
Concept explainers
Inventory Write-Down Palmquist Company has five different inventory items and applies the
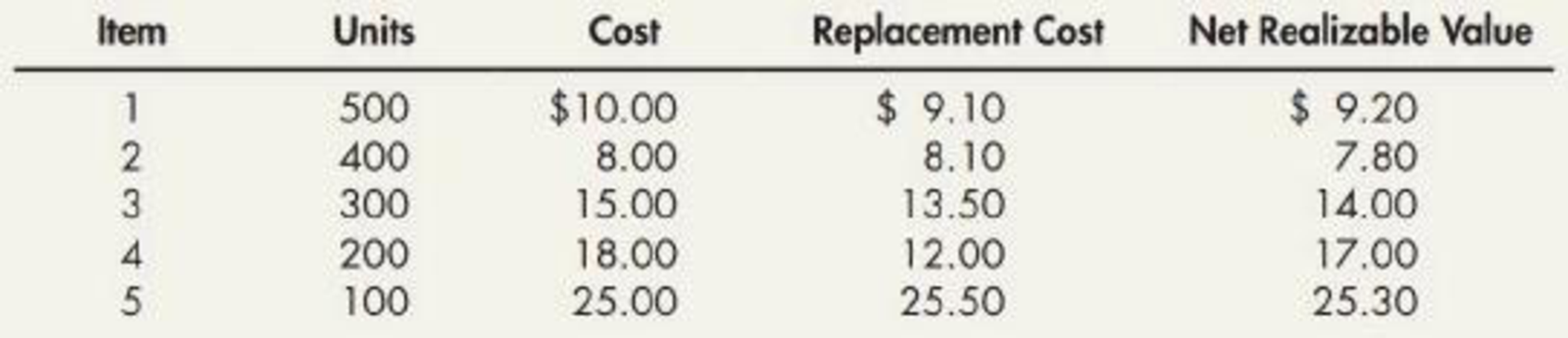
Required:
- 1. Assume that Palmquist uses the FIFO cost flow assumption. Compute the correct inventory value under the lower of cost or net realizable value rule.
- 2. Assume that Palmquist uses the LIFO cost flow assumption. Compute the correct inventory value under the lower of cost or market rule.
- 3. Assume that Palmquist uses IFRS. Compute the correct inventory value under the lower of cost or net realizable value rule.
- 4. Next Level Explain the differences between the inventory valuations reported under IFRS and U.S. GAAP.
1.
Calculate the correct value of inventory under LCM or NRV rule (if P uses FIFO method).
Explanation of Solution
Inventory Write-Downs: If the utilizing capacity of inventory by the company drops down below the acquisition cost of inventory, the inventory write-downs occur.
The following are the two situations for the inventory write-downs:
- When the inventory is damaged or is in non-salable state
- When the market value of inventory has dropped below the acquisition cost
FIFO: Under this inventory method, the units that are purchased first are sold first. Thus, it starts from the selling of the beginning inventory, followed by the units purchased in a chronological order of their purchases took place during a particular period.
Calculate the correct value of inventory under LCM or NRV rule (if P uses FIFO method):
If FIFO method is used:
| Case | Cost | Net realizable value | Lower of cost or NRV | |
| ($) | ($) | ($) | ||
| 1 | 10.00 | 9.20 | 9.20 | (NRV) |
| 2 | 8.00 | 7.80 | 7.80 | (NRV) |
| 3 | 15.00 | 14.00 | 14.00 | (NRV) |
| 4 | 18.00 | 17.00 | 17.00 | (NRV) |
| 5 | 25.00 | 25.30 | 25.00 | (Cost) |
Table (1)
If LCNRV rule is used:
| Item | Units | Valuation | Total |
| 1 | 500 | 9.20 | 4,600 |
| 2 | 400 | 7.80 | 3,120 |
| 3 | 300 | 14.00 | 4,200 |
| 4 | 200 | 17.00 | 3,400 |
| 5 | 100 | 25.00 | 2,500 |
| Total inventory valuation | $17,820 | ||
Table (2)
2.
Calculate the correct value of inventory under LCM or NRV rule (if P uses LIFO method).
Explanation of Solution
LIFO: Under this inventory method, the units that are purchased last are sold first. Thus, it starts from the selling of the units recently purchased and ending with the beginning inventory.
Calculate the correct value of inventory under LCM or NRV rule (if P uses LIFO method):
If LIFO method is used:
| Case | Cost | Replacement | NRV | NRV less normal profit margin | Lower of cost or Market |
| ($) | ($) | ($) | ($) | ($) | |
| 1 | 10.00 | 9.10 | 9.20 | 7.20 | 9.10 |
| 2 | 8.00 | 8.10 | 7.80 | 6.20 | 7.80 |
| 3 | 15.00 | 13.50 | 14.00 | 11.00 | 13.50 |
| 4 | 18.00 | 12.00 | 17.00 | 13.40 | 13.40 |
| 5 | 25.00 | 25.50 | 25.30 | 20.30 | 25.00 |
Table (3)
If LCM rule is used:
| Item | Units | Valuation | Total |
| 1 | 500 | 9.10 | 4,550 |
| 2 | 400 | 7.80 | 3,120 |
| 3 | 300 | 13.50 | 4,050 |
| 4 | 200 | 13.40 | 2,680 |
| 5 | 100 | 25.00 | 2,500 |
| Total inventory valuation | $16,900 | ||
Table (4)
Working note 1:
Calculate NRV less profit margin for item 1.
