 53
| ||
| Ending balance 56 | ||
Table (21)
| Cost of sales | ||
|
Beginning balance 1,306 d. 169 | ||
| Ending balance 1,475 | ||
Table (22)
| Advertising Expense | ||
| Beginning balance 145 | ||
| Ending balance 145 | ||
Table (23)
| Utilities Expense | ||
| Beginning balance 85 | ||
| Ending balance 85 | ||
Table (24)
| Wages Expense | ||
| Beginning balance 625 | ||
| Ending balance 625 | ||
Table (25)
| Depreciation Expense | ||
|
Beginning balance 0 f.1. 4 h. 21 | ||
| Ending balance 25 | ||
Table (26)
| Amortisation Expense | ||
|
Beginning balance 0 g. 30 | ||
| Ending balance 30 | ||
Table (27)
| Interest Expense | ||
| Beginning balance 1 | ||
| Ending balance 1 | ||
Table (28)
|
Beginning balance 0 C 6 | ||
| Ending balance 6 | ||
Table (28)
| Loss of sale of equipment | ||
|
Beginning balance 0 f.2. 1 | ||
| Ending balance 1 | ||
Table (29)
| Income Tax Expense | ||
|
Beginning balance 0 f.2. 33 | ||
| Ending balance 33 | ||
Table (30)
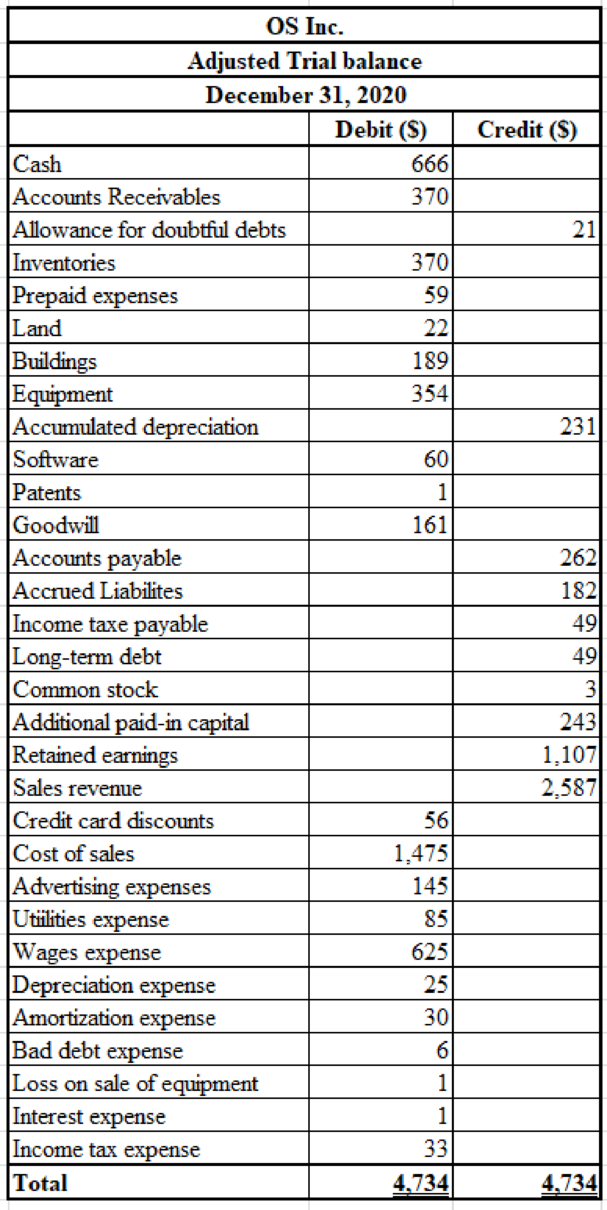
Table (31)
3.
Prepare an income statement, statement of
3.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare an income statement for OS Inc.
