
Concept explainers
Inventory Write-Down Palmquist Company has five different inventory items and applies the
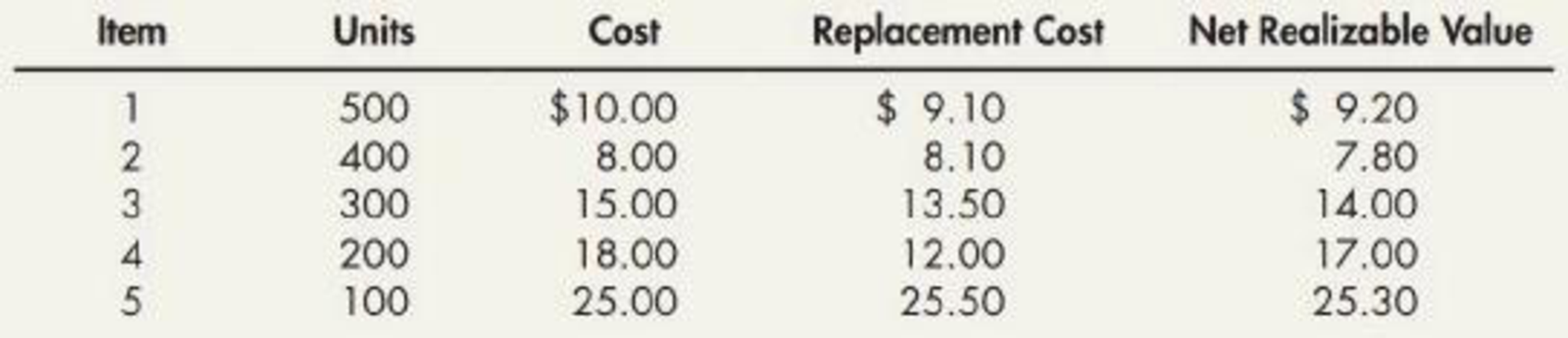
Required:
- 1. Assume that Palmquist uses the FIFO cost flow assumption. Compute the correct inventory value under the lower of cost or net realizable value rule.
- 2. Assume that Palmquist uses the LIFO cost flow assumption. Compute the correct inventory value under the lower of cost or market rule.
- 3. Assume that Palmquist uses IFRS. Compute the correct inventory value under the lower of cost or net realizable value rule.
- 4. Next Level Explain the differences between the inventory valuations reported under IFRS and U.S. GAAP.
1.
Calculate the correct value of inventory under LCM or NRV rule (if P uses FIFO method).
Explanation of Solution
Inventory Write-Downs: If the utilizing capacity of inventory by the company drops down below the acquisition cost of inventory, the inventory write-downs occur.
The following are the two situations for the inventory write-downs:
- When the inventory is damaged or is in non-salable state
- When the market value of inventory has dropped below the acquisition cost
FIFO: Under this inventory method, the units that are purchased first are sold first. Thus, it starts from the selling of the beginning inventory, followed by the units purchased in a chronological order of their purchases took place during a particular period.
Calculate the correct value of inventory under LCM or NRV rule (if P uses FIFO method):
If FIFO method is used:
| Case | Cost | Net realizable value | Lower of cost or NRV | |
| ($) | ($) | ($) | ||
| 1 | 10.00 | 9.20 | 9.20 | (NRV) |
| 2 | 8.00 | 7.80 | 7.80 | (NRV) |
| 3 | 15.00 | 14.00 | 14.00 | (NRV) |
| 4 | 18.00 | 17.00 | 17.00 | (NRV) |
| 5 | 25.00 | 25.30 | 25.00 | (Cost) |
Table (1)
If LCNRV rule is used:
| Item | Units | Valuation | Total |
| 1 | 500 | 9.20 | 4,600 |
| 2 | 400 | 7.80 | 3,120 |
| 3 | 300 | 14.00 | 4,200 |
| 4 | 200 | 17.00 | 3,400 |
| 5 | 100 | 25.00 | 2,500 |
| Total inventory valuation | $17,820 | ||
Table (2)
2.
Calculate the correct value of inventory under LCM or NRV rule (if P uses LIFO method).
Explanation of Solution
LIFO: Under this inventory method, the units that are purchased last are sold first. Thus, it starts from the selling of the units recently purchased and ending with the beginning inventory.