Working note 2:
Calculate NRV less profit margin for item 2.
Working note 3:
Calculate NRV less profit margin for item 3.
Working note 4:
Calculate NRV less profit margin for item 4.
Working note 5:
Calculate NRV less profit margin for item 5.
3.
Calculate the correct value of inventory under lower of cost or market rule (If P uses IFRS):
Explanation of Solution
Lower-of-cost-or-market: The lower-of-cost-or-market (LCM) is a method which requires the reporting of the ending merchandise inventory in the financial statement of a company, either at current market value or at historical cost price of the inventory, whichever is less.
If P uses IFRS:
| Item | Cost | NRV | LCM | |
| ($) | ($) | ($) | ||
| 1 | 10.00 | 9.20 | 9.20 | (NRV) |
| 2 | 8.00 | 7.80 | 7.80 | (NRV) |
| 3 | 15.00 | 14.00 | 14.00 | (NRV) |
| 4 | 18.00 | 17.00 | 17.00 | (NRV) |
| 5 | 25.00 | 25.30 | 25.00 | (Cost) |
Table (5)
If LCNRV rule is used:
| Item | Units | Valuation | Total |
| (a) | (b) | (c = a*b) | |
| 1 | 500 | 9.20 | 4,600 |
| 2 | 400 | 7.80 | 3,120 |
| 3 | 300 | 14.00 | 4,200 |
| 4 | 200 | 17.00 | 3,400 |
| 5 | 100 | 25.00 | 2,500 |
| Total inventory value | $17,820 | ||
Table (6)
4.
Describe the difference between the inventory valuation under U.S. GAAP and IFRS.
Explanation of Solution
Differences between the inventory valuation under U.S. GAAP and IFRS:
- If FIFO method is used, there would not be any difference between IFRS and U.S GAAP. However, the use of LIFO is not allowed by IFRS.
- Hence, IFRS would show the result in market value corresponding to the inventory valuation which is greater than the U.S. GAAP.
- FIFO method will result in lower inventory cost in the balance sheet relative to LIFO. As the inventory price is increasing, the inventory purchased last will have higher price than the inventory purchased first. Thus, under this method, the inventory purchased last with higher price will be sold first, thereby increasing the cost of goods sold. However, FIFO method gives lowest cost of goods sold and highest ending inventory since cost of goods are lower in the beginning because purchases are at lower rate and ending inventory is highest as the ending purchases are at higher rate.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Interm.acct.:reporting.(ll)-w/access
- Correct answerarrow_forwardMarin Company is a manufacturer of smartphones. Its controller resigned in October 2025. An inexperienced assistant accountant has prepared the following income statement for the month of October 2025. Marin Company Income Statement For the Month Ended October 31, 2025 Sales revenue $998,400 Less: Operating expenses Raw materials purchases $337,920 Direct labor cost 243,200 Advertising expense 115,200 Selling and administrative salaries 96,000 Rent on factory facilities 76,800 Depreciation on sales equipment 57,600 Depreciation on factory equipment 39,680 Indirect labor cost 35,840 Utilities expense 15,360 Insurance expense 10,240 1,027,840 Net loss $(29,440) Prior to October 2025, the company had been profitable every month. The company's president is concerned about the accuracy of the income statement. As her friend, you have been asked to review the income statement and make necessary corrections. After examining other manufacturing cost data, you have acquired additional…arrow_forwardProvide answerarrow_forward
- MCQarrow_forwardExercise 3-12A (Algo) Conducting sensitivity analysis using a spreadsheet LO 3-5 Use the below table to answer the following questions. Selling Price$27.00 Variable 2,100 3,100 Fixed Cost Cost Sales Volume 4,100 Profitability 5,100 6,100 $25,700 8 $14,200 $33,200 $52,200 $71,200 $90,200 25,700 9 12,100 30,100 48,100 66,100 84,100 25,700 10 10,000 27,000 44,000 61,000 78,000 35,700 8 4,200 23,200 42,200 61,200 80,200 35,700 9 2,100 20,100 38,100 56,100 74,100 35,700 10 17,000 34,000 51,000 68,000 45,700 8 (5,800) 13,200 32,200 51,200 70,200 45,700 9 (7,900) 10,100 28,100 46,100 64,100 45,700 10 (10,000) 7,000 24,000 41,000 58,000 Required a. Determine the sales volume, fixed cost, and variable cost per unit at the break-even point. b. Determine the expected profit if Rundle projects the following data for Delatine: sales, 4,100 bottles; fixed cost, $25,700; and variable cost per unit, $10. c. Rundle is considering new circumstances that would change the conditions described in…arrow_forwardWhich of the following would be classified as a current liability ?arrow_forward
 Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)AccountingISBN:9781305961883Author:Carl WarrenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)AccountingISBN:9781305961883Author:Carl WarrenPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,