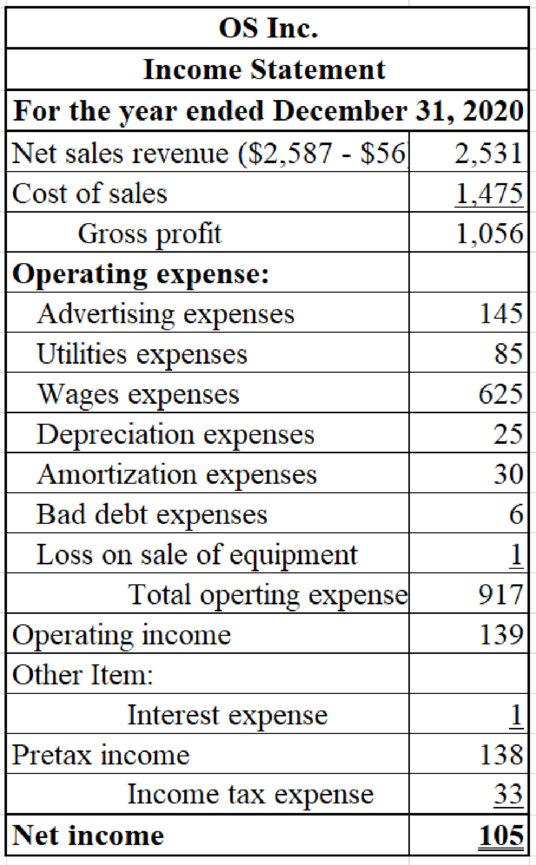
Table (32)
Prepare a statement of stockholders’ equity for OS Inc.
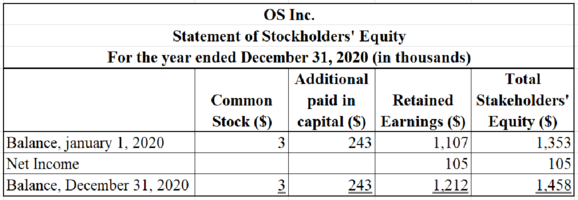
Table (33)
Prepare a balance sheet for OS Inc.
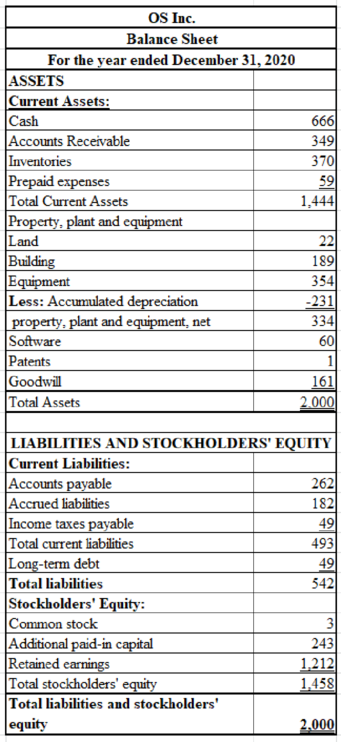
Table (34)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
INTRO TO FIN ACCT (LL W/ ACCESS-1 SMSTR
- How many years will it take for you to be debt free ??? General accountingarrow_forwardGeneral Accountingarrow_forwardDepreciation on a personal computer used in the marketing department of a manufacturing company would be classified as: a. a product cost that is fixed with respect to the company's output. b. a period cost that is fixed with respect to the company's output. c. a product cost that is variable with respect to the company's output. d. a period cost that is variable with respect to the company's output.arrow_forward
- What is the cost of the ending work in process inventory?arrow_forwardHii expert please provide correct answer general Accounting questionarrow_forwardCalculate the debt ratio based on the following information: cash = $14,870; accounts receivable = $22,108; prepaid $3,010; supplies = $927; equipment = $62,150; accumulated depreciation = 13,750; accounts payable = 28,000. Round to two decimal places.arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





