
Concept explainers
Complete the following concept map that summarizes some of the key ideas about energy.
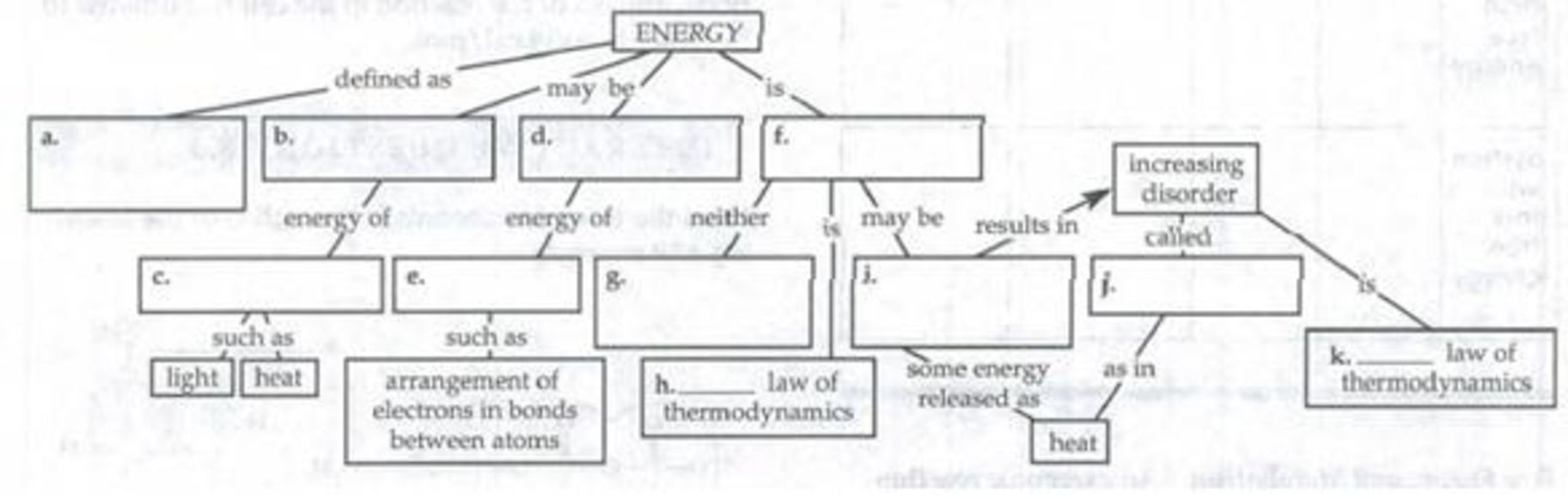
To complete: The concept map that summarizes some of the key ideas about energy.
Introduction: Thermodynamics is the study of energy and its transformation that drives all activities of the universe. The system that does not exchange energy with its surroundings is known as a closed system. The system that exchanges energy with its surroundings is known as an open system. There are two laws of thermodynamics, namely the first law and the second law.
Answer to Problem 1IQ
Pictorial representation: Fig.1 shows the concept map that summarizes some of the key ideas about energy.
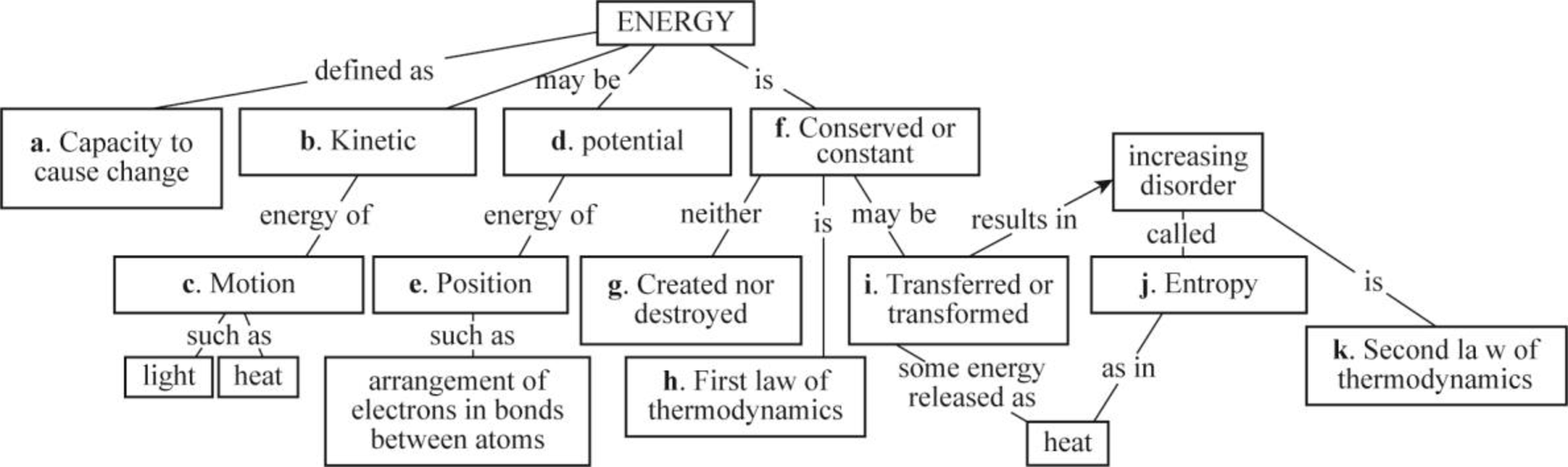
Fig.1: Concept map that summarizes some of the key ideas about energy.