Calculate the correct value of inventory under LCM or NRV rule (if P uses LIFO method):
If LIFO method is used:
| Case | Cost | Replacement | NRV | NRV less normal profit margin | Lower of cost or Market |
| ($) | ($) | ($) | ($) | ($) | |
| 1 | 10.00 | 9.10 | 9.20 | 7.20 | 9.10 |
| 2 | 8.00 | 8.10 | 7.80 | 6.20 | 7.80 |
| 3 | 15.00 | 13.50 | 14.00 | 11.00 | 13.50 |
| 4 | 18.00 | 12.00 | 17.00 | 13.40 | 13.40 |
| 5 | 25.00 | 25.50 | 25.30 | 20.30 | 25.00 |
Table (3)
If LCM rule is used:
| Item | Units | Valuation | Total |
| 1 | 500 | 9.10 | 4,550 |
| 2 | 400 | 7.80 | 3,120 |
| 3 | 300 | 13.50 | 4,050 |
| 4 | 200 | 13.40 | 2,680 |
| 5 | 100 | 25.00 | 2,500 |
| Total inventory valuation | $16,900 | ||
Table (4)
Working note 1:
Calculate NRV less profit margin for item 1.
Working note 2:
Calculate NRV less profit margin for item 2.
Working note 3:
Calculate NRV less profit margin for item 3.
Working note 4:
Calculate NRV less profit margin for item 4.
Working note 5:
Calculate NRV less profit margin for item 5.
3.
Calculate the correct value of inventory under lower of cost or market rule (If P uses IFRS):
Explanation of Solution
Lower-of-cost-or-market: The lower-of-cost-or-market (LCM) is a method which requires the reporting of the ending merchandise inventory in the financial statement of a company, either at current market value or at historical cost price of the inventory, whichever is less.
If P uses IFRS:
| Item | Cost | NRV | LCM | |
| ($) | ($) | ($) | ||
| 1 | 10.00 | 9.20 | 9.20 | (NRV) |
| 2 | 8.00 | 7.80 | 7.80 | (NRV) |
| 3 | 15.00 | 14.00 | 14.00 | (NRV) |
| 4 | 18.00 | 17.00 | 17.00 | (NRV) |
| 5 | 25.00 | 25.30 | 25.00 | (Cost) |
Table (5)
If LCNRV rule is used:
| Item | Units | Valuation | Total |
| (a) | (b) | (c = a*b) | |
| 1 | 500 | 9.20 | 4,600 |
| 2 | 400 | 7.80 | 3,120 |
| 3 | 300 | 14.00 | 4,200 |
| 4 | 200 | 17.00 | 3,400 |
| 5 | 100 | 25.00 | 2,500 |
| Total inventory value | $17,820 | ||
Table (6)
4.
Describe the difference between the inventory valuation under U.S. GAAP and IFRS.
Explanation of Solution
Differences between the inventory valuation under U.S. GAAP and IFRS:
- If FIFO method is used, there would not be any difference between IFRS and U.S GAAP. However, the use of LIFO is not allowed by IFRS.
- Hence, IFRS would show the result in market value corresponding to the inventory valuation which is greater than the U.S. GAAP.
- FIFO method will result in lower inventory cost in the balance sheet relative to LIFO. As the inventory price is increasing, the inventory purchased last will have higher price than the inventory purchased first. Thus, under this method, the inventory purchased last with higher price will be sold first, thereby increasing the cost of goods sold. However, FIFO method gives lowest cost of goods sold and highest ending inventory since cost of goods are lower in the beginning because purchases are at lower rate and ending inventory is highest as the ending purchases are at higher rate.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting and Analysis - With Access
- Burgundy Corporation had made $56,000 of tax payments to the IRS. Its adjustments to increase its $502,000 pretax financial income netted $60,000 to arrive at taxable income. Assuming the tax rate is 25%, how much will Burgundy report for income taxes payable on its balance sheet?arrow_forwardWhat are the budgeted cash payments for October on these financial accounting question?arrow_forwardThe book value of this equipment shown on its balance sheet will be?arrow_forward
 Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)AccountingISBN:9781305961883Author:Carl WarrenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)AccountingISBN:9781305961883Author:Carl WarrenPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,





