
(a)
The diameter of the disk as shown in the figure below using the scale bar provided below it.
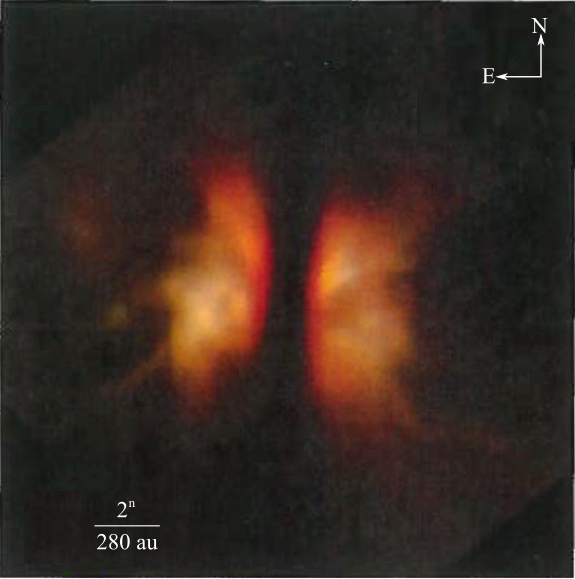
(a)
Answer to Problem 20Q
Solution:
The diameter is, approximately,
Explanation of Solution
This can be calculated directly by calibrating our usual scale with the scale bar provided below the figure and measuring the diameter of the disk. This diameter comes to be around
Conclusion:
Hence, the diameter of the disk is
(b)
The volume of the disk if its thickness is
(b)
Answer to Problem 20Q
Solution:
Volume of the disk is
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
The thickness of the disk is
Formula used:
The expression for volume of the disk is written as,
Here,
Use the conversion formula,
Explanation:
The expression for the radius of the disk (r) is written as,
Here, d is the diameter of disk.
Substitute
Recall the expression for the volume of the disk.
Substitute
Conclusion:
Thus, the volume of the disk is
(c)
The number of hydrogen atoms and hydrogen atoms per cubic meter of the disk if the total mass of the disk is
(c)
Answer to Problem 20Q
Solution:
The total number of hydrogen atoms in the disk is
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
The thickness of the disk is
Formula used:
The expression for the total number of hydrogen atoms
Here,
Explanation:
If the total mass of the disk and the mass of each hydrogen atom are given, provided that the disk is composed entirely of hydrogen atoms, the number of hydrogen atoms is:
Substitute
Conclusion:
Thus, the total number of hydrogen atoms in the entire disk is
(d)
The number of hydrogen atoms per cubic meter of the disk. Also compare it with the density of air, which contains about
(d)
Answer to Problem 20Q
Solution:
Number of hydrogen atoms per cubic meter is
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
The thickness of the disk is
Formula used:
The number of atoms per cubic meter
Here,
Explanation:
From part (c), total number of hydrogen atoms in the disk (N) is
From part (b), volume of the disk is
Recall the expression for number of atoms per cubic meter
Substitute
Thus, the disk has a density much less than that of the air we breathe, which is
Conclusion:
Thus, the number of hydrogen atoms per cubic meter is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
EBK LOOSE-LEAF VERSION OF UNIVERSE
- 3. If the force of gravity stopped acting on the planets in our solar system, what would happen? a) They would spiral slowly towards the sun. b) They would continue in straight lines tangent to their orbits. c) They would continue to orbit the sun. d) They would fly straight away from the sun. e) They would spiral slowly away from the sun. 4. 1 The free-body diagram of a wagon being pulled along a horizontal surface is best represented by A F N B C 0 Ꭰ FN E a) A b) B c) C app app The app 10 app d) e) ס ח D E 10 apparrow_forwardPls help ASAParrow_forwardPls help asaparrow_forward
- Pls help asaparrow_forwardThe acceleration of an object sliding along a frictionless ramp is inclined at an angle 0 is 9. a) g tano b) g cose c) g sino 10. d) g e) zero A 1.5 kg cart is pulled with a force of 7.3 N at an angle of 40° above the horizontal. If a kinetic friction force of 3.2 N acts against the motion, the cart's acceleration along the horizontal surface will be a) 5.0 m/s² b) 1.6 m/s² c) 2.4 m/s² 11. d) 1.0 m/s² e) 2.7 m/s² What is the net force acting on an object with a mass of 10 kg moving at a constant velocity of 10 m/s [North]? a) 100 N [North] b) 100 N [South] 10 N [North} d) 10 N [South] e) None of these.arrow_forwardModified True/False - indicate whether the sentence or statement is true or false. If the statement is false, correct the statement to make it true. 12. An object in uniform circular motion has a constant velocity while experiencing centripetal acceleration. 13. An object travelling in uniform circular motion experiences an outward centrifugal force that tends to pull the object out of the circular path. 14. An object with less inertia can resist changes in motion more than an object with more inertia. 15. For an object sliding on a horizontal surface with a horizontal applied force, the frictional force will always increase as the applied force increases.arrow_forward
- Pls help asaparrow_forwardAnswer the given question showing step by step by and all necessary working out.arrow_forward1. The piston in the figure has a mass of 0.5 kg. The infinitely long cylinder is pushed upward at a constant velocity. The diameters of the cylinder and piston are 10 cm and 9 cm, respectively, and there is oil between them with v = 10⁻⁴ m^2/s and γ = 8,000 N/m³. At what speed must the cylinder ascend for the piston to remain at rest?arrow_forward
 Horizons: Exploring the Universe (MindTap Course ...PhysicsISBN:9781305960961Author:Michael A. Seeds, Dana BackmanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Horizons: Exploring the Universe (MindTap Course ...PhysicsISBN:9781305960961Author:Michael A. Seeds, Dana BackmanPublisher:Cengage Learning Foundations of Astronomy (MindTap Course List)PhysicsISBN:9781337399920Author:Michael A. Seeds, Dana BackmanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Foundations of Astronomy (MindTap Course List)PhysicsISBN:9781337399920Author:Michael A. Seeds, Dana BackmanPublisher:Cengage Learning Stars and Galaxies (MindTap Course List)PhysicsISBN:9781337399944Author:Michael A. SeedsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Stars and Galaxies (MindTap Course List)PhysicsISBN:9781337399944Author:Michael A. SeedsPublisher:Cengage Learning
 AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9781938168284Author:Andrew Fraknoi; David Morrison; Sidney C. WolffPublisher:OpenStax
AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9781938168284Author:Andrew Fraknoi; David Morrison; Sidney C. WolffPublisher:OpenStax Stars and GalaxiesPhysicsISBN:9781305120785Author:Michael A. Seeds, Dana BackmanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Stars and GalaxiesPhysicsISBN:9781305120785Author:Michael A. Seeds, Dana BackmanPublisher:Cengage Learning