Explanation of Solution
Energy is necessary for all living organisms to carry out their life processes. Living cells obtain energy in different forms, and they also have the mechanisms to convert the energy from one form to different forms. Energy is defined as the capability to do work. When work is done, energy is transferred from one form to another form, or between systems. Energy is generally expressed in units of work that is kilojoules (kJ). Energy can also be expressed in units of heat energy that is kilocalories (kcal).
Potential energy and kinetic energy are the two forms of energy. Potential is the energy of position or stored energy such as the arrangement of electrons in bonds between atoms. Kinetic energy is the energy of motion such as light and heat. A person pulling an arrow back on a bow and holding a baseball in the backswing are examples of potential energy. When the bowstring pushes the arrow toward its target and throwing a baseball are examples of kinetic energy.
Energy cannot be created and destroyed, but it can be converted from one form to another. It can tend to spread or disperse until no part of the system has more than one part. Entropy is a measure of how much energy a particular system has dispersed. The entropy of the system increases on heat dispersal, as molecule tends to disperse. This is a measure of randomness.
The first law of thermodynamics states that “energy cannot be created or destroyed, but it can be transformed from one form to another form”. This law explains that organisms cannot produce energy; however, they constantly capture energy from their surrounding as open systems and covert this energy from one form to another form for biological work.
The second law of thermodynamics states that “no energy transfer is 100% efficient; some energy is dispersed as heat”. According to this law, entropy in the universe is continuously increasing. As the organisms are open systems, they maintain their ordered states over time with a constant energy input from their surroundings.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Study Guide for Campbell Biology
- Molecular Biology Please help with question. Thank you in advance. Discuss, compare and contrast the structure of promoters inprokaryotes and eukaryotes.arrow_forwardMolecular Biology Please help with question. Thank you You are studying the expression of the lac operon. You have isolated mutants as described below. In the absence of glucose, explain/describe what would happen, for each mutant, to the expression of the lac operon when you add lactose AND what would happen when the bacteria has used up all of the lactose (if the mutant is able to use lactose).1. Mutations in the lac repressor gene that would prevent the binding of lactose2. Mutations in the lac repressor gene that would prevent release of lactose once lactose hadbound3. Normally the lac repressor gene is located next to (a few hundred base pairs) and upstreamfrom the lac operon. Mutations in the lac repressor gene that move the lac repressor gene 100,000base pairs downstream.4. Mutations in the lac operator that would prevent binding of lac repressorarrow_forwardYou have returned to college to become a phylogeneticist. One of the first things you wish to do is determine how mammals, birds, and reptiles are related. Like any good scientist, you need to consider all available data objectively and without a preconceived “correct” answer. In pursuit of that, you should produce a phylogenetic tree based only on morphological features that show birds and mammals are more closely related. You will then produce a totally different tree, also using morphological features, that shows birds and reptiles are more closely related. Do not forget to include all three groups in both your trees. Based solely off the trees you produce, which relationship would you consider the more likely and why? Once you have answered that question, provide a brief summary of the “modern” understanding of the relationship between these three groups.arrow_forward
- true or false, the reason geckos can walk on walls is hydrogen bonding between their foot pads and the moisture on the wall.arrow_forwardBiology laboratory problem Please help. thank you You have 20 ul of DNA solution and 6X DNA loading buffer solution. You have to mix your DNA solution and DNA loading buffer before load DNA in an agarose gel. The concentration of the DNA loading buffer must be 1X in the DNA and DNA-loading buffer mixture after you mix them. For that, I will add _____ ul of 6X loading buffer to the 20 ul DNA solution.arrow_forwardBiology lab problem To make 20 ul of 5 mM MgCl2 solution using 50 mM MgCl2 stock solution and distilled water, I will mix ________ ul of 50 mM MgCl2 solution and ________ ul of distilled water. Please help . Thank youarrow_forward
- Biology Please help. Thank you. Biology laboratory question You need 50 ml of 1% (w/v) agarose gel. Agarose is a powder. How would you make it? You can ignore the volume of agarose powder. Don't forget the unit.TBE buffer is used to make an agarose gel, not distilled water. I will add _______ of agarose powder into 50 ml of distilled water (final 50 ml).arrow_forwardAn urgent care center experienced the average patient admissions shown in the Table below during the weeks from the first week of December through the second week of April. Week Average Daily Admissions 1-Dec 11 2-Dec 14 3-Dec 17 4-Dec 15 1-Jan 12 2-Jan 11 3-Jan 9 4-Jan 9 1-Feb 12 2-Feb 8 3-Feb 13 4-Feb 11 1-Mar 15 2-Mar 17 3-Mar 14 4-Mar 19 5-Mar 13 1-Apr 17 2-Apr 13 Forecast admissions for the periods from the first week of December through the second week of April. Compare the forecast admissions to the actual admissions; What do you conclude?arrow_forwardAnalyze the effectiveness of the a drug treatment program based on the needs of 18-65 year olds who are in need of treatment by critically describing 4 things in the program is doing effectively and 4 things the program needs some improvement.arrow_forward
- I have the first half finished... just need the bottom half.arrow_forward13. Practice Calculations: 3 colonies were suspended in the following dilution series and then a viable plate count and microscope count was performed. Calculate IDF's, TDF's and then calculate the CFU/mL in each tube by both methods. Finally calculate the cells in 1 colony by both methods. Show all of your calculations in the space provided on the following pages. 3 colonies 56 cells 10 μL 10 μL 100 μL 500 με m OS A B D 5.0 mL 990 με 990 με 900 με 500 μL EN 2 100 με 100 μL 118 colonies 12 coloniesarrow_forwardDescribe and give a specific example of how successionary stage is related to species diversity?arrow_forward
 Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337711067Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna BalacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337711067Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna BalacPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning





